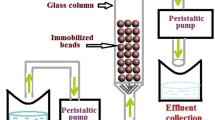
Abstract
The current study proposes the use of magnetic beads for the treatment of nickel ions of the industrial wastewater system. More specifically, the removal of nickel ions is studied in single and multi-metal ion systems which enabled the scalability of nano-enabled technology to industrial systems. The current synthesis neither involves expensive precursors nor complex procedures. Indeed, the improved surface properties of the adsorbent are due to the use of Lantana camara, in the synthesis. The surface properties and functional attributes of the magnetic beads were characterized by FTIR and SEM analyses. The breakthrough experiments were done for selected column depths, varying feed flow rates and metal ion concentrations. In particular, the interventions of the interfering ions of the electroplating effluents are captured in the breakthrough analysis. Besides the lowest bed capacity reported in the multi-metal systems, the column operated with nickel ions showed a maximum bed capacity of 12.36 mg/g at a flow rate of 2 mL/min in the 20 cm bed. Furthermore, an extended breakthrough time of 780 min is obtained for 50 mg/L nickel ion solution at a flow rate of 2 mL/min. In addition, the modelling of breakthrough curves using Thomas, Yoon–Nelson and BDST models have shown reasonable fits. In addition, repeated cycles of regeneration studies showed improved efficiency of 65% in the first cycle. More specifically, the alginate validated the selective preferential adsorption of cationic substances over anionic components in the studied column.
Graphic abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed MJ, Hameed BH (2018) Removal of emerging pharmaceutical contaminants by adsorption in a fixed-bed column: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 149:257–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.12.012
Barquilha CER, Cossich ES, Tavares CRG, Silva EA (2017) Biosorption of nickel (II) and copper (II) ions in batch and fi xed-bed columns by free and immobilized marine algae Sargassum sp. J Clean Prod 150:58–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.02.199
Beji R, Hamdi W, Kesraoui A, Seffen M (2018) Adsorption of phosphorus by alkaline Tunisian soil in a fixed bed column. Water Sci Technol 78(4):751–763. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2018.341
Brion-Roby R, Gagnon J, Deschênes JS, Chabot B (2018) Investigation of fixed bed adsorption column operation parameters using a chitosan material for treatment of arsenate contaminated water. J Environ Chem Eng 6:505–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.12.032
Chowdhury ZZ, Abd Hamid SB, Zain SM (2015) Evaluating design parameters for breakthrough curve analysis and kinetics of fixed bed columns for Cu(II) cations using lignocellulosic wastes. BioResources 10:732–749. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.10.1.732-749
Du Z, Zheng T, Wang P (2018) Experimental and modelling studies on fixed bed adsorption for Cu(II) removal from aqueous solution by carboxyl modified jute fiber. Powder Technol 338:952–959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2018.06.015
Essien EA, Kavaz D, Solomon MM et al (2018) Olive leaves extract mediated zero-valent iron nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and assessment as adsorbent for nickel (II) ions in aqueous medium. Chem Eng Commun. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2018.1461089
Germanos G, Youssef S, Abboud M et al (2017) Diffusion and agglomeration of iron oxide nanoparticles in magnetic calcium alginate beads initiated by copper sorption. J Environ Chem Eng 5:3727–3733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.07.033
Golie WM, Upadhyayula S (2016) Continuous fixed-bed column study for the removal of nitrate from water using chitosan/alumina composite. J Water Process Eng 12:58–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2016.06.007
Kafshgari F, Keshtkar AR, Mousavian MA (2013) Study of Mo (VI) removal from aqueous solution: application of different mathematical models to continuous biosorption data. J Environ Heal Sci Eng 10:1–11
Kavand M, Fakoor E, Mahzoon S, Soleimani M (2018) An improved film–pore–surface diffusion model in the fixed-bed column adsorption for heavy metal ions: single and multi-component systems. Process Saf Environ Prot 113:330–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.11.009
Khan MMR, Rahman MW, Mozumder MSI et al (2016) Performance of a submerged adsorption column compared with conventional fixed-bed adsorption. Desalin Water Treat 57:9705–9717. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1030779
Khan U, Ali R, Rao K (2017) adsorbent) for the removal of Cu (II) and Ni (II) from aqueous solution: synthesis. Process Saf Environ Prot. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.02.008
Kizito S, Wu S, Wandera SM et al (2016) Evaluation of ammonium adsorption in biochar-fixed beds for treatment of anaerobically digested swine slurry: experimental optimization and modeling. Sci Total Environ 563–564:1095–1104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.05.149
Kumar A, Jena HM (2017) Adsorption of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by prepared high surface area activated carbon from Fox nutshell by chemical activation with H3PO4. J Environ Chem Eng 5:2032–2041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.03.035
Kusuktham B, Prasertgul J, Srinun P (2014) Morphology and property of calcium silicate encapsulated with alginate beads. Silicon 6:191–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-013-9173-z
Lim AP, Aris AZ (2014) Continuous fixed-bed column study and adsorption modeling: removal of cadmium (II) and lead (II) ions in aqueous solution by dead calcareous skeletons. Biochem Eng J 87:50–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2014.03.019
Long Y, Li Q, Ni J et al (2015) Treatment of metal wastewater in pilot-scale packed bed systems: efficiency of single-vs. mixed-mushrooms. RSC Adv 5:29145–29152. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA02409A
Luísa A, Xavier P, Fernando O et al (2018) Modeling adsorption of copper (II), cobalt (II) and nickel (II) metal ions from aqueous solution onto a new carboxylated sugarcane bagasse. Part II : optimization of monocomponent fixed-bed column adsorption. J Colloid Interface Sci 516:431–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.01.068
Mangaleshwaran L, Thirulogachandar A, Rajasekar V et al (2015) Batch and fixed bed column studies on nickel (II) adsorption from aqueous solution by treated polyurethane foam. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 55:112–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2015.03.034
Maria ME, Mansur MB (2017) Mathematical modeling of manganese adsorption onto bone char in a continuous fixed bed column incorporating backmixing and shriking core approaches. Braz J Chem Eng 34:901–909
Mishra A, Dutt B, Kumar A (2016) Packed-bed column biosorption of chromium (VI) and nickel (II) onto Fenton modified Hydrilla verticillata dried biomass. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 132:420–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.06.026
Moscatello N, Swayambhu G, Jones CH et al (2018) Continuous removal of copper, magnesium, and nickel from industrial wastewater utilizing the natural product yersiniabactin immobilized within a packed-bed column. Chem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.02.093
Nithya K, Sathish A, Senthil Kumar P, Ramachandran T (2018) Fast kinetics and high adsorption capacity of green extract capped superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for the adsorption of Ni(II) ions. J Ind Eng Chem 59:230–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2017.10.028
Nithya K, Sathish A, Kumar PS (2020) Packed bed column optimization and modeling studies for removal of chromium ions using chemically modified Lantana camara adsorbent. J Water Process Eng 33:101069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.101069
Patel H (2019) Fixed-bed column adsorption study: a comprehensive review. Appl Water Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-0927-7
Rangabhashiyam S, Nandagopal MSG, Nakkeeran E, Selvaraju N (2016) Adsorption of hexavalent chromium from synthetic and electroplating effluent on chemically modified Swietenia mahagoni shell in a packed bed column. Environ Monit Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5415-z
Saadat S, Hekmatzadeh AA, Jashni AK (2015) Mathematical modeling of the Ni (II) removal from aqueous solutions onto pre-treated rice husk in fixed-bed columns: a comparison. Desalin Water Treat 57(36):16907–16918. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1087877
Saadi Z, Saadi R, Fazaeli R (2013) Fixed-bed adsorption dynamics of Pb(II) adsorption from aqueous solution using nanostructured γ-alumina. J Nanostructure Chem 3:2–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-8865-3-48
Selim KA, Youssef MA, Abd El-Rahiem FH, Hassan MS (2014) Dye removal using some surface modified silicate minerals. Int J Min Sci Technol 24:183–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2014.01.007
Taylor P, Kapur M, Mondal MK (2015) Design and model parameters estimation for fixed–bed column adsorption of Cu (II) and Ni (II) ions using magnetized saw dust. Desalin Water Treat. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1049961
Tsai W, De Luna MDG, Bermillo-arriesgado HLP et al (2016) Competitive fixed-bed adsorption of Pb(II), Cu (II), and Ni (II) from aqueous solution using chitosan-coated bentonite. Int J Poly Sci. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/1608939
Xu Z, Cai JG, Pan BC (2013) Mathematically modeling fixed-bed adsorption in aqueous systems. J Zhejiang Univ Sci A 14:155–176. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1300029
Yildiz I, Sizirici B (2019) Iron oxide-coated gravel fixed bed column study performance to remove mixed metals from landfill leachate, pp 01002:1–6
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Center of Excellence in Advanced Materials and Green Technologies (CoE-AMGT), Amrita School of Engineering, Coimbatore, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, India for the research support.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nithya, K., Sathish, A. & Senthil Kumar, P. Magnetite encapsulated alginates tailored material for the sustainable treatment of electroplating industrial wastewater: column dynamics and mass transfer studies. Clean Techn Environ Policy 23, 89–102 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-020-01961-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-020-01961-5