Abstract
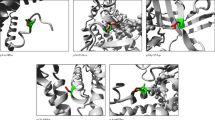
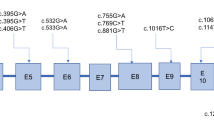
Glutaric aciduria type 1 (GA-1) is a rare but treatable inherited disease caused by deficiency of glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase activity due to GCDH gene mutations. In this study, we report 24 symptomatic GA-1 Brazilian patients, and present their clinical, biochemical, and molecular findings. Patients were diagnosed by high levels of glutaric and/or 3-hydroxyglutaric and glutarylcarnitine. Diagnosis was confirmed by genetic analysis. Most patients had the early-onset severe form of the disease and the main features were neurological deterioration, seizures and dystonia, usually following an episode of metabolic decompensation. Despite the early symptomatology, diagnosis took a long time for most patients. We identified 13 variants in the GCDH gene, four of them were novel: c.91 + 5G > A, c.167T > G, c.257C > T, and c.10A > T. The most common mutation was c.1204C > T (p.R402W). Surprisingly, the second most frequent mutation was the new mutation c.91 + 5G > A (IVS1 ds G-A + 5). Our results allowed a complete characterization of the GA-1 Brazilian patients. Besides, they expand the mutational spectrum of GA-1, with the description of four new mutations. This work reinforces the importance of awareness of GA-1 among doctors in order to allow early diagnosis and treatment in countries like Brazil where the disease has not been included in newborn screening programs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data of this study are not publicly available due to privacy or ethical restrictions.
References
Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L, Ramensk VE, Gerasimova A, Bork P, Kondrashov AS, Sunyaev SR (2010) A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat Methods 7(4):248–249. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth0410-248
Afroze B, Yunus ZM (2014) Glutaric aciduria type 1 - Importance of early diagnosis and treatment. J Pak Med Assoc 64(5):593–595. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25272554
Anikster Y, Shaag A, Joseph A, Mandel H, Ben-Zeev B, Christensen E, Elpeleg ON (1996) Glutaric aciduria type I in the Arab and Jewish communities in Israel. Am J Hum Genet 59(5):1012–1018
Barić I, Zschocke J, Christensen E, Duran M, Goodman SI, Leonard JV, Müller E, Morton DH, Superti-Furga A, Hoffmann GF (1998) Diagnosis and management of glutaric aciduria type I. J Inherit Metab Dis 21(4):326–340. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005390105171
Beauchamp MH, Boneh A, Anderson V (2009) Cognitive, behavioural and adaptive profiles of children with glutaric aciduria type I detected through newborn screening. J Inherit Metab Dis 32(SUPPL. 1):207–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-009-1167-z
Bergman I, Finegold D, Gartner JC, Zitelli BJ, Claassen D, Scarano J, Roe CR, Stanley C, Goodman SI (1989) Acute profound dystonia in infants with glutaric acidemia. Pediatrics 83(2):228–234
Biery BJ, Stein DE, Morton DH, Goodman SI (1996) Gene structure and mutations of glutaryl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase: Impaired association of enzyme subunits that is due to an A421V substitution causes glutaric acidemia type I in the amish. Am J Hum Genet 59(5):1006–1011
Boy N, Mühlhausen C, Maier EM, Heringer J, Assmann B, Burgard P, Dixon M, Fleissner S, Greenberg CR, Harting I, Hoffmann GF, Karall D, Koeller DM, Krawinkel MB, Okun JG, Opladen T, Posset R, Sahm K, Zschocke J, vom Dahl S (2017) Proposed recommendations for diagnosing and managing individuals with glutaric aciduria type I: second revision. J Inherit Metab Dis 40(1):75–101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-016-9999-9
Busquets C, Coll MJ, Ribes A (2000) Evidence of a single origin for the most frequent mutation (R402W) causing glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency: Identification of 3 novel polymorphisms and haplotype definition. Hum Mutat 15(2):207–207. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1098-1004(200002)15:2<207::aid-humu15>3.0.co;2-f
Busquets C, Merinero B, Christensen E, Gelpí JL, Campistol J, Pineda M, Fernández-Alvarez E, Prats JM, Sans A, Arteaga R, Martí M, Campos J, Martínez-Pardo M, Martínez-Bermejo A, Vaquerizo J, Orozco M, Ugarte M, Coll MJ, Ribes A (2000b) Glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency in Spain: Evidence of two groups of patients, genetically, and biochemically distinct. Pediatr Res 48(3):315–322. https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-200009000-00009
Christensen E, Ribes A, Busquets C, Pineda M, Duran M, Poll-The BT, Greenberg CR, Leffers H, Schwartz M (1997) Compound heterozygosity in the glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase gene with R227P mutation in one allele is associated with no or very low free glutarate excretion. J Inherit Metab Dis 20(3):383–386. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005390214391
Desmet FO, Hamroun D, Lalande M, Collod-Bëroud G, Claustres M, Béroud C (2009) Human splicing finder: an online bioinformatics tool to predict splicing signals. Nucleic Acids Res 37(9):e67. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp215
Goodman SI, Frerman FE (2001) Organic acidemias due to defects in lysine oxidation: 2-ketoadipic acidemia and glutaric acidemia. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D, Childs B, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (eds) The Metabolic & Molecular Basis of Inherited Disease, 8th edn. McGrawHill, New York, pp 2357–2365
Goodman SI, Moe P, Markey SP (1975) Glutaric acidemia: A new inborn error of amino acid metabolism. Clin Res 22(2)
Goodman SI, Stein DE, Schlesinger S, Christensen E, Schwartz M, Greenberg CR, Elpeleg ON (1998) Glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase mutations in glutaric acidemia (type I): Review and report of thirty novel mutations. Hum Mutat 12(3):141–144. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(1998)12:3<141::AID-HUMU1>3.0.CO;2-K
Harting I, Boy N, Heringer J, Seitz A, Bendszus M, Pouwels PJW, Kölker S (2015) 1H-MRS in glutaric aciduria type 1: impact of biochemical phenotype and age on the cerebral accumulation of neurotoxic metabolites. J Inherit Metab Dis 38(5):829–838. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-015-9826-8
Kölker S, Koeller DM, Okun JG, Hoffmann GF (2004) Pathomechanisms of neurodegeneration in glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. Ann Neurol 55(1):7–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.10784
Korman SH, Jakobs C, Darmin PS, Gutman A, van der Knaap MS, Ben-Neriah Z, Dweikat I, Wexler ID, Salomons GS (2007) Glutaric aciduria type 1: Clinical, biochemical and molecular findings in patients from Israel. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 11(2):81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpn.2006.11.006
Külkens S, Harting I, Sauer S, Zschocke J, Hoffmann GF, Gruber S, Bodamer OA, Kölker S (2005) Late-onset neurologic disease in glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. Neurology 64(12):2142–2144. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.WNL.0000167428.12417.B2
Kumar P, Henikoff S, Ng PC (2009) Predicting the effects of coding non-synonymous variants on protein function using the SIFT algorithm. Nat Protoc 4(7):1073–1082. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2009.86
Kurkina MV, Mihaylova SV, Baydakova GV, Saifullina EV, Korostelev SA, Pyankov DV, Kanivets IV, Yunin MA, Pechatnikova NL, Zakharova EY (2020) Molecular and biochemical study of glutaric aciduria type 1 in 49 Russian families: nine novel mutations in the GCDH gene. Metab Brain Dis 35(6):1009–1016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00554-x
Lindner M, Kölker S, Schulze A, Christensen E, Greenberg CR, Hoffmann GF (2004) Neonatal screening for glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. J Inherit Metab Dis 27(6):851–859. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BOLI.0000045769.96657.af
Lisyova J, Petrovic R, Jurickova K, Brennerova K, Urbanova D, Behulova D, Bzduch V, Chandoga J (2016) GAI - distinct genotype and phenotype characteristics in reported Slovak patients. Bratislava Med J 117(11):631–638. https://doi.org/10.4149/BLL_2016_123
Mosaeilhy A, Mohamed MM, George Priya Doss C, El Abd HSA, Gamal R, Zaki OK, Zayed H (2017) Genotype-phenotype correlation in 18 Egyptian patients with glutaric acidemia type I. Metab Brain Dis 32(5):1417–1426
Nelson DL, Cox MM (2006) Princípios de Bioquímica de Lehninger. Artmed, Porto Alegre
Pfeil J, Listl S, Hoffmann GF, Kölker S, Lindne M, Burgard P (2013) Newborn screening by tandem mass spectrometry for glutaric aciduria type 1: A cost-effectiveness analysis. Orphanet J Rare Dis 8(1):167. https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1172-8-167
Rashed MS, Bucknall MP, Little D, Awad A, Jacob M, Alamoudi M, Alwattar M, Ozand PT (1997) Screening blood spots for inborn errors of metabolism by electrospray tandem mass spectrometry with a microplate batch process and a computer algorithm for automated flagging of abnormal profiles. Clin Chem 43(7):129–1141. https://doi.org/10.1093/clinchem/43.7.1129
Schwartz M, Christensen E, Superti-Furga A, Brandt NJ (1998) The human glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase gene: Report of intronic sequences and of 13 novel mutations causing glutaric aciduria type I. Hum Genet 102(4):452–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390050720
Strauss KA, Morton DH (2003) Type I glutaric aciduria, part 2: A model of acute striatal necrosis. Am J Med Genet 121C(1):53–70. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.c.20008
Sweetman L (2006) Organic acid analysis. In: Hommes FA (ed) Techniques in diagnostic human biochemical genetics: a laboratory manual. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 143–176
Vargas CR, Ribas GS, da Silva JM, Sitta A, Deon M, Coelho DM, Wajner M (2018) Selective screening of fatty acids oxidation defects and organic acidemias by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry acylcarnitine analysis in Brazilian patients. Arch Med Res 49(3):205–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2018.08.004
Wajner M, Sitta A, Kayser A, Deon M, Groehs AC, Coelho DM, Vargas CR (2019) Screening for organic acidurias and aminoacidopathies in high-risk brazilian patients: Eleven-year experience of a reference center. Genet Mol Biol 42(1):178–185. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-4685-gmb-2018-0105
Zschocke J, Quak E, Guldberg P, Hoffmann GF (2000) Mutation analysis in glutaric aciduria type I. J Med Genet 37(3):177–181. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmg.37.3.177
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support of Fundo de Incentivo à Pesquisa e Eventos (FIPE/HCPA) (Porto Alegre, Brazil), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) (Brasília, Brazil), and Pró-Reitoria de Pesquisa/ UFRGS (PROPESP/UFRGS) (Porto Alegre, Brazil). We would like also to thank all staff, but especially the doctors of the Medical Genetics Service of the Clinical Hospital of Porto Alegre, as well as the physicians from the other hospitals of Brazil.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.S, L.V. e C.R.V. conceived and planned the study. A.S. wrote the manuscript with the support from G.G., L.V., C.S., M.W. and C.R.V. A.S, D.M.C, V.V.R. and B.G.R performed the organic acids and acylcarnitines analysis and performed the compilation of patients’ data. C.S. performed the molecular analysis. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Clinical Hospital of Porto Alegre (2015 − 0616).
Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 407 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sitta, A., Guerreiro, G., de Moura Coelho, D. et al. Clinical, biochemical and molecular findings of 24 Brazilian patients with glutaric acidemia type 1: 4 novel mutations in the GCDH gene. Metab Brain Dis 36, 205–212 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00632-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00632-0