Abstract—
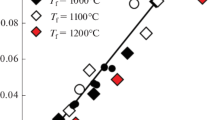
When water diffuses into silica glass it reacts chemically forming nanometre sized pores that change the physical properties of the glass, for example, affect its strength. Here we discuss the effect of water on Young’s modulus, and show how it is reduced by the water reaction, whereby a proportional behaviour applies to small amounts of water involved in the reaction. The value of the elastic modulus will be not linear with the hydroxyl-quantity in the glass for very high concentrations. The relationship between hydroxyl concentration and Young’s modulus can be determined from measurements of sound wave velocity and will be represented by damage and pore models from literature.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Doremus, R.H., Diffusion of water in silica glass, J. Mater. Res., 1995, vol. 10, pp. 2379–2389.
Brückner, R., The structure-modifying influence of the hydroxyl content of vitreous silicas, Glass Ber., 1970, vol. 43, pp. 8–12.
Brückner, R., Metastable equilibrium density of hydroxyl-free synthetic vitreous silica, J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 1971, vol. 5, pp. 281–285.
Shackelford, J.F., Masaryk, J.S., and Fulrath, R.M., Water content, fictive temperature, and density relations for fused silica, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1970, vol. 53, p. 417.
Shelby, J.E., Density of vitreous silica, J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 2004, vol. 349, pp. 331–336.
Kachanov, L.M., Time of the rupture process under creep conditions, Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR,Otd. Tek., 1958, vol. 8, pp. 26–31.
Lemaitre, J., How to use damage mechanics, Nucl. Eng. Des., 1984, vol. 80, pp. 233–245.
Lemaitre, J., Evaluation of dissipation and damage in metals submitted to dynamic loadings, in Proceedings of the International Congress of Mathematicians ICM,1971, Kyoto, Japan, p. 1.
Fett, T., Schell, K.G., Hoffmann, M.J., and Wiederhorn, S.M., Effect of damage by hydroxyl generation on strength of silica fibers, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2018, vol. 101, no. 7.
Fraser, D.B., Factors influencing the acoustic properties of vitreous silica, J. Appl. Phys., 1968, vol. 39, pp. 5868–5878.
Le Parc, R., Levelut, C., and Pelous, J., Influence of fictive temperature and composition of silica glass on anomalous elastic behaviour, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2006, vol. 18, pp. 7507–7527.
Ashkin, D., Haber, R.A., and Wachtman, J.B., Elastic properties of porous silica derived from colloidal gels, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1990, vol. 73, pp. 3376–3381.
Kushibiki, J., Arakawa, M., and Ohashi, Y., A super-precise CTE evaluation method for ultra-low-expansion glasses using the LFB ultrasonic material characterization system, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2005, vol. 44, pp. 4374–4380.
Knudsen, F.P., Effect of porosity on Young’s modulus of alumina, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1962, vol. 45, pp. 94–95.
Wang, J.C., Young’s modulus of porous materials. Part 2: Young’s modulus of porous alumina with changing pore structure, J. Mater. Sci., 1984, vol. 19, pp. 809–814.
Phani, K.K. and Niyogi, S.K., Elastic modulus-porosity relationship for Si3N4, J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 1987, vol. 6, pp. 511–515.
Phani, K.K., Niyogi, S.K., and De, A.K., Porosity dependence of fracture mechanical properties of reaction sintered Si3N4, J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 1988, vol. 7, pp. 1253–1256.
Adachi, T. and Sakka, S., Dependence of the elastic moduli of porous silica gel prepared by the sol-gel method on heat-treatment, J. Mater. Sci., 1990, vol. 25, pp. 4732–4737.
Yu, C., Ji, S., and Li, Q., Effects of porosity on seismic velocities, elastic moduli and Poisson’s ratios of solid materials and rocks, J. Rock. Mech. Geotech. Eng., 2016, vol. 8, pp. 35–49.
Wang, J.C., Young’s modulus of porous materials. Part 1: Theoretical derivation of modulus-porosity correlation, J. Mater. Sci., 1984, vol. 19, pp. 801–808.
Phani, K.K. and Niyogi, S.K., Young’s modulus of porous brittle solids, J. Mater. Sci., 1987, vol. 22, pp. 257–263.
Wiederhorn, S.M., Fett, T., and Rizzi, G., Water penetration—its effect on the strength and toughness of silica glass, Metall. Mater Trans. A, 2013, vol. 44, pp. 1164–1174.
Wiederhorn, S.M., Rizzi, G., Hoffmann, M.J., and Guin, J.-P., The effect of water penetration on crack growth in silica glass, Eng. Fract. Mech., 2013, vol. 100, pp. 3–16.
Zouine, A., Dersch, O., Walter, G., and Rauch, F., Diffusivity and solubility of water in silica glass in the temperature range 23-200°C, Phys. Chem. Glasses – Eur.J. Glas. Sci. Technol., 2007, vol. 48, pp. 85–91.
Wiederhorn, S.M., Yi, F., and LaVan, D., Volume expansion caused by water penetration into silica glass, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2015, vol. 98, pp. 78–87.
Wiederhorn, S.M., Rizzi, G., and Wagner, S., Stress-enhanced swelling of silica: Effect on strength, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2016, vol. 99, pp. 2956–2963.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schell, K.G., Fett, T., Bucharsky, E.C. et al. Damage by Hydroxyl Generation in Silica. Glass Phys Chem 46, 424–428 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1087659620050077
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1087659620050077