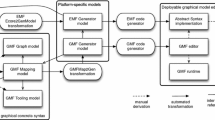
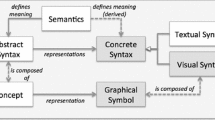
Abstract
The rise of domain-specific (Visual) languages and the inherent complexity of developing graphical editors for these languages have led to the emergence of proposals that provide support for this task. Most of these proposals are principally based on EMF and GMF, which effectively help to simplify and increase the level of automation of the development process of the editors, but it is important to recall that these proposals have some important disadvantages, mainly related to the learning curve of these technologies, poor documentation or the complexity of providing all the customisation possibilities to the user. In addition, in the process of developing a domain-specific language, issues related to graphical conventions have historically been undervalued, while most of the effort has been focused on semantic aspects. In fact, definitions of the concrete (visual) syntax of modelling languages in Software Engineering are usually based on common sense, intuition, the reuse of existing notations or emulation of common practices. In order to alleviate the inherent complexity of the EMF/GMF approach for the development of graphical editors and to support the evaluation of the quality of visual notations of modelling languages, this article presents CEViNEdit, an intuitive tool that simultaneously supports the semi-automatic generation of graphical editors and the assessment of the cognitive effectiveness of the visual notation implemented by the editor.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
EuGENia GMF Tutorial: https://www.eclipse.org/epsilon/doc/articles/eugenia-gmf-tutorial/.
Generation of GMF Graphical Editors for the Entity—Relationship Model: https://www.kybele.es/cevinedit/EditorsPractice.pdf.
First questionnaire—Knowledge and Preferences: https://www.kybele.es/cevinedit/Q1.pdf.
Graphical editor development with GMF (Spanish): https://www.kybele.es/cevinedit/GMFTutorial.pdf.
Second questionnaire—Tools Evaluation: https://www.kybele.es/cevinedit/Q2.pdf.
Members of the Kybele research group: https://www.kybele.es/es/miembros/.
Cognitively Effective Visual Notations: https://www.kybele.es/cevinedit/VNPrinciples.pdf.
References
Mernik, M., Heering, J., Sloane, A.M.: When and how to develop domain-specific languages. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 37(4), 316–344 (2005)
Bézivin, J.: In search of a basic principle for Model Driven Engineering. Novatica J. Spec. Issue 5(2), 21–24 (2004)
Ghosh, D.: DSL for the uninitiated. Commun. ACM 54(7), 44–50 (2011)
Gray, J., Rumpe, B.: Models for the digital transformation. Softw. Syst. Model. 16(2), 307–308 (2017)
Schmidt, D.C.: Model-driven engineering. Comput. IEEE Comput. Soc. 39(2), 25 (2006)
Brambilla, M., Cabot, J., Wimmer, M.: Model-driven software engineering in practice. Synth. Lect. Softw. Eng. 3(1), 1–207 (2017)
Gronback, R.C.: Eclipse Modeling Project: A Domain-Specific Language (DSL) Toolkit. Pearson Education, London (2009)
Whittle, J., Hutchinson, J., Rouncefield, M., Burden, H., Heldal, R.: Industrial adoption of Model-Driven Engineering: are the tools really the problem? In: International Conference on Model Driven Engineering Languages and Systems, pp. 1–17. Springer (2013)
Granada, D., Vara, J.M., Blanco, F.P., Marcos, E.: Model-based tool support for the development of visual editors-a systematic mapping study. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Software Technologies, ICSOFT 2017, pp. 330–337 (2017)
Volter, M.: From programming to modeling-and back again. IEEE Softw. 28(6), 20–25 (2011)
Selic, B.: What will it take? A view on adoption of model-based methods in practice. Softw. Syst. Model. 11(4), 513–526 (2012)
Moody, D.L.: The Physics of Notations: a scientific approach to designing visual notations in software engineering. In: 2010 ACM/IEEE 32nd International Conference on Software Engineering, vol. 2, pp. 485–486. IEEE (2010)
Zhang, J., Norman, D.A.: Representations in distributed cognitive tasks. Cognit. Sci. 18(1), 87–122 (1994)
Wheildon, C., Ogilvy, D., Heard, G.: Type and Layout: Are You Communicating Or Just Making Pretty Shapes?. Worsley Press, Kent (2005)
Clark, T., Sammut, P., Willans, J.: Applied metamodelling: a foundation for language driven development. arXiv preprint arXiv:1505.00149 (2015)
Morris, S.J., Gotel, O.C.Z.: Flow diagrams: rise and fall of the first software engineering notation. In: International Conference on Theory and Application of Diagrams, pp. 130–144. Springer (2006)
Bertin, J.: Semiology of Graphics: Diagrams, Networks, Maps. University of Wisconsin Press, Madison (1983)
Kolovos, D.S., García-Domínguez, A., Rose, L.M., Paige, R.F.: EuGENia: towards disciplined and automated development of GMF-based graphical model editors. Softw. Syst. Model. 16(1), 229–255 (2017)
Budinsky, F., Steinberg, D., Ellersick, R., Grose, T.J., Merks, E.: Eclipse Modeling Framework: A Developer’s Guide. Addison-Wesley Professional, Boston (2004)
Kolovos, D.S., Paige, R.F., Polack, F.A.C.: The Epsilon Object Language (EOL). In: European Conference on Model Driven Architecture-Foundations and Applications, pp. 128–142. Springer (2006)
Kolovos, D.S, Rose, L.M, Abid, S.B., Paige, R.F., Polack, F.A.C., Botterweck, G.: Taming EMF and GMF using model transformation. In: International Conference on Model Driven Engineering Languages and Systems, pp. 211–225. Springer (2010)
Goodman, N.: Languages of Art: An Approach to a Theory of Symbols. Hackett publishing, Indianapolis (1976)
Lohse, G.L.: A cognitive model for understanding graphical perception. Hum. Comput. Interact. 8(4), 353–388 (1993)
Miller, G.A.: The magical number seven, plus or minus two: some limits on our capacity for processing information. Psychol. Rev. 63(2), 81 (1956)
Moody, D.L.: Review of ArchiMate: The road to international standardisation. Report commissioned by the ArchiMate Foundation and BiZZDesign BV, Enschede, The Netherlands, 77 (2007)
Moody, D.L., Heymans, P., Matulevicius, R.: Improving the effectiveness of visual representations in requirements engineering: An evaluation of i* visual syntax. In: 2009 17th IEEE International Requirements Engineering Conference, pp. 171–180. IEEE (2009)
Genon, N., Heymans, P., Amyot, D.: Analysing the cognitive effectiveness of the BPMN 2.0 visual notation. In: International Conference on Software Language Engineering, pp. 377–396. Springer (2010)
Moody, D., van Hillegersberg, J.: Evaluating the visual syntax of UML: an analysis of the cognitive effectiveness of the UML family of diagrams. In: International Conference on Software Language Engineering, pp. 16–34. Springer (2008)
Genon, N., Amyot, D., Heymans, P.: Analysing the cognitive effectiveness of the UCM visual notation. In: International Workshop on System Analysis and Modeling, pp. 221–240. Springer (2010)
Thomas, J.C., Diament, J., Martino, J., Bellamy, R.K.E.: Using the Physics” of Notations to analyze a visual representation of Business Decision Modeling. In: 2012 IEEE Symposium on Visual Languages and Human-Centric Computing (VL/HCC), pp. 41–44. IEEE (2012)
Popescu, G., Wegmann, A.: Using the Physics of Notations theory to evaluate the visual notation of seam. In: 2014 IEEE 16th Conference on Business Informatics, vol. 2, pp. 166–173. IEEE (2014)
Granada, D., Vara, J.M., Brambilla, M., Bollati, V., Marcos, E.: Analysing the cognitive effectiveness of the WebML visual notation. Softw. Syst. Model. 16(1), 195–227 (2017)
Kish, L.: Some statistical problems in research design. Am. Sociol. Rev. 24, 328–338 (1959)
Kitchenham, B.A., Dyba, T., Jorgensen, M.: Evidence-based software engineering. In: Proceedings. 26th International Conference on Software Engineering, pp. 273–281. IEEE (2004)
El Kouhen, A., Dumoulin, C., Gerard, S., Boulet, P.: Evaluation of modeling tools adaptation. Technical Report. Laboratoire d’Intgration des Systmes et des Technologies. https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00706701v1 (2012)
Pérez-Blanco, F.J., Vara, J.M., Gómez, C., De Castro, V., Marcos, E.: Model-based tool support for service design. In: International Conference on Fundamental Approaches to Software Engineering, pp. 266–272. Springer (2020)
Estañol, M., Marcos, E., Oriol, X., Pérez, F.J., Teniente, E., Vara, J.M.: Validation of service blueprint models by means of formal simulation techniques. In: International Conference on Service-Oriented Computing, pp. 80–95. Springer (2017)
Chen, P.P.-S.: The Entity-Relationship model-toward a unified view of data. ACM Trans. Database Syst. (TODS) 1(1), 9–36 (1976)
Moss, K.: The Entity-Relationship model. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2012)
Connolly, T.M., Begg, C.E.: Database Systems: A Practical Approach to Design, Implementation, and Management. Pearson Education, London (2005)
Shull, F.J., Carver, J.C., Vegas, S., Juristo, N.: The role of replications in empirical software engineering. Empir. Softw. Eng. 13(2), 211–218 (2008)
Mora, B., García, F., Ruiz, F., Piattini, M.: Graphical versus textual software measurement modelling: an empirical study. Softw. Qual. J. 19(1), 201–233 (2011)
Fisher, R.A.: On the probable error of a coefficient of correlation deduced from a small sample. Metron 1, 1–32 (1921)
Koo, T.K., Li, M.Y.: A guideline of selecting and reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for reliability research. J. Chiropractic Med. 15(2), 155–163 (2016)
McGraw, K.O., Wong, S.P.: Forming inferences about some Intraclass Correlation Coefficients. Psychol. Methods 1(1), 30 (1996)
Fleiss, J.L.: Design and analysis of clinical experiments (Wiley Classics Library). J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 94(448), 1384 (1999)
Kazemzadeh, Y., Milton, S.K., Johnson, L.W., et al.: Process Chain Network (PCN) and Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN): a comparison of concepts. J. Manag. Strategy 6(1), 88–99 (2015)
Wohlin, C., Runeson, P., Höst, M., Ohlsson, M.C., Regnell, B., Wesslén, A.: Experimentation in Software Engineering. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Cairns, P., Soegaard, M., Dam, R.F.: Experimental methods in Human-Computer Interaction, Encyclopedia of Human-Computer Interaction (2016)
Minas, M., Köth, O.: Generating diagram editors with DiaGen. In: International Workshop on Applications of Graph Transformations with Industrial Relevance, pp. 433–440. Springer (1999)
Pescador, A., Garmendia, A., Guerra, E., Cuadrado, J.S., de Lara, J.: Pattern-based development of domain-specific modelling languages. In: 2015 ACM/IEEE 18th International Conference on Model Driven Engineering Languages and Systems (MODELS), pp. 166–175. IEEE (2015)
Brand, C., Gorning, M., Kaiser, T., Pasch, J., Wenz, M.: Development of high-quality graphical model editors. Eclipse Magazine (2011)
Tolvanen, J.-P., Kelly, S.: MetaEdit+ defining and using integrated domain-specific modeling languages. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGPLAN Conference Companion on Object Oriented Programming Systems Languages and Applications, pp. 819–820. ACM (2009)
Juliot, E., Benois, J.: Viewpoints creation using Obeo Designer or how to build Eclipse DSM without being an expert developer. Obeo Designer Whitepaper. http://archive.is/bnAUd (2010)
Viyović, V., Maksimović, M., Perisić, B.: Sirius: a rapid development of DSM graphical editor. In: IEEE 18th International Conference on Intelligent Engineering Systems INES 2014, pp. 233–238. IEEE (2014)
Ehrig, K., Ermel, C., Hänsgen, S., Taentzer, G.: Towards graph transformation based generation of visual editors using eclipse. Electron. Notes Theor. Comput. Sci. 127(4), 127–143 (2005)
Pontisso, N., Chemouil, D.: Topcased combining formal methods with Model-Driven Engineering. In: 21st IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering (ASE’06), pp. 359–360. IEEE (2006)
Gutwenger, C., Kupke, J., Klein, K., Leipert, S.: GoVisual for CASE tools borland together control center and Gentleware Poseidon-system demonstration. In: International Symposium on Graph Drawing, pp. 123–128. Springer (2003)
López-Fernández, J.J., Garmendia, A., Guerra, E., de Lara, J.: An example is worth a thousand words: creating graphical modelling environments by example. Softw. Syst. Model. 18(2), 961–993 (2019)
Garmendia, A., Guerra, E., de Lara, J., García-Domínguez, A., Kolovos, D.: Scaling-up domain-specific modelling languages through modularity services. Inf. Softw. Technol. 115, 97–118 (2019)
Taentzer, G.: Towards generating domain-specific model editors with complex editing commands. In: Proceedings of International Workshop Eclipse Technology eXchange (eTX), Satellite Event of ECOOP (2006)
Ehrig, K., Ermel, C., Hänsgen, S., Taentzer, G.: Generation of visual editors as eclipse plug-ins. In: Proceedings of the 20th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering, pp. 134–143 (2005)
Pelechano, V., Albert, M., Muñoz, J., Cetina, C.: Building Tools for Model Driven Development. Comparing Microsoft DSL Tools and Eclipse Modeling Plug-ins. In: Actas del Taller sobre Desarrollo de Software Dirigido por Modelos. MDA y Aplicaciones. Sitges, Spain, October 3, 2006, volume 227 of CEUR Workshop Proceedings (2006)
Amyot, D., Farah, H., Roy, J.-F.: Evaluation of development tools for domain-specific modeling languages. In: International Workshop on System Analysis and Modeling, pp. 183–197. Springer (2006)
Sentosa, P., Möller, R., Gollmann, D., Garcia, M.: Generation of Text Editors for Custom Domain Specific Language on the Eclipse Platform. Master’s thesis, Hamburg University of Technology (2007)
Kelly, S.: Comparison of Eclipse EMF/GEF and MetaEdit+ for DSM. In: 19th Annual ACM Conference on Object-Oriented Programming, Systems, Languages, and Applications, OOPSLA, Portland, pp. 87–96. https://s23m.com/oopsla2004/kelly.pdf (2004)
Kern, H., Hummel, A., Kühne, S.: Towards a comparative analysis of meta-metamodels. In: Proceedings of the compilation of the co-located workshops on DSM’11, TMC’11, AGERE! 2011, AOOPES’11, NEAT’11, & VMIL’11, pp. 7–12 (2011)
Frankel, D.S.: Model Driven Architecture Applying MDA to Enterprise Computing. OMG Press, Wiley Publishing Inc, New York (2003)
Krogstie, J., Sindre, G., Jørgensen, H.: Process models representing knowledge for action: A revised quality framework. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 15(1), 91–102 (2006)
Schuette, R., Rotthowe, T.: The guidelines of modeling–an approach to enhance the quality in information models. In: International Conference on Conceptual Modeling, pp. 240–254. Springer (1998)
Green, T.R.G.: Cognitive dimensions of notations. In: Sutcliffe, A., Macaulay, L. (eds.) People and Computers V, pp. 443–460. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1989)
Green, T.R.G., Petre, M.: Usability analysis of visual programming environments: a cognitive dimensions framework. J. Visual Lang. Comput. 7(2), 131–174 (1996)
Störrle, H., Fish, A.: Towards an operationalization of the physics of notations for the analysis of visual languages. In: International Conference on Model Driven Engineering Languages and Systems, pp. 104–120. Springer (2013)
Acknowledgements
This research has been partially funded by the Regional Government of Madrid under the FORTE-CM project (S2018/TCS-4314) and the MADRID (TIN2017-88557-R) and MINECO/FEDER FAME (RTI2018-093608-B-C31) projects, financed by the Spanish Ministry of Economy, Industry and Competitiveness.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Richard Freeman Paige.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Granada, D., Vara, J.M., Merayo, M. et al. CEViNEdit: improving the process of creating cognitively effective graphical editors with GMF. Softw Syst Model 20, 867–895 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10270-020-00833-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10270-020-00833-2