Abstract
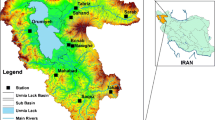
Climate change impacts on soil moisture have caused numerous environmental problems in different regions of the world, especially the arid and semiarid regions. The present study was carried out to examine the effect of climate change on soil moisture variations across a semiarid region of Iran, namely Meyghan wetland, using the multivariate regression. Mean Modified Normalized Difference Water Index (mMNDWI) was utilized to monitor soil moisture variations over the 28-year study period (1990–2017). The association between alteration in soil surface moisture (SM) and Dust Storm Index (DSI) was also explored using the bivariate regression method. Results showed that the area has experienced an increasing trend of soil moisture losses with a rate of 0.02 per 28 years. Increased wind velocity and decreased precipitation were recognized as the major driving forces in wetland degradation. The standardized regression coefficients for these factors were estimated at + 0.34 and − 0.28, respectively. However, no significant relationship was found between air temperature and evapotranspiration with mMNDWI. Based on adjusted determination coefficient (R2Adj), 75% of variations in soil moisture could be explained by rainfall and surface winds velocity changes across the study area. Our results showed that the ridge regression was able to show the dependence of mMNDWI variations on meteorological elements. It was also indicated that 23% of incremental changes in sand-dust events were due to wetland destruction. These findings provided a theoretical basis for understanding the climate change effects on soil moisture and the wetland degradation on dust emission over a semiarid region.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abderrezek, M., & Fathi, M. (2017). Experimental study of the dust effect on photovoltaic panels’ energy yield. Solar Energy, 142, 308–320.
Adib, A., Oulapour, M., & Chatroze, A. (2018). Effects of wind velocity and soil characteristics on dust storm generation in Hawr-al-Azim Wetland, Southwest Iran. Caspian Journal of Environmental Sciences, 16(4), 333–347.
Ahmadi, R. (2018). Evaluation of the central part of Arak Miqan sodium sulfate deposit using geometric and geostatistical methods. Geological research, 9(36), 19–32. (In persian).
Alizadeh-Choobari, O., Zawar-Reza, P., & Sturman, A. (2014). The “wind of 120 days” and dust storm activity over the Sistan Basin. Atmospheric Research, 143, 328–341.
Alongi, D. M. (2015). The impact of climate change on mangrove forests. Current Climate Change Reports, 1(1), 30–39.
Ansari, A., & Golabi, M. H. (2018). Prediction of spatial land use changes based on LCM in a GIS environment for Desert Wetlands—A case study: Meighan Wetland, Iran. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 7, 64–70.
Arsanjani, T. J., Javidan, R., Nazemosadat, M. J., Arsanjani, J. J., & Vaz, E. (2015). Spatiotemporal monitoring of Bakhtegan Lake’s areal fluctuations and an exploration of its future status by applying a cellular automata model. Computers and Geosciences, 78, 37–43.
Atabey Peker, E., Kamil Yilmaz, K., & Lutfi Suzen, M. (2018). Long-term water extent mapping of lakes in the Lakes Region, Turkey, using multiple satellites. In EGU general assembly conference abstracts (p. 12944).
Bartl, B., Mašková, L., Paulusová, H., Smolík, J., Bartlová, L., & Vodička, P. (2016). The effect of dust particles on cellulose degradation. Studies in Conservation, 61(4), 203–208.
Behrooz, R. D., Esmaili-Sari, A., Bahramifar, N., & Kaskaoutis, D. (2017). Analysis of the TSP, PM10 concentrations and water-soluble ionic species in airborne samples over Sistan, Iran during the summer dusty period. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 8(3), 403–417.
Bisal, F., & Hsieh, J. (1966). Influence of moisture on erodibility of soil by wind. Soil Science, 102(3), 143–146.
Buck, B. J., King, J., & Etyemezian, V. (2011). Effects of salt mineralogy on dust emissions, Salton Sea, California. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 75(5), 1971–1985.
Chander, G., Markham, B. L., & Helder, D. L. (2009). Summary of current radiometric calibration coefficients for Landsat MSS, TM, ETM + , and EO-1 ALI sensors. Remote Sensing of Environment, 113(5), 893–903.
Chen, J., Wang, S., & Mao, Z. (2011). Monitoring wetland changes in Yellow River Delta by remote sensing during 1976–2008. Progress in Geography, 30, 587–592.
Chepil, W. (1956). Influence of moisture on erodibility of soil by wind 1. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 20(2), 288–292.
Cohen, P., West, S. G., & Aiken, L. S. (2014). Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences. New York: Psychology Press.
Cracknell, A. P. (2007). Introduction to remote sensing. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Davarzani, H., Smits, K., Tolene, R. M., & Illangasekare, T. (2014). Study of the effect of wind speed on evaporation from soil through integrated modeling of the atmospheric boundary layer and shallow subsurface. Water Resources Research, 50(1), 661–680.
Deng, Q., Deng, L., Miao, Y., Guo, X., & Li, Y. (2019). Particle deposition in the human lung: Health implications of particulate matter from different sources. Environmental Research, 169, 237–245.
Ebrahimi-Khusfi, Z., Khosroshahi, M., Roustaei, F., & Mirakbari, M. (2020a). Spatial and seasonal variations of sand-dust events and their relation to atmospheric conditions and vegetation cover in semi-arid regions of central Iran. Geoderma, 365, 114225.
Ebrahimi-Khusfi, Z., Roustaei, F., Ebrahimi Khusfi, M., & Naghavi, S. (2020b). Investigation of the relationship between dust storm index, climatic parameters, and normalized difference vegetation index using the ridge regression method in arid regions of Central Iran. Arid Land Research and Management, 34, 239–263.
Ebrahimi-Khusfi, Z., Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R., & Mirakbari, M. (2020c). Evaluation of machine learning models for predicting the temporal variations of dust storm index in arid regions of Iran. Atmospheric Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2020.08.029.
Ebrahimi-Khusfi, Z., & Zarei, M. (2020). Relationships between meteorological drought and vegetation degradation using satellite and climatic data in a semi-arid environment in Markazi Province, Iran. Journal of Rangeland Science, 10(2), 204–216.
El-Asmar, H. M., Hereher, M. E., & El Kafrawy, S. B. (2013). Surface area change detection of the Burullus Lagoon, North of the Nile Delta, Egypt, using water indices: A remote sensing approach. The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Science, 16(1), 119–123.
Finlayson, C. M., Davidson, N., Fennessy, S., Coates, D., Gardner, R. C., Darwall, W., et al. (2018). Section 2: Status and trends. In R. C. Gardner & C. M. Finlayson (Eds.), Global wetland outlook: State of the world’s wetlands and their services to people. Gland: Ramsar Convention Secretariat.
Gardner, R. C., Barchiesi, S., Beltrame, C., Finlayson, C., Galewski, T., Harrison, I., et al. (2015). State of the world's wetlands and their services to people: a compilation of recent analyses. Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=2589447 or https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2589447.
Gautam, V. K., Gaurav, P. K., Murugan, P., & Annadurai, M. (2015). Assessment of surface water dynamicsin Bangalore using WRI, NDWI, MNDWI, supervised classification and KT transformation. Aquatic Procedia, 4, 739–746.
Ge, Z., Fang, S., Chen, H., Zhu, R., Peng, S., & Ruan, H. (2018). Soil aggregation and organic carbon dynamics in poplar plantations. Forests, 9(9), 508.
Gholampour, A., Nabizadeh, R., Hassanvand, M. S., Taghipour, H., Nazmara, S., & Mahvi, A. H. (2015). Characterization of saline dust emission resulted from Urmia Lake drying. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 13(1), 82.
Goudie, A. S. (2014). Desert dust and human health disorders. Environment International, 63, 101–113.
Goudie, A. (2018). Dust storms and ephemeral lakes. Desert, 23(1), 153–164.
Haibo, Y., Zongmin, W., Hongling, Z., & Yu, G. (2011). Water body extraction methods study based on RS and GIS. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 10, 2619–2624.
Hammad, B., Al-Abed, M., Al-Ghandoor, A., Al-Sardeah, A., & Al-Bashir, A. (2018). Modeling and analysis of dust and temperature effects on photovoltaic systems’ performance and optimal cleaning frequency: Jordan case study. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 82, 2218–2234.
Hegazy, A. A. (2001). Effect of dust accumulation on solar transmittance through glass covers of plate-type collectors. Renewable Energy, 22(4), 525–540.
Hirpo, L. A. (2011). Climate change and wetland resources vulnerability: Impacts on livelihoods and opportunities for enhancing in Ethiopia. In Impacts of climate change and population on tropical aquatic resources (p. 50).
Ho, L., Umitsu, M., & Yamaguchi, Y. (2010). Flood hazard mapping by satellite images and SRTM DEM in the Vu Gia-Thu Bon alluvial plain, Central Vietnam. International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Science, 38(Part 8), 275–280.
Hoerl, A. E., & Kennard, R. W. (1970). Ridge regression: Biased estimation for nonorthogonal problems. Technometrics, 12(1), 55–67.
Huang, J., Yu, H., Guan, X., Wang, G., & Guo, R. (2016). Accelerated dryland expansion under climate change. Nature Climate Change, 6(2), 166.
Ishizuka, M., Mikami, M., Yamada, Y., Zeng, F., & Gao, W. (2005). An observational study of soil moisture effects on wind erosion at a gobi site in the Taklimakan Desert. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 110(D18), D18S03.
Jaafari, S., Shabani, A. A., & Danehkar, A. (2013). Investigation of coastline change of the Urmia Lake using remote sensing and GIS (1990–2012). International Journal of Aquatic Biology, 1(5), 215–220.
Jafari, R., Bashari, H., & Tarkesh, M. (2017). Discriminating and monitoring rangeland condition classes with MODIS NDVI and EVI indices in Iranian arid and semi-arid lands. Arid Land Research and Management, 31(1), 94–110.
Jawak, S., & Luis, A. (2015). A rapid extraction of water body features from antarctic coastal oasis using very high-resolution satellite remote sensing data. Aquatic Procedia, 4, 125–132.
Karegar, E., Hamzeh, N. H., Jamali, J. B., Abadi, A. R. S., Moeinaddini, M., & Goshtasb, H. (2019). Numerical simulation of extreme dust storms in east of Iran by the WRF-Chem model. Natural Hazards, 99(2), 769–796.
Karydis, V., Kumar, P., Barahona, D., Sokolik, I., & Nenes, A. (2011). On the effect of dust particles on global cloud condensation nuclei and cloud droplet number. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 116(D23), D23204.
Kharazmi, R., Tavili, A., Rahdari, M. R., Chaban, L., Panidi, E., & Rodrigo-Comino, J. (2018). Monitoring and assessment of seasonal land cover changes using remote sensing: A 30-year (1987–2016) case study of Hamoun Wetland, Iran. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190(6), 356.
Khusfi, Z., Vali, A., Khosroshahi, M., & Ghazavi, R. (2017). The role of dried bed of Gavkhooni wetland on the production of the internal dust using remote sensing and storm roses (case study: Isfahan province). Iranian Journal of Range and Desert Research, 24(1), 152–163.
Kim, H., Zohaib, M., Cho, E., Kerr, Y. H., & Choi, M. (2017). Development and assessment of the sand dust prediction model by utilizing microwave-based satellite soil moisture and reanalysis datasets in East Asian desert areas. Advances in Meteorology. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1917372.
Kottek, M., Grieser, J., Beck, C., Rudolf, B., & Rubel, F. (2006). World map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated. Meteorologische Zeitschrift, 15(3), 259–263.
Li, W., Du, Z., Ling, F., Zhou, D., Wang, H., Gui, Y., et al. (2013). A comparison of land surface water mapping using the normalized difference water index from TM, ETM + and ALI. Remote Sensing, 5(11), 5530–5549.
Li, X., & Zhang, H. (2014). Soil moisture effects on sand saltation and dust emission observed over the Horqin Sandy Land area in China. Journal of Meteorological Research, 28(3), 444–452.
MacFeeters, S. (1995). The use of Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water feature. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 17(7), 1425–1432.
Mahdavi, S., Salehi, B., Granger, J., Amani, M., Brisco, B., & Huang, W. (2018). Remote sensing for wetland classification: A comprehensive review. GIScience and Remote Sensing, 55(5), 623–658.
Mahdianpari, M., Rezaee, M., Zhang, Y., & Salehi, B. (2018). Wetland classification using deep convolutional neural network. In IGARSS 2018-2018 IEEE international geoscience and remote sensing symposium. IEEE (pp. 9249–9252).
Mehrizi, E., Biglari, H., Amiri, R., Baneshi, M., Mobini, M., Ebrahimzadeh, G., et al. (2017). Determine the important heavy metals in air dust of zahedan, Iran. Pollution Research, 36, 474–480.
Miller, R., & Tegen, I. (1998). Climate response to soil dust aerosols. Journal of Climate, 11(12), 3247–3267.
Miri, A., Moghaddamnia, A., Pahlavanravi, A., & Panjehkeh, N. (2010). Dust storm frequency after the 1999 drought in the Sistan region, Iran. Climate Research, 41(1), 83–90.
Montgomery, D. C., Peck, E. A., & Vining, G. G. (2012). Introduction to linear regression analysis. Hoboken: Wiley.
Norouzian, R., & Plonsky, L. (2018). Correlation and simple linear regression in applied linguistics. In The Palgrave handbook of applied linguistics research methodology (pp. 395–421). Springer.
Ohsowski, B. M., Dunfield, K. E., Klironomos, J. N., & Hart, M. M. (2016). Improving plant biomass estimation in the field using partial least squares regression and ridge regression. Botany, 94(7), 501–508.
Olive, D. J. (2017). Multiple linear regression. In Linear regression (pp. 17–83). Springer.
O’Loingsigh, T., McTainsh, G., Tews, E., Strong, C., Leys, J., Shinkfield, P., et al. (2014). The Dust Storm Index (DSI): A method for monitoring broadscale wind erosion using meteorological records. Aeolian Research, 12, 29–40.
Osland, M. J., Enwright, N. M., Day, R. H., Gabler, C. A., Stagg, C. L., & Grace, J. B. (2016). Beyond just sea-level rise: Considering macroclimatic drivers within coastal wetland vulnerability assessments to climate change. Global Change Biology, 22(1), 1–11.
Ozesmi, S. L., & Bauer, M. E. (2002). Satellite remote sensing of wetlands. Wetlands Ecology and Management, 10(5), 381–402.
Pecl, G. T., Araújo, M. B., Bell, J. D., Blanchard, J., Bonebrake, T. C., Chen, I.-C., et al. (2017). Biodiversity redistribution under climate change: Impacts on ecosystems and human well-being. Science, 355(6332), eaai9214.
Rashki, A., Kaskaoutis, D., Goudie, A., & Kahn, R. (2013). Dryness of ephemeral lakes and consequences for dust activity: The case of the Hamoun drainage basin, southeastern Iran. Science of the Total Environment, 463, 552–564.
Rawat, J., & Kumar, M. (2015). Monitoring land use/cover change using remote sensing and GIS techniques: A case study of Hawalbagh block, district Almora, Uttarakhand, India. The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Science, 18(1), 77–84.
Rebelo, A. J., Scheunders, P., Esler, K. J., & Meire, P. (2017). Detecting, mapping and classifying wetland fragments at a landscape scale. Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment, 8, 212–223.
Reheis, M. C., & Urban, F. E. (2011). Regional and climatic controls on seasonal dust deposition in the southwestern US. Aeolian Research, 3(1), 3–21.
Reynolds, R. L., Yount, J. C., Reheis, M., Goldstein, H., Chavez, P., Jr., Fulton, R., et al. (2007). Dust emission from wet and dry playas in the Mojave Desert, USA. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms: The Journal of the British Geomorphological Research Group, 32(12), 1811–1827.
Rezaee, M., Mahdianpari, M., Zhang, Y., & Salehi, B. (2018). Deep convolutional neural network for complex wetland classification using optical remote sensing imagery. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 11(9), 3030–3039.
Rezazadeh, M., Irannejad, P., & Shao, Y. (2013). Climatology of the middle east dust events. Aeolian Research, 10, 103–109.
Robertson, H. A., Ausseil, A.-G., Rance, B., Betts, H., & Pomeroy, E. (2019). Loss of wetlands since 1990 in Southland, New Zealand. New Zealand Journal of Ecology, 43(1), 1–9.
Sajedipour, S., Zarei, H., & Oryan, S. (2017). Estimation of environmental water requirements via an ecological approach: A case study of Bakhtegan Lake, Iran. Ecological Engineering, 100, 246–255.
Sanson, G., Perrone, A., Fascì, A., & D’agostino, F. (2018). Prevalence, defining characteristics, and related factors of the nursing diagnosis of anxiety in hospitalized medical-surgical patients. Journal of Nursing Scholarship, 50(2), 181–190.
Scaramuzza, P., & Barsi, J. (2005). Landsat 7 scan line corrector-off gap-filled product development. In Proceeding of Pecora (pp. 23–27).
Sibanda, S. (2018) An assessment of the impacts of climate and land use/cover changes on wetland extent within Mzingwane catchment, Zimbabwe (Doctoral dissertation). https://hdl.handle.net/10539/25841.
Teferi, E., Uhlenbrook, S., Bewket, W., Wenninger, J., & Simane, B. (2010). The use of remote sensing to quantify wetland loss in the Choke Mountain range, Upper Blue Nile basin, Ethiopia. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 14(12), 2415–2428.
Tegen, I., & Fung, I. (1994). Modeling of mineral dust in the atmosphere: Sources, transport, and optical thickness. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 99(D11), 22897–22914.
Thornthwaite, C. W., & Holzman, B. (1942). Measurement of evaporation from land and water surfaces. US Department of Agriculture.
Welikhe, P., Quansah, J., Fall, S., & McElhenney, W. (2017). Estimation of soil moisture percentage using LANDSAT-based moisture stress index. Journal of Remote Sensing and GIS, 6, 1–5.
WMO. (1974). Manual on Codes. Volume 1, International Codes. Geneva: WMO Publications.
Wójcicki, K. J., & Woskowicz-Ślęzak, B. (2015). Anthropogenic causes of wetland loss and degradation in the lower Kłodnica valley (southern Poland). Environmental and Socio-Economic Studies, 3(4), 20–29.
Xu, H. (2006). Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 27(14), 3025–3033.
Yang, Y., Liu, Y., Zhou, M., Zhang, S., Zhan, W., Sun, C., et al. (2015). Landsat 8 OLI image based terrestrial water extraction from heterogeneous backgrounds using a reflectance homogenization approach. Remote Sensing of Environment, 171, 14–32.
Zalaki, N., et al. (2017). Assessment of anthropogenic influences on the micro-climate of wetland ecosystems: The case of hoor-alazim wetland in Iran. International Journal of Mining Science (IJMS), 3, 34–51.
Zou, K. H., Tuncali, K., & Silverman, S. G. (2003). Correlation and simple linear regression. Radiology, 227(3), 617–628.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and Iran Meteorological Organization for making, respectively, the Landsat and meteorological data freely available.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Ebrahimi-Khusfi, Z., Ghazavi, R. & Zarei, M. The Effect of Climate Changes on the Wetland Moisture Variations and Its Correlation with Sand-Dust Events in a Semiarid Environment, Northwestern Iran. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 48, 1797–1808 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-020-01203-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-020-01203-7