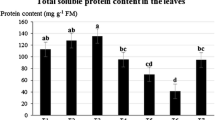
Abstract
Agronomic biofortification can be used to alleviate the deficient intake of selenium (Se) and zinc (Zn) by livestock. These two essential micronutrients for human and animals play an important role in many physiological functions and biological processes. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the suitability of forage peas, crop with an increasing importance as plant protein source, to be biofortified with a combined treatment of Zn (as ZnSO4-7H2O) and Se (as Na2SeO4). A 2-year field experiment was established in southern Spain under semiarid Mediterranean conditions, by following a split-split-plot design. The study year (2017/2018, 2018/2019) was considered the main-plot factor, soil Zn application (50 kg Zn ha−1, nil Zn) as a subplot factor, and foliar application (nil, 10 g Se ha−1, 8 kg Zn ha−1, 10 g Se ha−1 + 8 kg Zn ha−1) as a sub-subplot factor. The combined application of 50-kg soil Zn ha−1 and the foliar application of 10 g Se ha−1 + 8 kg Zn ha−1 was the most effective treatment to increase the concentration in forage of Zn and Se, 4-fold and 5-fold, respectively, as well as the Zn bioavailability, forage yield (close to 30%), and crude protein (~ 8%). Thus, forage peas could be considered a very suitable crop to be included in biofortification programs under Mediterranean conditions with Zn and Se as target minerals.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All authors declare that all data and materials support their published claims and comply with field standards.
References
Adams ML, Lombi E, Zhao FJ, McGrath SP (2002) Evidence of low selenium concentration in UK bread-making wheat grain. J Sci Food Agric 82:1160–1165. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.1167
Allmang C, Krol A (2006) Selenoprotein synthesis: UGA does not end the story. Biochimie 88:1561–1571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2006.04.015
Alloway BJ (2008) Zinc in soils and crop nutrition, 2nd edn. IZA and IFA, Brussels and Paris
Alloway BJ (2009) Soil factors associated with zinc deficiency in crops and humans. Environ Geochem Health 31:537–548. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-009-9255-4
AOCS (2006) Official methods of analysis. Association of Official Analytical Chemists. AOCS, Washington DC
Arthur JR (2003) Selenium supplementation: does soil supplement help and why? Proc Nutr Soc 62:393–397. https://doi.org/10.1079/PNS2003254
Bremner JM (1996) Nitrogen total. In: Sparks DL (ed) Methods of soil analysis, part 3. Chemical Methods, Madison, pp 1085–1121
Broadley MR, White PJ, Bryson RJ, Meacham MC, Bowen HC, Johnson SE, Hawkesford MJ, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ, Breward N, Harriman M, Tucker M (2006) Biofortification of UK food crops with selenium. Proc Nutr Soc 65:169–181. https://doi.org/10.1079/PNS2006490
Broadley M, Brown P, Cakmak I, Rengel Z, Zhao F (2012) Function of nutrients: micronutrients. In: Marchner P (ed) Marschner’s mineral nutrition of higher plants, 3rd edn. Academic Press, London, pp 191–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-384905-2.00007-8
Cakmak I (2008) Zinc crops 2007: improving crop production and human health. Plant Soil 306:1–2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9584-6
Cakmak I, Marschner H, Bangerth F (1989) Effect of zinc nutritional status on growth, protein metabolism and level of indole-3-acetic acid and other phytohormones in bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J Exp Bot 40:405–412. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/40.3.405
Cakmak I, Kalayci M, Kaya Y, Torun AA, Aydin N, Wang Y, Arisoy Z, Erdem H, Yazici A, Gokmen O, Ozturk L, Horst WJ (2010) Biofortification and localization of zinc in wheat grain. J Agric Food Chem 58:9092–9102. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf101197h
Chen X, Ludewig U (2018) Biomass increase under zinc deficiency caused by delay of early flowering in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 69:1269–1279. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erx478
Chibani C, Chabaca R, Boulberhane D (2010) Fourrages algériens. 1. Composition chimique et modèles de prédiction de la valeur énergétique et azotée. Livest Res Rural Dev 22:Article #153. Retrieved from http://www.lrrd.org/lrrd22/8/chab22153.htm
Das S, Chaki AK, Hossain A (2019) Breeding and agronomic approaches for the biofortification of zinc in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to combat zinc deficiency in millions of a population: a Bangladesh perspective. Acta Agrobot 72:1–13. https://doi.org/10.5586/aa.1770
Day PR (1965) Particle fractionation and particle-size analysis. In: Black CA (ed) Methods of soil analysis, part I. Agronomy 9. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp 545–566. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronmonogr9.1.c43
Dinh QT, Cui Z, Huang J, Tran T, Wang D, Yang W, Zhou F, Wang M, Yu D, Liang D (2018) Selenium distribution in the Chinese environment and its relationship with human health: a review. Environ Int 112:294–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2017.12.035
Fan Q, Wang Z, Chang S, Peng Z, Wanapat M, Bowatte S, Hou F (2020) Relationship of mineral elements in sheep grazing in the highland agro-ecosystem. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci 33:44–52. https://doi.org/10.5713/ajas.18.0955
Fernández V, Sotiropoulos T, Brown P (2013) Foliar fertilization: scientific principles and field practices. International Fertilizer Industry Association (IFA), Paris
Gawalko E, Garrett RG, Warkentin TD, Wang N, Richter A (2009) Trace elements in Canadian peas: a grain safety assurance perspective. Food Addit Contam 26:1002–1012. https://doi.org/10.1080/02652030902894389
Germ M, Pongrac P, Regvar M, Vogel-Mikuš K, Stibilj V, Jaćimović R, Kreft I (2013) Impact of double Zn and Se biofortification of wheat plants on the element concentrations in the grain. Plant Soil Environ 59:316–321. https://doi.org/10.17221/6/2013-PSE
Ghaderzadeh S, Mirzaei Aghjeh-Gheshlagh F, Nikbin S, Navidshad B (2016) A review on properties of selenium in animal nutrition. Iran J Appl Anim Sci 6:753–761
Ghasemi S, Khoshgoftarmanesh AH, Afyuni M, Hadadzadeh H (2013) The effectiveness of foliar applications of synthesized zinc-amino acid chelates in comparison with zinc sulphate to increase yield and grain nutritional quality of wheat. Eur J Agron 45:68–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2012.10.012
Gomez-Coronado F, Poblaciones MJ, Almeida A, Cakmak I (2016) Zinc (Zn) concentration of bread wheat grown under Mediterranean conditions as affected by genotype and soil/foliar Zn application. Plant Soil 401:331–346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2758-0
Gupta RK, Gangoliya SS, Singh NK (2015) Reduction of phytic acid enhancement of bioavailable micronutrients in food grains. J Food Sci Technol 52:676–684. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-013-0978-y
Hazelton P, Murphy B (2016) Interpreting soil test results. What do all the numbers mean? 3th edn. CSIRO Publishing, Collingwood. https://doi.org/10.1111/sum.12402
Hill GM, Shannon MC (2019) Copper and zinc nutritional issues for agricultural animal production. Biol Trace Elem Res 188:148–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1578-5
Hla Hla E, Tengda Z, Muhammad Umer F, Rui Z, Yang S, Xin H, Yujie Z, Yuanke L, Zhichen T, Ye X, Xiaomei J, Jianqing Z (2019) Evaluation on zinc and selenium nutrients in polished rice of rice genotypes under zinc biofortification. Biomed J Sci Tech Res 21:16205–16212. https://doi.org/10.26717/BJSTR.2019.21.003666
Karimian K, Yasrebi J (1995) Prediction of residual effects of zinc sulfate on growth and zinc uptake of corn plants using three zinc soil tests. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 26:277–287. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103629509369296
Li C, Wang P, Lombi E, Cheng M, Tang C, Howard DL, Menzies NW, Kopittke PM (2018) Absorption of foliar applied Zn fertilizers by trichomes in soybean and tomato. J Exp Bot 69:2717–2729. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ery085
Li C, Wang P, Van der Ent A, Cheng M, Jiang H, Read TL, Lombi E, Tang C, de Jonge M, Menzies NW, Kopittke PM (2019) Absorption of foliar-applied Zn in sunflower (Helianthus annuus): importance of the cuticle, stomata, and trichomes. Ann Bot 123:57–68. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcy135
Linn JG, Martin NP (1991) Forage quality test and interpretation. Vet Clin North Am: Food Anim Pract 7:509–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0749-0720(15)30790-8
Manojlović MS, Lončarić Z, Cabilovski RR, Popović B, Karalić K, Ivezić V, Ademi A, Singh BR (2019) Biofortification of wheat cultivars with selenium. Acta Agric Scand Sect B Soil Plant Sci 69:715–724. https://doi.org/10.1080/09064710.2019.1645204
MAPA (Spanish Ministry of Agriculture, Fishering and Food) (2020) Anuario de estadística alimentaria del 2018. MAPA, Madrid Retrieved from https://www.mapa.gob.es/es/estadistica/temas/publicaciones/anuario-de-estadistica/default.aspx. Accesed 6 Oct 2020
Mehdi Y, Dufrasne I (2016) Selenium in cattle: a review. Molecules 21:545. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040545
Moraghan JT, Mascagni HJ Jr (1991) Environmental and soil factors affecting micronutrient deficiencies and toxicities. In: Mordvedt JJ, Cox FR, Shumann LM, Welch RM (eds) Micronutrients in agriculture. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, pp 371–425. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssabookser4.2ed.c11
Morris ER, Ellis R (1989) Usefulness of the dietary phytic acid/zinc molar ratio as an index of zinc bioavailability to rats and humans. Biol Trace Elem Res 19:107–117. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02925452
Na GN, Salt DE (2011) The role of sulfur assimilation and sulfur-containing compounds in trace element homeostasis in plants. Environ Exp Bot 72:18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2010.04.004
Novoselec J, Klir Ž, Domaćinović M, Lončarić Z, Antunović Z (2018) Biofortification of feedstuffs with microelements in animal nutrition. Agric 24:25–34. https://doi.org/10.18047/poljo.24.1.4
Oropeza-Moe M, Wisløff H, Bernhoft A (2015) Selenium deficiency associated porcine and human cardiomyopathies. J Trace Elem Med Biol 31:148–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2014.09.011
Pandey N, Gupta B, Pathak GC (2013) Enhanced yield and nutritional enrichment of seeds of Pisum sativum L. through foliar application of zinc. Sci Hortic 164:474–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2013.10.013
Páscoa P, Gouveia CM, Russo A, Trigo RM (2017) The role of drought on wheat yield interannual variability in the Iberian Peninsula from 1929 to 2012. Int J Biometeorol 61:439–451. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-016-1224-x
Petković K, Manojlović M, Čabilovski R, Krstić Đ, Lončarić Z, Lombnæs P (2019) Foliar application of selenium, zinc and copper in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) biofortification. Turkish J Field Crop 24:81–90. https://doi.org/10.17557/tjfc.569363
Poblaciones MJ, Rengel Z (2016) Soil and foliar zinc biofortification in field pea (Pisum sativum L.): grain accumulation and bioavailability in raw and cooked grains. Food Chem 212:427–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.05.189
Poblaciones MJ, Rengel Z (2017) Combined foliar selenium and zinc biofortification in field pea (Pisum sativum): accumulation and bioavailability in raw and cooked grains. Crop Pasture Sci 68:265–271. https://doi.org/10.1071/CP17082
Poblaciones MJ, Rengel Z (2018) The effect of processing on Pisum sativum L. biofortified with sodium selenate. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 181:932–937. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201800251
Poblaciones MJ, Rodrigo S, Santamaria O (2013) Evaluation of the potential of peas (Pisum sativum L.) to be used in selenium biofortification programs under Mediterranean conditions. Biol Trace Elem Res 151:132–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-012-9539-x
Poblaciones MJ, Rodrigo S, Santamaria O, Chen Y, McGrath SP (2014) Selenium accumulation and speciation in biofortified chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) under Mediterranean conditions. J Sci Food Agric 94:1101–1106. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.6372
Ram H, Rashid A, Zhang W, Duarte AP, Phattarakul N, Simunji S, Kalayci M, Freitas R, Rerkasem B, Bal RS, Mahmood K, Savasli E, Lungu O, Wang ZH, de Barros VLNP, Malik SS, Arisoy RZ, Guo JX, Sohu VS, Zou CQ, Cakmak I (2016) Biofortification of wheat, rice and common bean by applying foliar zinc fertilizer along with pesticides in seven countries. Plant Soil 403:389–401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-2815-3
Reich HJ, Hondal RJ (2016) Why nature chose selenium. ACS Chem Biol 11:821–841. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00216-y
René PJJR, Heinen M, Dimkpa CO, Bindraban PS (2017) Effects of nutrient antagonism and synergism on yield and fertilizer use efficiency. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 48:1895–1920. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2017.1407429
Robinson GHJ, Balk J, Domoney C (2019) Improving pulse crops as a source of protein, starch and micronutrients. Nutr Bull 44:202–215. https://doi.org/10.1111/nbu.12399
Rodrigo S, Santamaria O, Lopez-Bellido FJ, Poblaciones MJ (2013) Agronomic selenium biofortification of two-rowed barley under Mediterranean conditions. Plant Soil Environ 59:115–120. https://doi.org/10.17221/691/2012-PSE
Rodrigo S, Santamaria O, Poblaciones MJ (2014) Selenium application timing: influence in wheat grain and flour selenium accumulation under Mediterranean conditions. J Agric Sci 6:23–30. https://doi.org/10.5539/jas.v6n3p23
Saha S, Chakraborty M, Padhan D, Saha B, Murmu S, Batabyal K, Seth A, Hazra GC, Mandal B, Bell RW (2017) Agronomic biofortification of zinc in rice: influence of cultivars and zinc application methods on grain yield and zinc bioavailability. Field Crop Res 210:52–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2017.05.023
Santamaria O, Rodrigo S, Poblaciones MJ, Olea L (2014) Fertilizer application (P, K, S, Ca and Mg) on pasture in calcareous dehesas: effects on herbage yield, botanical composition and nutritive value. Plant Soil Environ 60:303–308. https://doi.org/10.17221/114/2014-PSE
Shan AS, Davis RH (1994) Effect of dietary phytate on growth and selenium status of chicks fed selenite or selenomethionine. Br Poult Sci 35:725–741. https://doi.org/10.1080/00071669408417738
Shaver TM, Westfall DG, Ronaghi M (2007) Zinc fertilizer solubility and its effects on zinc bioavailability over time. J Plant Nutr 30:123–133. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904160601055145
Silva VM, Boleta EHM, Martins JT, dos Santos FLM, da Rocha Silva AC, Alcock TD, Wilson L, de Sá ME, Young SD, Broadley MR, White PJ, dos Reis AR (2019) Agronomic biofortification of cowpea with selenium: effects of selenate and selenite applications on selenium and phytate concentrations in seeds. J Sci Food Agric 99:5969–5983. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.9872
Sims JT, Johnson GV (1991) Micronutrient soil tests. In: Mortvedt JJ, Cox FR, Shuman LM, Welch MR (eds) Micronutrients in agriculture (Book series 4). Ed. SSSA, Madison, pp 427–476. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssabookser4.2ed
Singh AK, Bhatt BP (2013) Effects of foliar application of zinc on growth and seed yield of late-sown lentil. Indian J Agril Sci 83:622–626
Sosulski FW, Imafidon GI (1990) Amino acid composition and nitrogen-to-protein conversion factors for animal and plant foods. J Agric Food Chem 38:1351–1356. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf00096a011
Suttle NF (2010) Mineral nutrition of livestock, 4th edn. CABI, Cambridge. https://doi.org/10.1079/9781845934729.0000
Thavarajah D, Thavarajah P, Sarker A, Vandernberg A (2009) Lentils (Lens culinaris Medikus subs. culinaris): a whole food for increased iron and zinc intake. J Agric Food Chem 57:5413–5419. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf900786e
Thavarajah D, Warkentin T, Vandenberg A (2010) Natural enrichment of selenium in Saskatchewan field peas (Pisum sativum L.). Can J Plant Sci 90:383–389. https://doi.org/10.4141/CJPS09154
Ullah A, Farooq M, Nadeem F, Rehman A, Hussain M, Nawaz A Naveed M (2020) Zinc application in combination with zinc solubilizing Enterobacter sp. MN17 improved productivity, profitability, zinc efficiency, and quality of Desi chickpea. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr In press: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00281-3
USDA United States Department of Agriculture (1998) Soil taxonomy, keys to soil taxonomy, 11th edn. USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service, Washington DC
Van Soest PJ (1967) Development of a comprehensive system of feed analyses and its application to forages. J Anim Sci 26:119–128. https://doi.org/10.2527/jas1967.261119x
Villani PJ, Demason DA (1999) The Af gene regulates timing and direction of major developmental events during leaf morphogenesis in garden pea (Pisum sativum). Ann Bot 83:117–128. https://doi.org/10.1006/anbo.1998.0805
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining organic carbon in soils: effect of variations in digestion conditions and of inorganic soil constituents. Soil Sci 63:251–263. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-194704000-00001
White PJ, Broadley MR (2005) Biofortifying crops with essential mineral elements. Trends Plant Sci 10:586–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2005.10.001
Zhao FJ, McGrath SP (1994) Extractable sulphate and organic sulphur in soils and their availability to plants. Plant Soil 164:243–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010076
Zou C, Du Y, Rashid A, Ram H, Savasli E, Pieterse PJ, Ortiz-Monasterio I, Yazici A, Kaur C, Mahmood K, Singh S, Le Roux MR, Kuang W, Onder O, Kalayci M, Cakmak I (2019) Simultaneous biofortification of wheat with zinc, iodine, selenium, and iron through foliar treatment of a micronutrient cocktail in six countries. J Agric Food Chem 67:8096–8106. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b01829
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Teodoro García-White for his invaluable help with all the laboratory work.
Funding
This study was funded by the Regional Government of Extremadura (Spain) and by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) (grant number IB16093).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Reynolds-Marzal, Rivera-Martin, Rodrigo, and Poblaciones. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Santamaria, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
All authors consent to participate.
Consent for Publication (Include Appropriate Statements)
All authors consent to publication.
Code Availability
All authors declare that software applications or custom codes support their published claims and comply with field standards.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 71 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reynolds-Marzal, M.D., Rivera-Martín, A.M., Rodrigo, S.M. et al. Biofortification of Forage Peas with Combined Application of Selenium and Zinc Under Mediterranean Conditions. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 21, 286–300 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00360-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00360-5