Abstract
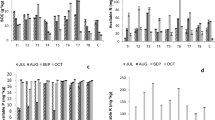
Rice was grown in soil co-amended with coal fly ash (FA) with municipal biosolids (MBS) to study the accumulation of heavy metal (HM) in rice seeds from FA with the co-amendment of MBS. Element-analyses of soil samples, plant-roots and seeds revealed the accumulation of HMs, Fe, Mn, Ni, Co, Zn, Cu and Pb proportionate to the FA doses. For ascertaining some suitable amendment-doses for maximal grain yield with the least accumulation of HMs, principal component analysis (PCA) was carried out with data from three rabi (winter) seasons. With PCA, the variance of performance of FA and MBS together was obtained, 87.25%. It could be concluded that the double amendment levels up to 10 Mg ha−1 FA + 7.5 Mg ha−1 MBS would be the desirable on soil with the accumulation of Pb12 ppb; nonetheless, the toxicity from other HMs was noted at the level 12 mg Mg−1 in rice grains.

Similar content being viewed by others

References
Alloway BJ (1990) Heavy metals in soils. Springer, Berlin, p 368
Baker AJM, Brooks RR (1989) Terrestrial plants which hyperaccumulate metallic elements: a review of their distribution, Ecology and phytochemistry. Biorecovery 1:81–126
Basta NT (2000) Examples and case studies of beneficial reuse of municipal by-products. In: Dick WA (ed) Land application of agricultural, Industrial and municipal by-product. Soil science society of america, Madison, WI, pp 481–504
Basu M, Pande M, Bhadoria PBS, Mahapatra SC (2009) Potential fly-ash utilization in agriculture: a global review. Prog Nat Sci 19:1173–1186
Bitew Y, Alemayehu M (2017) Impact of crop production inputs on soil health: a review. Asian J Plant Sci 16:109–131
Boehm MJ, Wu T, Stone AG, Krakman B, Iannotti DA, Wilson GE, Madden LV, Hoitink HAJ (1997) CP-MAS 13C-NMR spectroscopic characterization of soil organic matter relative to culturable species composition and sustained biological control of Pythium root-rot. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:162–168
Breslin VT (1999) Retention of metals in agricultural soils after amending with MSW and MSW-biosolids compost. Water Air Soil Pollut 109:163–178
Brown S, Chaney RL (2000) Beneficial uses flue gas desulfurisation by-products: examples and case studies of land application. In: Dick WA (ed) Land application of agricultural, industrial and municipal by-products. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, WI, pp 361–386
Campbell AG, Zhang X, Tripepi RR (1995) Composting and evaluating a pulp and paper sludge for use as a soil amendment/mulch. Compost Sci Utiliz 3:84–95
Eckert JW, Ogawa JM (1988) The chemical control of postharvest diseases: deciduous fruits, berries, vegetables and root/ tuber crops. Ann Rev Phytopath 26:433–469
Garrido S, Martin Del Campo G, Esteller MV, Vaca R, Lugo J (2005) Heavy metals in soil treated with sewage sludge composting, their effect on yield and uptake of broad bean seeds (Vicia faba L.). Water Air Soil Pollut 166:303–319
Goulding KWT (2016) Soil acidification and the importance of liming agricultural soils with particular reference to the United Kingdom. Soil Use Manag 32:390–399
Halofsky JE, McCormick LH (2005) Establishment and growth of experimental grass species mixtures on coal mine sites reclaimed with municipal biosolids. Environ Manage 35:569–578
Hartman C (1997) Beneficial use-disease/death: by design or ignorance? NSA public fact sheet 110. National Sludge Alliance, USA
Hodes SC (2010) Soil fertility basics: Soil Science Extension. North Carolina State University, North Carolina
Hodges SC (2010) Soil fertility basics. NC certified crop advisor training. Soil science extension, North carolina state university, 1-12, 1-75
Hoitink HAJ, Boehm MJ, Hadar Y (1992) Mechanisms of suppression of soilborne plant pathogens in compost-amended substrates. In: Hoitink HAJ, Keener HM (eds) Science and engineering of composting: Design, environmental, microbiological and utilization aspects. Renaissance Publications, Worthington, pp 601–621
Howard RJ, Garland JA, Seaman WL (1994) Diseases and pests of vegetable crops in Canada. Entomal Soceity of Canada, Can, p 554
Jala S, Goyal D (2006) Fly ash as a soil ameliorant for improving crop production-a review. Bioresour Technol 97:1136–1147
Kashmanian RM, Kluchinski D, Richard TL, Walker JM (2000) Quantities, characteristics, barriers and incentives for use of organic municipal by-products. In: Dick WA (ed) Land application of agricultural, industrial and municipal by-products. Soil science society of America, Madison, pp 127–168
Kataki S, Hazarika S, Baruah DC (2017) Assessment of by-products of bioenergy systems (anaerobic digestion and gasification) as potential crop nutrient. Waste Manag 59:102–117
Keeling AA, Paton IK, Mullet JAJ (1994) Germination and growth of plants in media containing unstable refuse-derived compost. Soil Biol Biochem 26:767–775
Korcak RF (1995) Utilization of coal combustion by-product in agriculture and horticulture. In: Karlen DL, Wright RJ, Kemper WD (eds) Agricultural Utilization of Urban and Industrial by-products. ASA Special Publication, Madison, pp 107–130
Lee H, Ha HS, Lee CH, Lee YB, Kim PJ (2006) Fly ash effect on improving soil properties and rice productivity in Korean paddy soils. Bioresour Technol 97:1490–1497
Logan TJ, Harrison BJ, Goins LE, Hatfield N (1995) Soil substitute from alkaline stabilization. Biocycle 36:80
Lü X, Zhai X, Huang M (2017) Characterization of the constitutive behavior of municipal solid waste considering particle compressibility. Waste Manag 69:3–12
Lumsden RD, Lewis JA, Millner PD (1983) Effect of composted sewage sludge on several soil borne pathogens and diseases. Phytopathology 73:1543–1548
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Academic press, New York
McCauley A, Jones C, Jacobsen J (2009) Soil pH and organic matter. Nutr Manag Module 8:1–12
Mishra M, Sahu RK, Padhy RK (2005a) Growth, yield, metabolism and elemental status of green gram (Phaseolus aureus) and til (Sesamum indicum) grown in soils amended with fly ash. Fresenius Environ Bull 14:559–564
Mishra M, Sahu RK, Padhy RN (2007) Growth, yield, metabolism and elemental status of rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown in fly ash amended soils. Ecotoxicology 16:271–278
Mishra M, Sahu RK, Sahu SK, Padhy RN (2005b) Effect of vermicomposted municipal solid wastes on growth, yield and heavy metal contents of rice (Oryza sativa). Fresenius Environ Bull 14:584–590
Nelson SR, Peitz RI (1995) Land application of biosolids: papers and publications by the research district-a bibliography 1968–1994. Rep. no. 95–19. Res. Develop. Dep., Metropolitan water reclamation. District greater Chicago, IL, 1995.
Olaniran AO, Balgobind A, Pillay B (2013) Bioavailability of heavy metals in soil: impact on microbial biodegradation of organic compounds and possible improvement strategies. Int J Mol Sci 14:10197–10228
Chandara P (2011) https://phatchandara.blogspot.in/2011/01/royal-university-of-phnompenh.html
Padhy RN, Nayak N, Dash-Mohini RR, Rath S, Sahu RK (2010) Growth, yield and metabolism of rice grown in soil amended with fly ash and cyanobacteria and metal loads in plant parts. Rice Sci 23:23–32
Pandey VC, Singh N (2010) Impact of fly ash incorporation in soil systems. Agric Ecosyst Environ 136:16–27
Parkinson JA, Allen SE (1975) A wet oxidation procedure suitable for the determination of N and mineral nutrients in biological materials. Commun Soil Sci Plant Analys 6:1–11
Rai LC, Gour JP, Kumar HD (1981) Phycology and heavy metal pollution. Biol Rev 56:99–151
Samy NT, Mishra M, Sahu RK, Padhy RN (2010) Growth, yield and metabolism of rice (Oryza sativa L.) during repeated applications of fly ash on soil. Advan Food Sci 32:110–117
Sharpley A, Meisinger JJ, Breeuwsma A, Sims JT, Daniel TC, Schepers JS (1998) Impacts of animal manure management on ground and surface water quality. In: Hatfield JL, Stewart BA (eds) Animal Waste Utilization: Effective use of manure as a soil resource. Ann arbor press, Chelsen
Sopper WE, Seaker M (1984) Use of municipal sludge to reclaim mine land. CRC Critical Rev Environ Cont 13:227–271
Sushil S, Vidya SB (2006) Analysis of fly ash heavy metal content and disposal in three thermal power plants in India. Fuel 85:2676–2679
Tripathi RD, Dwivedi S, Shukla MK, Mishra S, Srivastava S, Singh R, Rai UN, Gupta DK (2008) Role of blue green algae biofertilizer in ameliorating the nitrogen demand and fly ash stress to the growth and yield of rice (Oryza sativa L.) plants. Chemosphere 70:1919–1929
US Environmental Protection Agency (1989) The solid waste dilemma: An agenda for action, pp 1–70.
Werner W, Scherer HWS, Olfs HW (1988) Influence of long-term application of sewage sludge and compost from garbage with sewage sludge on soil fertility criteria. Zeit Acker Pflanzen 160:173–180
Yunusa IAM, Eamus D, DeSilva DL, Murray BR, Burchett MD, Skilbeck GC, Heidrich C (2006) Fly-ash: An exploitable resource for management of Australian agricultural soils. Fuel 85:2337–2344
Acknowledgements
We thank Director, Institute of minerals and materials technology, Bhubaneswar, for facilitating elemental analyses. A part of this work was supported by the project on rice soil, from C. S. I. R., New Delhi, India (Grant No. 21(0859)/11/EMR-II), to RN Padhy. CR Sahoo worked from centre for environmental studies, forest and environmental department, Government of Odisha.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahoo, C.R., Sahu, R.K. & Padhy, R.N. Growth, yield and element-analysis of rice (Oryza sativa L.), grown in soil amended with fly ash and municipal biosolids. Paddy Water Environ 19, 149–157 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-020-00826-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-020-00826-3