Abstract
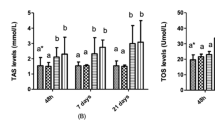
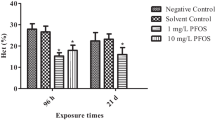
Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) is a legacy contaminant that has been detected globally within the environment and throughout numerous species, including humans. Despite an international ban on its use, this unique contaminant continues to persist in organisms and their surroundings due to PFOS’s inability to breakdown into nontoxic forms resulting in bioaccumulation. In this study, we analyzed the effects of a technical mixture of PFOS (linear and branched isomers) in the adult Eastern oyster, Crassostrea virginica, at 2 days and 7 days exposure. Biomarker analysis (lysosomal destabilization, lipid peroxidation, and glutathione assays) in oyster tissue along with chemical analysis (liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry) of PFOS in oyster tissue and water samples revealed the oysters’ ability to overcome exposures without significant damage to lipid membranes or the glutathione phase II enzyme system; however, significant cellular lysosomal damage was observed. The oysters were able to eliminate up to 96% of PFOS at 0.3 mg/L and 3 mg/L exposures when allowed to depurate for 2 days in clean seawater. Chemical analysis showed the linear isomer to be the prevailing fraction of the residual PFOS contained in oyster tissue. Results provide insight into possible detrimental cellular effects of PFOS exposure in addition to offering insight into contaminant persistence in oyster tissue.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data can be obtained from Allisan Aquilina-Beck on request (allisan.beck@noaa.gov).
References
Ankley GT, Kuehl DW, Kahl MD, Jensen KM, Butterworth BC, Nichols JW (2004) Partial life-cycle toxicity and bioconcentration modeling of perfluorooctanesulfonate in the northern leopard frog (Rana pipiens). Environ Toxicol Chem 23:2745–2755. https://doi.org/10.1897/03-667
Awad E et al (2011) Long-term environmental fate of perfluorinated compounds after accidental release at Toronto airport. Environ Sci Technol 45:8081–8089. https://doi.org/10.1021/es2001985
Beach SA, Newsted JL, Coady K, Giesy JP (2006) Ecotoxicological evaluation of perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS). Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 186:133–174. https://doi.org/10.1007/0-387-32883-1_5
Benskin JP, Holt A, Martin JW (2009) Isomer-specific biotransformation rates of a perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS)-precursor by Cytochrome P450 isozymes and human liver microsomes. Environ Sci Technol 43:8566–8572
Butenhoff JR (2015) Toxicology data for alternative “short chain” fluorinated substances. toxicological effects of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Humana Press, Totowa
Buck RC, Franklin J, Berger U, Conder JM, Cousins IT, De Voogt P, Jensen AA, Kannan K, Mabury SA, van Leeuwen SP (2011) Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the environment: Terminology, classification, and origins. Integr Environ Asses Manag 7:513–541
Conners DE, Ringwood AH (2000) Effects of glutathione depletion on copper cytotoxicity in oysters (Crassostrea virginica). Aquat Toxicol 50:341–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0166-445x(00)00092-8
Convention S (2009) Report of the conference of the parties of the Stockholm convention on persistent organic pollutants on the work of its fourth meeting. UNEP/POPS/COP.4/38. 8 May 2009 (www.pops.int)
Convention S (2019) UN Experts recommend elimination of additional hazardous chemicals to protect human health and the environment. Geneva
DeLorenzo ME, De Leon RG (2010) Toxicity of the insecticide etofenprox to three life stages of the grass shrimp, Palaemonetes pugio. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 58:985–990. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-010-9496-3
DeLorenzo ME, Serrano L, Chung KW, Hoguet J, Key PB (2006a) Effects of the insecticide permethrin on three life stages of the grass shrimp, Palaemonetes pugio. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 64:122–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2006.02.001
DeLorenzo ME, Serrano L, Chung KW, Hoguet J, Key PB (2006b) Effects of the insecticide permethrin on three life stages of the grass shrimp, Palaemonetes pugio. Ecotox Environ Safe 64:122–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2006.02.001
DeLorenzo ME et al (2018) Comparative toxicity of two chemical dispersants and dispersed oil in estuarine organisms. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 74:414–430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-017-0430-9
DeWitt J (2015) Toxicological effects of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Humana Press, Totowa
Ding GH et al (2015) Toxicity and DNA methylation changes induced by perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) in sea urchin Glyptocidaris crenularis. Chemosphere 128:225–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.01.045
EPA U (2000) Perfluoroocyly sulfonates: proposed significant new use rule, vol 65
Fair PA, Houde M, Hulsey TC, Bossart GD, Adams J, Balthis L, Muir DCG (2012) Assessment of perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) in plasma of bottlenose dolphins from two southeast US estuarine areas: relationship with age, sex and geographic locations. Mar Pollut Bull 64:66–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.10.022
Fair PA, Wolf B, White ND, Arnott SA, Kannan K, Karthikraj R, Vena JE (2019) Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in edible fish species from Charleston Harbor and tributaries, South Carolina, United States: exposure and risk assessment. Environ Res 171:266–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.01.021
Giesy JP, Kannan K (2001) Global distribution of perfluorooctane sulfonate in wildlife. Environ Sci Technol 35:1339–1342. https://doi.org/10.1021/es001834k
Hoguet J, Key PB (2007) Activities of biomarkers in multiple life stages of the model crustacean, Palaemonetes pugio. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 353:235–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2007.09.011
Hong S et al (2015) Bioaccumulation characteristics of perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) in coastal organisms from the west coast of South Korea. Chemosphere 129:157–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.06.023
Houde M, Czub G, Small JM, Backus S, Wang X, Alaee M, Muir DC (2008) Fractionation and bioaccumulation of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) isomers in a Lake Ontario food web. Environ Sci Technol 42:9397–9403. https://doi.org/10.1021/es800906r
Houde M, De Silva AO, Muir DCG, Letcher RJ (2011) Monitoring of perfluorinated compounds in aquatic biota: an updated review PFCs in aquatic biota. Environ Sci Technol 45:7962–7973. https://doi.org/10.1021/es104326w
Hunter AC, Moghimi SM (2010) Cationic carriers of genetic material and cell death: a mitochondrial tale. Bba-Bioenergetics 1797:1203–1209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2010.03.026
Hwang HM, Wade TL, Sericano JL (2002) Relationship between lysosomal membrane destabilization and chemical body burden in eastern oysters (Crassostrea virginica) from Galveston Bay, Texas, USA. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:1268–1271. https://doi.org/10.1897/1551-5028(2002)021%3c1268:Rblmda%3e2.0.Co;2
Jeon J, Kannan K, Lim HK, Moon HB, Kim SD (2010a) Bioconcentration of perfluorinated compounds in blackrock fish, sebastes schlegeli, at different salinity levels. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:2529–2535. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.310
Jeon J, Kannan K, Lim HK, Moon HB, Ra JS, Kim SD (2010b) Bioaccumulation of perfluorochemicals in Pacific oyster under different salinity gradients. Environ Sci Technol 44:2695–2701. https://doi.org/10.1021/es100151r
Kannan K, Hansen KJ, Wade TL, Giesy JP (2002) Perfluorooctane sulfonate in oysters, Crassostrea virginica, from the Gulf of Mexico and the Chesapeake Bay, USA. Arch Environ Con Toxicol 42:313–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-001-0003-8
Key BD, Howell RD, Criddle CS (1997) Fluorinated organics in the biosphere. Environ Sci Technol 31:2445–2454. https://doi.org/10.1021/es961007c
Khan B, Adeleye AS, Burgess RM, Russo SM, Ho KT (2019) Effects of graphene oxide nanomaterial exposures on the marine bivalve, Crassostrea virginica. Aquat Toxicol 216:105297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.105297
Kissa E (2001) Fluorinated surfactants and repellents, 2nd edn. Marcel Dekker, New York
Lau C (2015) Perfluorinated compounds: an overview. In: DeWitt J (ed) Toxicological effects of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 1–22
Liu CS, Yu K, Shi XJ, Wang JX, Lam PKS, Wu RSS, Zhou BS (2007) Induction of oxidative stress and apoptosis by PFOS and PFOA in primary cultured hepatocytes of freshwater tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquatic Toxicol 82:135–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2007.02.006
Liu J, Qu R, Yan L, Wang L, Wang Z (2016) Evaluation of single and joint toxicity of perfluorooctane sulfonate and zinc to Limnodrilus hoffmeisteri: acute toxicity, bioaccumulation and oxidative stress. J Hazard Mater 301:342–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.09.010
Martin JW, Whittle DM, Muir DC, Mabury SA (2004) Perfluoroalkyl contaminants in a food web from Lake Ontario. Environ Sci Technol 38:5379–5385. https://doi.org/10.1021/es049331s
McCarthy MP, Carroll DL, Ringwood AH (2013) Tissue specific responses of oysters, Crassostrea virginica, to silver nanoparticles. Aquat Toxicol 138–139:123–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.04.015
Moody CA, Martin JW, Kwan WC, Muir DC, Mabury SA (2002) Monitoring perfluorinated surfactants in biota and surface water samples following an accidental release of fire-fighting foam into Etobicoke Creek. Environ Sci Technol 36:545–551. https://doi.org/10.1021/es011001+
Moore MN (1985) Cellular responces to pollutants. Mar Pollut Bull 16:134–139
NMFS (2016) Fisheries of the United States 2015. Current Fishery Statistics No. 2015. Silver Spring, MD
O’Connor TP (1996) Trends in chemical concentrations in Mussels and oysters collected along the US coast from 1986 to 1993. Mar Environ Res 41:183–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/0141-1136(95)00011-9
Reiner JL et al (2012) Determination of perfluorinated alkyl acid concentrations in biological standard reference materials. Anal Bioanal Chem 404:2683–2692. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-5943-5
Ringwood AH, Conners DE, Hoguet J (1998) Effects of natural and anthropogenic stressors on lysosomal destabilization in oysters Crassostrea virginica. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 166:163–171. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps166163
Ringwood AH, Hoguet J, Keppler CJ (2002) Seasonal variation in lysosomal destabilization in oysters, Crassostrea virginica. Mar Environ Res 54:793–797. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-1136(02)00181-2
Ringwood AH, Hoguet J, Keppler CJ, Gielazyn ML, Ward BP, Rourk AR (2003) Cellular biomarkers (lysosomal destabilization, glutathione and lipid peroxidation) in three common estuarine species: a methods handbook
Viberg HM (2015) Neurotoxicity. In: DeWitt J (ed) Toxicological effects of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Humama Press, Totowa, pp 219–238
Wu G, Fang YZ, Yang S, Lupton JR, Turner ND (2004) Glutathione metabolism and its implications for health. J Nutr 134:489–492. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/134.3.489
Young WM, South P, Begley TH, Noonan GO (2013) Determination of perfluorochemicals in fish and shellfish using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 61:11166–11172. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf403935g
Yuan ZQ, Zhang JY, Meng W, Zhou Y (2014) Effects of perfluorooctane sulfonate on behavioural activity, regeneration and antioxidant enzymes in planarian Dugesia japonica. Chem Ecol 30:187–195. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2013.831081
Zhao Z, Xie Z, Moller A, Sturm R, Tang J, Zhang G, Ebinghaus R (2012) Distribution and long-range transport of polyfluoroalkyl substances in the Arctic, Atlantic Ocean and Antarctic coast. Environ Pollut 170:71–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2012.06.004
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Dr. Paul Pennington (NOAA, Charleston, SC) for the statistical assistance, along with Blaine West and James Daugomah for help with oyster collection. Special thanks to Emily Pisarski, Dr. Erik Davenport, and Dr. Katherine Peter for their critical review of this manuscript.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
244_2020_765_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplementary material 1: Extracted ion chromatogram of PFOS (transition 499 > 80) in water samples 24 h post dose (1) control water, (2) 0.3 ppm dosed water, and (3) 3.0 ppm dosed water. (DOCX 52 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aquilina-Beck, A.A., Reiner, J.L., Chung, K.W. et al. Uptake and Biological Effects of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate Exposure in the Adult Eastern Oyster Crassostrea virginica. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 79, 333–342 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-020-00765-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-020-00765-4