Abstract
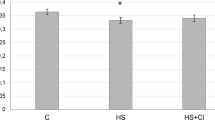
Gravitational unloading leads to a slow-to-fast shift in the myosin phenotype. The reason for these changes is a decrease in the expression of the genes encoding heavy chains of myosin (MyHC) of the slow type, and an increase in the expression of the genes encoding MyHC of the fast types. Signal cascades such as calcineurin/NFAT and HDAC4/MEF-2D are known to regulate MyHC I gene expression. There is almost no data in the literature on the content of transcription factors NFATc1 and MEF-2D involved in the regulation of the gene expression of MyHC I, as well as histone deacetylase HDAC4 and MAP kinase ERK2 in the rat soleus muscle under the gravitational unloading. The aim of this study was to explore the role of various mechanisms controlling the expression of MyHC type I at each stage of gravitational unloading. The levels of proteins MEF-2D and ERK2 in the nuclear fraction were decreased significantly after 3 and 7 days of unloading, and the level of NFATc1 was decreased on the first and seventh days. However, the content of NFATc1, HDAC4, MEF-2D and ERK2 in the nuclear fraction after 14 days of gravitational unloading corresponded to the control level. These data indicate that the content of transcriptional regulators in the muscle nuclei at a late stage of gravitational unloading is not a limiting factor for maintaining their transcriptional activity.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Kandarian S.C., Stevenson E.J. 2002. Molecular events in skeletal muscle during disuse atrophy. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 30, 111–116.
Shenkman B.S. 2016. From fast to slow. Gravitational rearrangement of the myosine phenotype of muscle fibers. Acta Naturae. 8 (4), 52–64.
Shen T., Liu Y., Randall W.R., Schneider M.F. 2006. Parallel mechanisms for resting nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling and activity dependent translocation provide dual control of transcriptional regulators HDAC and NFAT in skeletal muscle fiber type plasticity. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil.27, 405–411.
Chin E.R., Olson E.N., Richardson J.A., Yang Q., Humphries C., Shelton J.M., Wu H., Zhu W., Bassel-Duby R., Williams R.S. 1998. A calcineurin-dependent transcriptional pathway controls skeletal muscle fiber type. Genes Dev. 12, 2499–2509.
Meissner J.D., Umeda P.K., Chang K.C., Gros G., Scheibe R.J. 2007. Activation of the beta myosin heavy chain promoter by MEF-2D, MyoD, p300, and the calcineurin/NFATc1 pathway. J. Cell. Physiol.211, 138–148.
Meissner J.D., Freund R., Krone D., Umeda P.K., Chang K.C., Gros G., Scheibe R.J. 2011. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2-mediated phosphorylation of p300 enhances myosin heavy chain I/beta gene expression via acetylation of nuclear factor of activated T cells c1. Nucleic Acids Res. 39, 5907–5925.
Dunn S.E., Simard A.R., Bassel-Duby R., Williams R.S., Michel R.N. 2001. Nerve activity-dependent modulation of calcineurin signaling in adult fast and slow skeletal muscle fibers. J. Biol. Chem.276, 45243–45254.
Wu H., Rothermel B., Kanatous S., Rosenberg P., Naya F.J., Shelton J.M., Hutcheson K.A., DiMaio J.M., Olson E.N., Bassel-Duby R., Williams R.S. 2001. Activation of MEF2 by muscle activity is mediated through a calcineurin-dependent pathway. EMBO J.20, 6414–6423.
McGee S.L., Swinton C., Morrison S., Gaur V., Campbell D.E., Jorgensen S.B., Kemp B.E., Baar K., Steinberg G.R., Hargreaves M. 2014. Compensatory regulation of HDAC5 in muscle maintains metabolic adaptive responses and metabolism in response to energetic stress. FASEB J.28, 3384–3395.
Liu Y., Randall W.R., Schneider M.F. 2005. Activity-dependent and -independent nuclear fluxes of HDAC4 mediated by different kinases in adult skeletal muscle. J. Cell Biol. 168, 887–897.
Morey-Holton E.R.,Globus R.K. 2002. Hindlimb unloading rodent model: Technical aspects. J. Appl. Physiol. 92, 1367–1377.
Giger J.M., Bodell P.W., Zeng M., Baldwin K.M., Haddad F. 2009. Rapid muscle atrophy response to unloading: Pretranslational processes involving MHC and actin. J. Appl. Physiol. 107, 1204–1212.
Krasnyi A.M., Lysenko E.A., Kozlovskaya I.B., Shenkman B.S., Lomonosova Yu.N. 2013. Phosphoryltion of the elongation factor and the expression of its kinase in rat m. soleus during 3 days of the gravitational unloading. Dokl. Akad. Nauk (Rus.).453, 106–108.
Lomonosova Y.N., Turtikova O.V., Shenkman B.S. 2016. Reduced expression of MyHC slow isoform in rat soleus during unloading is accompanied by alterations of endogenous inhibitors of calcineurin/NFAT signaling pathway. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 37, 7–16.
Mirzoev T., Tyganov S., Vilchinskaya N., Lomonosova Y., Shenkman B. 2016. Key markers of mTORC1-dependent and mTORC1-independent signaling pathways regulating protein synthesis in rat soleus muscle during early stages of hindlimb unloading. Cell. Physiol. Biochem.39, 1011–1020.
Ingalls C.P., Wenke J.C., Armstrong R.B. 2001. Time course changes in [Ca2+]i, force, and protein content in hindlimb-suspended mouse soleus muscles. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 72, 471–476.
Sharlo K.A., Lomonosova Yu.N., Turtikova O.V., Mitrofanova O.V., Kalamkarov G.R., Bugrova A.E., Shevchenko T.F., Shenkman B.S. 2017. the role of the GSK-3β phosphorylation in the regulation processes of the expression of slow myosine in m. soleus upon functional unloading. Biol. Membrany (Rus.).34 (6), 164–171.
Dupont-Versteegden E.E., Knox M., Gurley C.M., Houle J.D., Peterson C.A. 2002. Maintenance of muscle mass is not dependent on the calcineurin-NFAT pathway. Am. J. Physiol. 282, C1387–C1395.
Xia L., Cheung K.K., Yeung S.S., Yeung E.W. 2016. The involvement of transient receptor potential canonical type 1 in skeletal muscle regrowth after unloading-induced atrophy. J. Physiol. 594 (11), 3111–3126.
van der Velden J.L., Langen R.C., Kelders M.C., Willems J., Wouters E.F., Janssen-Heininge, Y.M., Schols A.M. 2007. Myogenic differentiation during regrowth of atrophied skeletal muscle is associated with inactivation of GSK-3beta. Am. J. Physiol. 292, C1636–C1644.
Mirzoev T.M., Tyganov S.A., Petrova I.O., Shenkman B.S. 2017. Signaling pathways of protein synthesis regulation in the rat postural muscle during the readaptation period after functional unloading. Aviakosmich. Ekologich. Meditsyna (Rus.).51 (7), 99–105.
Miska E.A., Karlsson C., Langley E., Nielsen S.J., Pines J., Kouzarides T. 1999. HDAC4 deacetylase associates with and represses the MEF2 transcription factor. EMBO J.18, 5099–5107.
Cohen T.J., Choi M.C., Kapur M., Lira V.A., Yan Z., Yao T.P. 2015. HDAC4 regulates muscle fiber type-specific gene expression programs. Mol. Cells.38, 343–348.
Vilchinskaya N.A., Mochalova E.P., Nemirovskaya T.L., Mirzoev T.M., Turtikova O.V., Shenkman B.S. 2017. Rapid decline in MyHC I(beta) mRNA expression in rat soleus during hindlimb unloading is associated with AMPK dephosphorylation. J. Physiol. 595, 7123–7134.
Vilchinskaya N.A., Mochalova E.P., Belova S.P., Shenkman B.S. 2016. Dephosphorylation of ampactivated protein kinase in postural muscle is a key signal event of the first day of functional unloading. Biofizika (Rus.).61, 1228–1235.
Yoshihara T., Machida S., Kurosaka Y., Kakigi, R., Sugiura T., Naito H. 2016. Immobilization induces nuclear accumulation of HDAC4 in rat skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. Sci.66, 337–343.
Lynch J., Guo L., Gelebart P., Chilibeck K., Xu J., Molkentin J.D., Agellon L.B., Michalak M. 2005. Calreticulin signals upstream of calcineurin and MEF2C in a critical Ca2+-dependent signaling cascade. J. Cell Biol. 170, 37–47.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project no. 18-15-00107).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors state that there is no conflict of interest.
All procedures with animals were approved by the Commission on Biomedical Ethics of the SSC RF-IBP RAS, and with the rules and requirements set out in the European Communities Council Directive 1986 (86/609/EEC) and Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Additional information
Translated by E. Puchkov
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paramonova, I.I., Sharlo, K.A., Vilchinskaya, N.A. et al. The Time Course of Muscle Nuclear Content of Transcription Factors Regulating the MyHC I(β) Expression in the Rat Soleus Muscle under Gravitational Unloading. Biochem. Moscow Suppl. Ser. A 14, 242–248 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990747820020099
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990747820020099