Abstract
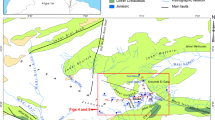
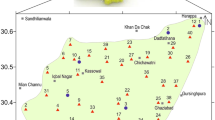
Due to unbalanced spatial distribution and insufficient capacity allocation of water resources in the Jinqu Basin, developing and utilizing the red bed groundwater require an effective method to address emergency water supply in this area. In this paper, geoelectric surveys employing high-density electrical resistivity tomography method were conducted to explore the geoelectric characteristics of red bed aquifer; six survey lines were arranged. The inverted resistivity profiles were validated by available borehole data and geological information. According to the notable resistivity differences between adjacent formations, the results revealed four primary geoelectric layers (Quaternary sediments, fractured siltstone aquifer, sandy conglomerate aquifer and calcareous siltstone beds) and two groundwater-storage structures (layered pore–fissure structure and vein–fault structure). Moreover, a water-rich region was delineated based on groundwater distribution and water yield of neighboring wells (> 500 m3/day). To assess further the potential of red bed groundwater, we established a hydro-geological numerical model of the water-rich region using groundwater modeling system. Aquifer permeability heterogeneity was considered by fitting the permeability coefficients collected from outcrops. The model was identified and verified by the water table at observed wells and subsequently employed to predict variation of groundwater level under different exploitation schemes. The simulation showed that short-term emergency exploitation has relatively less impact on regional groundwater environment, which demonstrates that the recovery capacity of water-rich region is good enough to cope with emergency exploitation. These findings provide important references for rational allocation and exploitation of red bed groundwater.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhter, G., & Hasan, M. (2016). Determination of aquifer parameters using geoelectrical sounding and pumping test data in Khanewal District, Pakistan. Open Geosciences, 8(1), 630–638.
Baines, D., Smith, D. G., Froese, D. G., Bauman, P., & Nimeck, G. (2002). Electrical resistivity ground imaging (ERGI): A new tool for mapping the lithology and geometry of channel-belts and valley-fills. Sedimentology, 49, 441–449.
Burgess, W. G., Hoque, M. A., Michael, H. A., Voss, C. I., Breit, G. N., & Ahmed, K. M. (2010). Vulnerability of deep groundwater in the Bengal Aquifer System to contamination by arsenic. Nature Geoscience, 3(2), 83–87.
Chen, J. S., Chen, X. M., & Liu, X. J. (2019). Sedimentary dynamics and climatic implications of Cretaceous loess-like red beds in the Lanzhou basin, Northwest China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.05.010.
Cho, J., Mostaghimi, S., & Kang, M. S. (2010). Development and application of a modeling approach for surface water and groundwater interaction. Agricultural Water Management, 97(1), 123–130.
Collins, B. D., & Stock, G. M. (2016). Rockfall triggering by cyclic thermal stressing of exfoliation fractures. Nature Geoscience, 9(5), 395.
Davis, J. M., Roy, N. D., Mozley, P. S., & Hall, J. S. (2006). The effect of carbonate cementation on permeability heterogeneity in fluvial aquifers: An outcrop analog study. Sedimentary Geology, 184(3–4), 267–280.
Duan, X. L., Ma, F. S., Zhao, H. J., Guo, J., Gu, H. Y., Lu, R., et al. (2019). Determining mine water sources and mixing ratios affected by mining in a coastal gold mine, in China. Environmental Earth Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8310-4.
Evans, U. F., George, N. J., Akpan, A. E., Obot, I. B., & Ikot, A. N. (2010). A study of superficial sediments and aquifers in parts of Uyo local government area, Akwa Ibom State, Southern Nigeria, using electrical sounding method. E-Journal of Chemistry, 7(3), 1018–1022.
Fang, N. F., Zeng, Y., Ni, L. S., & Shi, Z. H. (2019). Estimation of sediment trapping behind check dams using high-density electrical resistivity tomography. Journal of Hydrology, 568, 1007–1016.
Gao, B. L., Zhang, H. X., Yang, Z. F., Fu, Y., & Luo, L. J. (2019). The development mechanism and control technology visualization of the vault cracks in the ancient underground cavern of Longyou. Episodes, 42(4), 287–299.
Gu, H. Y., Ma, F. S., Guo, J., Li, K. P., & Lu, R. (2017). Hydrochemistry, multidimensional statistics, and rock mechanics investigations for Sanshandao Gold Mine, China. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2841-3.
Guo, F., Jiang, G. H., Polk, J. S., Huang, X. F., & Huang, S. Y. (2015). Resilience of groundwater impacted by land use and climate change in a karst aquifer, South China. Water Environment Research, 87(11), 1990–1998.
Hamzah, U., Samsudin, A. R., & Malim, E. P. (2006). Groundwater investigation in Kuala Selangor using vertical electrical sounding (VES) surveys. Environmental Geology, 51(8), 1349–1359.
Harland, W. B. (1992). Stratigraphic regulation and guidance—a critique of current tendencies in stratigraphic codes and guides. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 104(10), 1231–1235.
Hauck, C., Vonder Mühll, D., & Maurer, H. (2003). Using DC resistivity tomography to detect and characterize mountain permafrost. Geophysical Prospect, 51, 273–284.
Ibuot, J. C., Akpabio, G. T., & George, N. J. (2013). A survey of repository of groundwater potential and distribution using geoelectrical resistivity method in Itu L.G.A., Akwa Ibom State, Southern Nigeria. Central European Journal of Geosciences, 5(4), 538–547.
Jiang, Z., Liu, Q., Dekkers, M. J., Zhao, X., Roberts, A. P., Yang, Z., et al. (2017). Remagnetization mechanisms in Triassic red beds from South China. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 479, 219–230.
Koukadaki, M. A., Karatzas, G. P., Papadopoulou, M. P., & Vafidis, A. (2007). Identification of the saline zone in a coastal aquifer using electrical tomography data and simulation. Water Resources Management, 21(11), 1881.
Li, J. H., Ma, Z. L., Zhang, Y. Q., Dong, S. W., Li, Y., Lu, M. A., et al. (2014). Tectonic evolution of Cretaceous extensional basins in Zhejiang Province, eastern South China: Structural and geochronological constraints. International Geology Review, 56(13), 1602–1629.
Li, P. Y., Qian, H., Wu, J. H., Zhang, Y. Q., & Zhang, H. B. (2013). Major ion chemistry of shallow groundwater in the Dongsheng Coalfield, Ordos Basin, China. Mine Water and the Environment, 32(3), 195–206.
Ling, H., Guo, B., Xu, H., & Fu, J. (2014). Configuration of water resources for a typical river basin in an arid region of China based on the ecological water requirements (EWRs) of desert riparian vegetation. Global and Planetary Change, 122, 292–304.
Liu, Y. C., Santos, A., Wang, S. M., Shi, Y. L., Liu, H. L., & Yuen, D. A. (2007). Tsunami hazards along Chinese coast from potential earthquakes in South China Sea. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 163(1–4), 233–244.
Loke, M. H. (1996). Least-squares deconvolution of apparent resistivity pseudosections (vol. 60, p. 1682, 1995). Geophysics, 61(2), 621.
Martinez-Moreno, F. J., Pedrera, A., Ruano, P., Galindo-Zaldivar, J., Martos-Rosillo, S., Gonzalez-Castillo, L., et al. (2013). Combined microgravity, electrical resistivity tomography and induced polarization to detect deeply buried caves: Algaidilla cave (Southern Spain). Engineering Geology, 162, 67–78.
Meyerhoff, S. B., Maxwell, R. M., Revil, A., Martin, J. B., Karaoulis, M., & Graham, W. D. (2014). Characterization of groundwater and surface water mixing in a semiconfined karst aquifer using time-lapse electrical resistivity tomography. Water Resources Research, 50(3), 2566–2585.
Mohammed, I. N., Aboh, H. O., & Emenike, E. A. (2008). Hydrogeophysical investigation for groundwater potential in central Minna. Nigeria. Science World Journal, 3, 4. https://doi.org/10.4314/swj.v3i4.51827.
Muller, K., Vanderborght, J., Englert, A., Kemna, A., & Vereecken, H. (2005). Characterization of transport processes in a heterogeneous aquifer using electrical resistivity tomography (ERT). Bringing Groundwater Quality Research to the Watershed Scale, 297, 182–190.
Nan, T. C., Li, K. X., Wu, J. C., & Yin, L. H. (2018). Assessment of groundwater exploitation in an aquifer using the random walk on grid method: A case study at Ordos, China. Hydrogeology Journal, 26(5), 1669–1681.
Obiora, D. N., Ibuot, J. C., & George, N. J. (2015). Evaluation of aquifer potential, geoelectric and hydraulic parameters in Ezza North, southeastern Nigeria, using geoelectric sounding. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 13(2), 435–444.
Owen, S. J., Jones, N. L., & Holland, J. P. (1996). A comprehensive modeling environment for the simulation of groundwater flow and transport. Engineering with Computers, 12, 235–242.
Puckett, T. M., Colin, J. P., & Mitchell, S. (2012). New species and genera of Ostracoda from the Maastrichtian (Late Cretaceous) of Jamaica. Micropaleontology, 58(5), 397–455.
Ren, M. J., & Cao, F. X. (2009). Application of high density resistivity method to prospecting groundwater in red bed region. Science and Technology of West China, 08(5), 51–53.
Ritz, M., Parisot, J. C., Diouf, S., Beauvais, A., Dione, F., & Niang, M. (1999). Electrical imaging of lateritic weathering mantles over granitic and metamorphic basement of eastern Senegal, West Africa. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 41, 335–344.
Roy, P. K., Roy, S. S., Giri, A., Banerjee, G., Majumder, A., & Mazumdar, A. (2015). Study of impact on surface water and groundwater around flow fields due to changes in river stage using groundwater modeling system. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 17(1), 145–154.
Saar, M. O. (2011). Review: Geothermal heat as a tracer of large-scale groundwater flow and as a means to determine permeability fields. Hydrogeology Journal, 19(1), 31–52.
Sefelnasr, A., Gossel, W., & Wycisk, P. (2015). Groundwater management options in an arid environment: The Nubian Sandstone Aquifer System, Eastern Sahara. Journal of Arid Environments, 122(2), 46–58.
Seyfi, A., Afzalzadeh, R., & Hajnorouzi, A. (2017). Increase in water evaporation rate with increase in static magnetic field perpendicular to water–air interface. Chemical Engineering and Processing-Process Intensification, 120, 195–200.
Shao, J., Li, L., Cui, Y., & Zhang, Z. (2013). Groundwater flow simulation and its application in groundwater resource evaluation in the North China Plain. China Acta Geologica Sinica-English Edition, 87, 243–253.
Sharma, S. P., & Baranwal, V. C. (2005). Delineation of groundwater-bearing fracture zones in a hard rock area integrating very low frequency electromagnetic and resistivity data. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 57(2), 155–166.
Stel, H. (2009). Diagenetic crystallization and oxidation of siderite in red bed (Buntsandstein) sediments from the Central Iberian Chain, Spain. Sedimentary Geology, 213(3–4), 89–96.
Swanson-Hysell, N. L., Fairchild, L. M., & Slotznick, S. P. (2019). Primary and secondary red bed magnetization constrained by fluvial intraclasts. Journal of Geophysical Research-Solid Earth, 124(5), 4276–4289.
Wang, J., Cao, Y. C., Liu, K. Y., Liu, J., Xue, X. J., & Xu, Q. S. (2016). Pore fluid evolution, distribution and water–rock interactions of carbonate cements in red-bed sandstone reservoirs in the Dongying Depression, China. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 72, 279–294.
Wang, W. K., Kong, J. L., Duan, L., Wang, Y. L., & Ma, X. D. (2004). Research on the conversion relationships between the river and groundwater in the Yellow River drainage area. Science in China Series E-Engineering and Materials Science, 47, 25–41.
Wu, G., Yang, G., & Tan, H. (2016). Mapping coalmine goaf using transient electromagnetic method and high density resistivity method in Ordos City, China. Geodesy and Geodynamics, 7, 340–347.
Xian, H. B., Zhang, S. H., Li, H. Y., Xiao, Q. S., Chang, L. X., Yang, T. S., et al. (2019). How did South China connect to and separate from Gondwana? New Paleomagnetic constraints from the Middle Devonian red beds in South China. Geophysical Research Letters. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019gl083123.
Yan, Y. J., Yan, Y. S., Zhao, G. Z., Zhang, T. L., & Sun, Q. (2019). Study on moisture migration in natural slope using high-density electrical resistivity tomography method. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 40(7), 2807–2814.
Zenone, T., Morelli, G., Teobaldelli, M., Fischanger, F., Matteucci, M., Sordini, M., et al. (2008). Preliminary use of ground-penetrating radar and electrical resistivity tomography to study tree roots in pine forests and poplar plantations. Functional Plant Biology, 35(9–10), 1047–1058.
Zhan, J. W., Wang, Q., Zhang, W., Shangguan, Y. L., Song, S. Y., & Chen, J. P. (2019). Soil-engineering properties and failure mechanisms of shallow landslides in soft-rock materials. CATENA. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.104093.
Zhang, S. H. (2010). Investigation of groundwater pollution at a landfill site using high-density electric resistivity tomography. In Near-surface geophysics and geohazards—Proceedings of/the 4th international conference on environmental and engineering geophysics (Vols. 1–2, pp. 391–394).
Zhang, Y. Q., Gong, H. L., Gu, Z. Q., Wang, R., Li, X. J., & Zhao, W. J. (2014). Characterization of land subsidence induced by groundwater withdrawals in the plain of Beijing city, China. Hydrogeology Journal, 22(2), 397–409.
Zhang, Z. J., Li, L. H., Xu, W. J., Fu, Y., & Feng, J. (2015). Flat-plate roof collapse of shallow caverns and protective measures: A case study of Longyou ancient siltstone caverns. Natural Hazards, 76(1), 191–213.
Zhang, Y. F., Zhao, Y., Yang, H. Q., & Wang, C. L. (2020). A semianalytical solution for a griffith crack nonuniformly pressurized by internal fluid. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02052-z.
Zhao, Y., He, P. F., Zhang, Y. F., & Wang, C. L. (2019). A new criterion for a toughness-dominated hydraulic fracture crossing a natural frictional interface. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 52(8), 2617–2629.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51374257, 50804060), the Research Fund for Talents of Guizhou University (Grant No. 201901) and the Special Research Funds of Guizhou University (Grant No. 201903).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Zhang, Y., Yang, H. et al. Assessment of Red Bed Groundwater in the Jinqu Basin, Southeastern China: Its Enrichment Regularity and Emergency Exploitation Potential. Nat Resour Res 29, 3743–3769 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-020-09688-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-020-09688-2