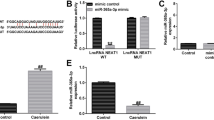
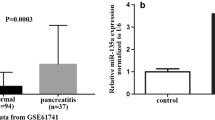
Abstract
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a common acute abdominal disease with high mortality and mortality rates. Increasing evidences clarified that Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) adjuvant therapy for AP can be used and it gives a positive effect. Quercetin (3,3′,4′,5,7-pentahydroxyflavone, QE) is a type of flavone compound with positive effect on cancer and inflammation prevention. The current study aims to identify the effect of QE on AP and potential molecular effect. In this case, caerulein (CAE) induced AP cell and mice model were used. QE alleviated inflammatory mediators TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 in experiments. In addition, miR-216b was increased based on QE treatment. In further study, MAP2K6 of p38/MAPK signaling pathway was identified as a direct target of miR-216b, and QE inhibited p38/MAPK signaling pathway through up-regulating miR-216b. Our study also first confirmed that long non-coding RNA NEAT1 is a direct target of miR-216b and can be suppressed by QE. Because of the target, NEAT1, miR-216b, and MAP2K6 formed a competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network. Besides direct target mediated by QE, it also decreased TNF-α which down-regulated TRAF2 and MAP3K5 located on upstream of p38/MAPK signaling and formed a feedback loop. In conclusion, QE has a protective effect on AP through inhibiting p38/MAPK signaling pathway by up-regulating miR-216b and suppressing TNF-α.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bhaskar S, Sudhakaran PR, Helen A (2016) Quercetin attenuates atherosclerotic inflammation and adhesion molecule expression by modulating TLR-NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Cell Immunol 310:131–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellimm.2016.08.011
Choi SB, Bae GS, Jo IJ, Wang S, Song HJ, Park SJ (2016) Berberine inhibits inflammatory mediators and attenuates acute pancreatitis through deactivation of JNK signaling pathways. Mol Immunol 74:27–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2016.04.011
Cofaru FA, Nica S, Fierbinteanu-Braticevici C (2020) Assessment of severity of acute pancreatitis over time. Rom J Intern Med. https://doi.org/10.2478/rjim-2020-0003
Dike CR et al (2020) Clinical and practice variations in pediatric acute recurrent or chronic pancreatitis: report from the insppire study. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0000000000002661
Guo YJ, Pan WW, Liu SB, Shen ZF, Xu Y, Hu LL (2020) ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp Ther Med 19:1997–2007. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2020.8454
Habtezion A, Gukovskaya AS, Pandol SJ (2019) Acute pancreatitis: a multifaceted set of organelle and cellular interactions. Gastroenterology 156:1941–1950. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2018.11.082
Li Y et al (2016) Quercetin, inflammation and immunity. Nutrients 8:167. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8030167
Li J, Zhang S, Zhou R, Zhang J, Li ZF (2017) Perspectives of traditional Chinese medicine in pancreas protection for acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 23:3615–3623. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i20.3615
Ling L, Wang HF, Li J, Li Y, Gu CD (2019) Downregulated microRNA-92a-3p inhibits apoptosis and promotes proliferation of pancreatic acinar cells in acute pancreatitis by enhancing KLF2 expression. J Cell Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.29517
Liu S et al (2018) miR-155–5p is negatively associated with acute pancreatitis and inversely regulates pancreatic acinar cell progression by targeting Rela and Traf3. Cell Physiol Biochem 51:1584–1599. https://doi.org/10.1159/000495648
Memariani H, Memariani M, Ghasemian A (2019) An overview on anti-biofilm properties of quercetin against bacterial pathogens. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 35:143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-019-2719-5
Miao B et al (2019) miR-148a suppresses autophagy by down-regulation of IL-6/STAT3 signaling in cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 19:557–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pan.2019.04.014
Nagaleekar VK et al (2011) Translational control of NKT cell cytokine production by p38 MAPK. J Immunol 186:4140–4146. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1002614
Pandol SJ, Saluja AK, Imrie CW, Banks PA (2007) Acute pancreatitis: bench to the bedside. Gastroenterology 132:1127–1151. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2007.01.055
Pu WL et al (2018) Baicalein inhibits acinar-to-ductal metaplasia of pancreatic acinal cell AR42J via improving the inflammatory microenvironment. J Cell Physiol 233:5747–5755. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26293
Reyes-Farias M, Carrasco-Pozo C (2019) The anti-cancer effect of quercetin: molecular implications in cancer metabolism. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133177
Seo JY, Pandey RP, Lee J, Sohng JK, Namkung W, Park YI (2019) Quercetin 3-O-xyloside ameliorates acute pancreatitis in vitro via the reduction of ER stress and enhancement of apoptosis. Phytomedicine 55:40–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2018.07.011
Tseng HL, Li CJ, Huang LH, Chen CY, Tsai CH, Lin CN, Hsu HY (2012) Quercetin 3-O-methyl ether protects FL83B cells from copper induced oxidative stress through the PI3K/Akt and MAPK/Erk pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 264:104–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2012.07.022
Wu XM, Ji KQ, Wang HY, Zhao Y, Jia J, Gao XP, Zang B (2018) MicroRNA-339–3p alleviates inflammation and edema and suppresses pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell apoptosis in mice with severe acute pancreatitis-associated acute lung injury by regulating Anxa3 via the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem 119:6704–6714. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26859
Yang Y, Huang Q, Luo C, Wen Y, Liu R, Sun H, Tang L (2020) MicroRNAs in acute pancreatitis: from pathogenesis to novel diagnosis and therapy. J Cell Physiol 235:1948–1961. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29212
Zhang Z, Liu Q, Zang H, Shao Q, Sun T (2019) Oxymatrine protects against l-arginine-induced acute pancreatitis and intestine injury involving Th1/Th17 cytokines and MAPK/NF-kappaB signalling. Pharm Biol 57:595–603. https://doi.org/10.1080/13880209.2019.1657906
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BS and WC contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by BS, LZ, XZ, JZ, YL, and WB. The first draft of the manuscript was written by BS and WC, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All animal studies have been approved by Ethics Committee of Beijing Shijitan Hospital, CMU with Admission Number 2019-72-T25, and the study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheng, B., Zhao, L., Zang, X. et al. Quercetin inhibits caerulein-induced acute pancreatitis through regulating miR-216b by targeting MAP2K6 and NEAT1. Inflammopharmacol 29, 549–559 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-020-00767-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-020-00767-7