Abstract
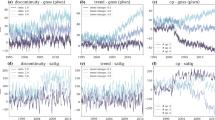
We present an improved clustering approach for grouping regional GPS stations with similar annual signals into four similarity levels. A newly introduced criterion, the annual phase difference among stations, reinforces the clustering process and resolves the discrepancy among the annual signals of stations classified into several clusters. Comparisons show that the improved method enhances the accuracy and representativeness of the land surface deformation features derived from the mean annual signals of clustered stations. With respect to CMONOC stations throughout mainland China, the observed GPS coordinate time series are probably more reliable for acquiring real land surface deformations when employing the 25 regional clusters derived from the improved approach in comparison with some modeled surface loading models (SLMs), which potentially contain mistakes. Based on the results of the improved technique, descriptions of the annual land surface deformation throughout China are given to illustrate the characteristics of the annual signals of GPS station motions in different regions. For the annual signals of the 25 clusters discussed, those of 10 clusters show obvious sinusoidal shapes, including 7 clusters in Southwest China. The peaks and troughs of these annual motion signals happen during different times of a year for northern and southern station signals. In applications to land surface deformation, the improved method can play a preliminary but significant role in searching for the most stable stations before comparing the results of GPS with other geodetic techniques, such as the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment and SLMs.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The GPS datasets employed in this manuscript was acquired from the China Earthquake Administration (CEA, ftp://ftp.cgps.ac.cn/products/position/gamit/). If this site is not working, the data will be available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Blewitt G, Lavallee D, Clarke P, Nurutdinov K (2001) A new global mode of earth deformation: seasonal cycle detected. Science 294:2342–2345. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1065328
Bos MS, Fernandes RMS (2016) Hector user manual version 1.6. http://segal.ubi.pt/hector. Accessed 25 Sept 2020
Bos MS, Fernandes RMS, Williams SDP, Bastos L (2013) Fast error analysis of continuous GNSS observations with missing data. J Geod 87(4):351–360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-012-0605-0
Chanard K, Fleitout L, Calais E, Rebischung P, Avouac JP (2018) Toward a global horizontal and vertical elastic load deformation model derived from GRACE and GNSS station position time series. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 123:3225–3237. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JB015245
Freymueller JT (2009) Seasonal position variations and regional reference frame realization. In: International association of geodesy symposia, vol 134. Springer, Berlin, pp 191–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-00860-3_30
Gu Y, Yuan L, Fan D, You W, Su Y (2017) Seasonal crustal vertical deformation induced by environmental mass loading in mainland China derived from GPS, GRACE and surface loading models. Adv Space Res 59(1):88–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2016.09.008
Herring RTA, King W, McClusky SC (2010) GAMIT/GLOBK reference manuals, release 10.4. MIT Technical Reports, Cambridge
Liu R, Zou R, Li J, Zhang C, Zhao B, Zhang Y (2018) Vertical displacements driven by groundwater storage changes in the North China plain detected by GPS observations. Remote Sens 10(2):259–271. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020259
Ray J (2006) Systematic errors in GPS position estimates. Presentation at IGS 2006 workshop, Darmstadt. ftp://igs.org/pub/resource/pubs/06_darmstadt/IGS%20Abstracts%20PDF/11_Ray_abs.pdf. Accessed 25 Sept 2020
Rebischung P, Griffiths J, Ray J, Schmid R, Collilieux X, Garayt B (2012) IGS08: the IGS realization of ITRF2008. GPS Solut 16(1):483–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-011-0248-2
Santamaría-Gómez A, Bouin MN, Collilieux X, Wöppelmann G (2011) Correlated errors in GPS position time series: implications for velocity estimates. J Geophys Res 116:B01405. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JB007701
Tesmer V, Steigenberger P, Rothacher M, Boehm J, Meisel B (2009) Annual deformation signals from homogeneously reprocessed VLBI and GPS height time series. J Geod 83:973–988. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-009-0316-3
Tesmer V, Steigenberger P, van Dam T, Mayer-Gürr T (2011) Vertical deformations from homogeneously processed GRACE and global GPS long-term series. J Geod 85:291–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-010-0437-8
van Dam T, Blewitt G, Heflin MB (1994) Atmospheric pressure loading effects on global positioning system coordinate determinations. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 99(B12):23939. https://doi.org/10.1029/94JB02122
van Dam T, Wahr J, Chao Y, Leuliette E (1997) Predictions of crustal deformation and of geoid and sea-level variability caused by oceanic and atmospheric loading. Geophys J Int 129(3):507–517. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.1997.tb04490.x
van Dam T, Wahr J, Milly PCD, Shmakin AB, Blewitt G, Lavallée D, Larson KM (2001) Crustal displacements due to continental water loading. Geophys Res Lett 28(4):651–654. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000GL012120
Williams SDP (2008) CATS: GPS coordinate time series analysis software. GPS Solut 12(2):147–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-007-0086-4
Williams SDP, Penna NT (2011) Nontidal ocean loading effects on geodetic GPS heights. Geophys Res Lett 38:L09314. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011gl046940
Williams SDP, Bock Y, Fang P, Jamason P, Nikolaidis RM, Prawirodirdjo L, Miller M, Johnson DJ (2004) Error analysis of continuous GPS position time series. J Geophys Res 109:B03412. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003JB002741
Wu S, Nie G, Liu J, Xue C, Wang J, Li H, Peng F (2019) Analysis of deterministic and stochastic models of GPS stations in the crustal movement observation network of China. Adv Space Res 64(2):335–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2019.04.032
Xiang Y, Yue J, Li Z (2018) Joint analysis of seasonal oscillations derived from GPS observations and hydrological loading for mainland China. Adv Space Res 62(11):3148–3161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2018.08.028
Yang C, Zhang D, Zhao C, Han B, Sun R, Du J, Chen L (2019) Ground deformation revealed by sentinel-1 MSBAS-InSAR time-series over Karamay Oilfield, China. Remote Sens 11(17):2027. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11172027
Yuan P, Li Z, Jiang W, Ma Y, Chen W, Sneeuw N (2018) Influences of environmental loading corrections on the nonlinear variations and velocity uncertainties for the reprocessed global positioning system height time series of the crustal movement observation network of China. Remote Sens 10(6):958. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060958
Acknowledgements
The GPS height time series of CMONOC stations are from the China Earthquake Administration (CEA, ftp://ftp.cgps.ac.cn/products/position/gamit/). We apply the software Hector (http://segal.ubi.pt/hector/) to compute and analyze GPS coordinate time series. The Chinese Scholarship Council (CSC) has provided the first author a scholarship which allows him to visit the University of Nottingham in the UK for 1 year from September 2019. This work is supported by the 2018 Joint R&D and Demonstration Project of the Strategic International Science and Technology Innovation Cooperation Key Project (Project No. 2018YFE0206500). In addition, figures in this paper are displayed using GMT and MATLAB. We express our sincere gratitude to these organizations and software providers.
Funding
This work was supported by Chinese Government Scholarship (Grant No. 201906270213).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, S., Nie, G., Meng, X. et al. Application of an annual phase-augmented clustering approach to annual detection of vertical GPS station deformation. GPS Solut 25, 7 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-020-01042-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-020-01042-6