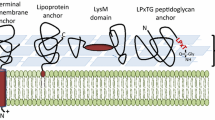
Abstract
The surface-layer (S-layer) protein of Lactobacillus acidophilus is a crystalline array of self-assembling subunits, non-covalently bound to the most outer cell wall envelope, which constitutes up to 20% of the total cell protein content. These attributes make S-layer proteins an excellent anchor for the development of microbial cell-surface display systems. In L. acidophilus, the S-layer is formed predominantly by the protein SlpA. We have previously shown that the C-terminal domain of SlpA is responsible for the cell wall anchorage on L. acidophilus ATCC 4356. In the present study, we evaluated the C-terminal domain of SlpA of L. acidophilus ATCC 4356 as a potential anchor domain to display functional proteins on the surface of non-genetically modified lactic acid bacteria (LAB). To this end, green fluorescent protein (GFP)-CTSlpA was firstly produced in Escherichia coli and the recombinant proteins were able to spontaneously bind to the cell wall of LAB in a binding assay. GFP was successfully displayed on the S-layer stripped surface of L. acidophilus. Both the binding stability and cell survival of L. acidophilus decorated with the recombinant protein were then studied in simulated gastrointestinal conditions. Furthermore, NaCl was tested as a safer alternative to LiCl for S-layer removal. This study presents the development of a protein delivery platform involving L. acidophilus, a microorganism generally regarded as safe, which utilizes the contiguous, non-covalently attached S-layer at the cell surface of the bacterium without introducing any genetic modification.
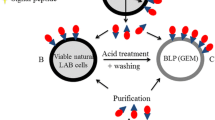
Graphic abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allievi MC, Ruzal SM, Palomino MM (2019) Modifications of Lactobacillus surface under environmental stress conditions. In: Ruzal SM (ed) Lactobacillus genomics and metabolic engineering. Caister Academic Press, New York, pp 81–104
Antikainen J, Anton L, Sillanpää J, Korhonen TK (2002) Domains in the S-layer protein CbsA of Lactobacillus crispatus involved in adherence to collagens, laminin and lipoteichoic acids and in self-assembly. Mol Microbiol 46(2):381–394
Bezkorovainy A (2001) Probiotics: determinants of survival and growth in the gut. Am J Clin Nutr 73(2 Suppl):399S–405S
Bosma T, Kanninga R, Neef J, Audouy SAL, van Roosmalen ML, Steen A, Buist G, Kok J, Kuipers OP, Robillard G, Leenhouts K (2006) Novel surface display system for proteins on non-genetically modified gram-positive bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(1):880–889
Brinster S, Furlan S, Serror P (2007) C-Terminal WxL domain mediates cell Wall binding in Enterococcus faecalis and other Gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol 189(4):1244–1253
Bull MJ, Jolley KA, Bray JE et al (2014) The domestication of the probiotic bacterium Lactobacillus acidophilus. Sci Rep 4:7202
Chen X, Chen Y, Li X, Chen N, Fang W (2009) Characterization of surface layer proteins in Lactobacillus crispatus isolate ZJ001. J Microbiol Biotechnol 19(10):1176–1183
Dieterle ME, Bowman C, Batthyany C, Lanzarotti E, Turjanski A, Hatfull G, Piuri M (2014) Exposing the secrets of two well-known Lactobacillus casei phages, J-1 and PL-1, by genomic and structural analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 80(22):7107–7121
do Carmo FLR, Rabah H, Carvalho RDD, Gaucher F, Cordeiro BF, da Silva SH, Le Loir Y, Azevedo V, Jan G (2018) Extractable bacterial surface proteins in probiotic-host interaction. Front Microbiol 9:645
Eslami N, Kermanshahi RK, Erfan M (2013) Studying the stability of S-layer protein of Lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC 4356 in simulated gastrointestinal fluids using SDS-PAGE and circular dichroism. Iran J Pharm Res 12(Suppl):47–56
Feilmeier BJ, Iseminger G, Schroeder D, Webber H, Phillips GJ (2000) Green fluorescent protein functions as a reporter for protein localization in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 182(14):4068–4076
Fina-Martin J, Palomino MM, Cutine AM, Modenutti CP, Do Porto DAF, Allievi MC, Zanini SH, Mariño KV, Barquero AA, Ruzal SM (2019) Exploring lectin-like activity of the S-layer protein of Lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC 4356. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103:4839–4857
Guarner F, Sanders ME, Eliakim R et al (2017) WGO practice guideline—probiotics and prebiotics, vol 2018. World Gastroenterology Organisation: Milwaukee, WI. http://www.worldgastroenterology.org/guidelines/global-guidelines/probiotics-and-prebiotics. Accessed 1 April 2018
Hu S, Kong J, Kong W, Guo T, Ji M (2010) Characterization of a novel LysM domain from Lactobacillus fermentum bacteriophage endolysin and its use as an anchor to display heterologous proteins on the surfaces of lactic acid bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(8):2410–2418
Hu S, Kong J, Sun Z, Han L, Kong W, Yang P (2011) Heterologous protein display on the cell surface of lactic acid bacteria mediated by the s-layer protein. Microb Cell Fact 10:86
Malamud M, Bolla PA, Carasi P, Gerbino E, Gómez-Zavaglia A, Mobili P, María de los Angeles Serradell MDLA (2019) S-Layer proteins from Lactobacilli: biogenesis, structure, functionality and biotechnological applications. In: Ruzal SM (ed) Lactobacillus genomics and metabolic engineering. Caister Academic Press, New York, pp 105–130
Mao R, Zhou K, Han Z, Wang Y (2016) Subtilisin QK-2: secretory expression in Lactococcus lactis and surface display onto gram-positive enhancer matrix (GEM) particles. Microb Cell Fact 15:80
Martínez MG, Prado Acosta M, Candurra NA, Ruzal SM (2012) S-layer proteins of Lactobacillus acidophilus inhibits JUNV infection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 422(4):590–595
Matsuguchi T, Takagi A, Matsuzaki T, Nagaoka M, Ishikawa K, Yokokura T, Yoshikai Y (2003) Lipoteichoic acids from Lactobacillus strains elicit strong tumor necrosis factor alpha-inducing activities in macrophages through Toll-like receptor 2. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 10(2):259–266
Meng J, Gao S-M, Zhang Q-X, Lu R-R (2015) Murein hydrolase activity of surface layer proteins from Lactobacillus acidophilus against Escherichia coli. Int J Biol Macromol 79:527–532
O’Flaherty S, Klaenhammer TR (2016) Multivalent chromosomal expression of the Clostridium botulinum serotype A neurotoxin heavy-chain antigen and the Bacillus anthracis protective antigen in Lactobacillus acidophilus. Appl Environ Microbiol 82(20):6091–6101
O’Flaherty S, Crawley AB, Theriot CM, Barrangou R (2018) The Lactobacillus bile salt hydrolase repertoire reveals niche-specific adaptation. mSphere 3(3):e00140–e00118
Palomino MM, Allievi MC, Fina Martin J, Waehner PM, Acosta MP, Rivas CS, Ruzal SM (2015) Draft genome sequence of the probiotic strain Lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC 4356. Genome Announc 3(1):e01421–e01414
Palomino MM, Waehner PM, Fina Martin J, Ojeda P, Malone L, Rivas CS, Acosta MP, Allievi MC, Ruzal SM (2016) Influence of osmotic stress on the profile and gene expression of surface layer proteins in Lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC 4356. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(19):8475–8484
Prado-Acosta M, Palomino MM, Allievi MC, Rivas CS, Ruzal SM (2008) Murein hydrolase activity in the surface layer of Lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC 4356. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(24):7824–7827
Prado-Acosta M, Ruzal SM, Allievi MC, Palomino MM, Rivas CS (2010) Synergistic effects of the Lactobacillus acidophilus surface layer and nisin on bacterial growth. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(3):974–977
Qin J, Wang X, Kong J, Ma C, Xu P (2014) Construction of a food-grade cell surface display system for Lactobacillus casei. Microbiol Res 169(9–10):733–740
Ramachandran P, Lacher DW, Pfeiler EA, Elkins CA (2013) Development of a tiered multilocus sequence typing scheme for members of the Lactobacillus acidophilus complex. Appl Environ Microbiol 79(23):7220–7228
Ribelles P, Benbouziane B, Langella P, Suárez JE, Bermúdez-Humarán LG (2013) Protection against human papillomavirus type 16-induced tumors in mice using non-genetically modified lactic acid bacteria displaying E7 antigen at its surface. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(3):1231–1239
Rocha-Ramírez LM, Pérez-Solano RA, Castañón-Alonso SL, Moreno Guerrero SS, Ramírez Pacheco A, García Garibay M, Eslava C (2017) Probiotic Lactobacillus strains stimulate the inflammatory response and activate human macrophages. J Immunol Res 2017:4607491
Sahay B, Ge Y, Colliou N, Zadeh M, Weiner C, Mila A, Owen JL, Mohamadzadeh M (2015) Advancing the use of Lactobacillus acidophilus surface layer protein A for the treatment of intestinal disorders in humans. Gut Microbes 6(6):392–397
Sleytr UB, Schuster B, Egelseer E-M, Pum D (2014) S-Layers: principles and applications. FEMS Microbiol Rev 38(5):823–864
Smit E, Oling F, Demel R, Martinez B, Pouwels PH (2001) The S-layer protein of Lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC 4356: identification and characterisation of domains responsible for S-protein assembly and cell wall binding. J Mol Biol 305(2):245–257
Sun Z, Kong J, Hu S, Kong W, Lu W, Liu W (2013) Characterization of a S-layer protein from Lactobacillus crispatus K313 and the domains responsible for binding to cell wall and adherence to collagen. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(5):1941–1952
Vizoso Pinto MG, Gómez MR, Seifert S, Watzl B, Holzapfel WH, Franz CMAP (2009) Lactobacilli stimulate the innate immune response and modulate the TLR expression of HT29 intestinal epithelial cells in vitro. Int J Food Microbiol 133(1–2):86–93
Whitehead K, Versalovic J, Roos S, Britton RA (2008) Genomic and genetic characterization of the bile stress response of probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri ATCC 55730. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(6):1812–1819
Yang L, Chu JS, Fix JA (2002) Colon-specific drug delivery: new approaches and in vitro/in vivo evaluation. Int J Pharm. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-5173(02)00004-2
Zadravec P, Štrukelj B, Berlec A (2015) Heterologous surface display on lactic acid bacteria: non-GMO alternative? Bioengineered 6(3):179–183
Zhang X, Hu S, Du X, Li T, Han L, Kong J (2016) Heterologous expression of carcinoembryonic antigen in Lactococcus lactis via LcsB-mediated surface displaying system for oral vaccine development. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 49(6):851–858
Funding
This work was supported by Grants from the Universidad de Buenos Aires (UBA) (20020170200329BA) and FONCyT (PICT 1337–2017), Argentina, to MMP, as well as by a doctoral Fellowship of the National Scientific and Technical Research Council (CONICET) to TBG, and an UBA undergraduate Fellowship to MCP. MCA, DFP, SMR, and MMP are members of CONICET.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gordillo, T.B., Palumbo, M.C., Allievi, M.C. et al. Strategies to display heterologous proteins on the cell surface of lactic acid bacteria using as anchor the C-terminal domain of Lactobacillus acidophilus SlpA. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 36, 169 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-020-02945-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-020-02945-9