Abstract
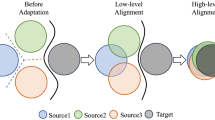
Most existing methods of domain adaptation are proposed for single-source settings, where the source data come from a single domain. However, in practice, the available data generally come from multiple domains with different distributions. In this paper, we propose asymmetric alignment joint consistent regularization (AACR) for multi-source domain adaptation. As for asymmetric alignment, we propose to learn asymmetric projections, explicitly treating each domain differently to avoid the loss of shared information. Data from different domains are encoded into a common subspace by these asymmetric projections, where the encoded features are further aligned to promote knowledge transfer. Further, we propose consistent regularization to better learn shared information and filter out domain-specific information. We formulate the two parts into a unified framework, and derive its global optimal solution. Comprehensive experiments are conducted to evaluate AACR, and the results verify the effectiveness and robustness of our method.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartels RH, Stewart GW (1972) Solution of the matrix equation ax+ xb= c [f4]. Commun ACM 15(9):820–826
Bruzzone L, Marconcini M (2009) Domain adaptation problems: A dasvm classification technique and a circular validation strategy. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 32(5):770–787
Chen Y-C, Zhu X, Zheng W-S, Lai J-H (2017) Person re-identification by camera correlation aware feature augmentation. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 40(2):392–408
Chen Y, Liu L, Tao J, Xia R, Zhang Q, Yang K, Xiong J, Chen X (2020) The improved image inpainting algorithm via encoder and similarity constraint, Vis Comput, 1–15
Chen Y, Tao J, Liu L, Xiong J, Xia R, Xie J, Zhang Q, Yang K (2020) Research of improving semantic image segmentation based on a feature fusion model, journal of ambient intelligence and humanized computing
Chen Y, Tao J, Zhang Q, Yang K, Chen X, Xiong J, Xia R, Xie J (2020) Saliency detection via the improved hierarchical principal component analysis method, Wirel Commun Mob Comput, 2020
Chen Y, Wang J, Chen X, Sangaiah AK, Yang K, Cao Z (2019) Image super-resolution algorithm based on dual-channel convolutional neural networks. Appl Sci 9(11):2316
Chen Y, Wang J, Chen X, Zhu M, Yang K, Wang Z, Xia R (2019) Single-image super-resolution algorithm based on structural self-similarity and deformation block features. IEEE Access 7:58791–58801
Chen Y, Wang J, Liu S, Chen X, Xiong J, Xie J, Yang K (2019) Multiscale fast correlation filtering tracking algorithm based on a feature fusion model, concurrency and computation: practice and experience, e5533
Chen Y, Wang J, Xia R, Zhang Q, Cao Z, Yang K (2019) The visual object tracking algorithm research based on adaptive combination kernel. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing 10(12):4855–4867
Chen Y, Xiong J, Xu W, Zuo J (2019) A novel online incremental and decremental learning algorithm based on variable support vector machine. Clust Comput 22(3):7435–7445
Chen Y, Xu W, Zuo J, Yang K (2019) The fire recognition algorithm using dynamic feature fusion and iv-svm classifier. Clust Comput 22(3):7665–7675
Chung FRK, Graham FC (1997) Spectral graph theory, american mathematical soc., 92
Fernando B, Habrard A, Sebban M, Tuytelaars T (2013) Unsupervised visual domain adaptation using subspace alignment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 2960–2967
Gong B, Shi Y, Sha F, Grauman K (2012) Geodesic flow kernel for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2066–2073
Griffin G, Holub A, Perona P (2007) Caltech-256 object category dataset
Gu Q, Li Z, Han J (2011) Joint feature selection and subspace learning. In: Twenty-second international joint conference on artificial intelligence, pp 1294–1299
Hoffman J, Kulis B, Darrell T, Saenko K (2012) Discovering latent domains for multisource domain adaptation. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, pp 702–715
Hoffman J, Tzeng E, Park T, Zhu J-Y, Isola P, Saenko K, Efros A, Darrell T (2018) Cycada: Cycle-consistent adversarial domain adaptation. In: International conference on machine learning, pp 1989–1998
Huang J, Zhou Z (2019) Transfer metric learning for unsupervised domain adaptation. IET Image Process 13(5):804–810
Jiang J, Zhai C (2007) Instance weighting for domain adaptation in nlp. In: Proceedings of the 45th annual meeting of the association of computational linguistics, pp 264–271
Kodirov E, Xiang T, Gong S (2017) Semantic autoencoder for zero-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 3174–3183
Li J, Lu K, Huang Z, Zhu L, Shen HT (2018) Heterogeneous domain adaptation through progressive alignment. IEEE transactions on neural networks and learning systems 30(5):1381–1391
Li J, Cheng K, Wang S, Morstatter F, Trevino RP, Tang J, Liu H (2018) Feature selection: A data perspective. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR) 50(6):94
Liao X, Yin J, Chen M, Qin Z (2020) Adaptive payload distribution in multiple images steganography based on image texture features, ieee transactions on dependable and secure computing
Liu J, Li J, Lu K (2018) Coupled local–global adaptation for multi-source transfer learning. Neurocomputing 275:247–254
Long M, Cao Y, Wang J, Jordan M (2015) Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks. In: International conference on machine learning, PMLR, pp 97–105
Long M, Wang J, Ding G, Sun J, Yu PS (2013) Transfer feature learning with joint distribution adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 2200–2207
Long M, Wang J, Ding G, Sun J, Yu PS (2014) Transfer joint matching for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1410–1417
Lu X, Ma C, Ni B, Yang X, Reid I, Yang M-H (2018) Deep regression tracking with shrinkage loss. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 353–369
Lu X, Wang W, Shen J, Tai Y-W, Crandall DJ, Hoi SCH (2020) Learning video object segmentation from unlabeled videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 8960–8970
Luo Y, Qin J, Xiang X, Tan Y, Liu Q, Xiang L (2020) Coverless real-time image information hiding based on image block matching and dense convolutional network. J Real-Time Image Proc 17(1):125–135
Maaten L, Hinton G (2008) Visualizing data using t-sne. Journal of machine learning research 9:2579–2605
Pan SJ, Tsang IW, Kwok JT, Yang Q (2010) Domain adaptation via transfer component analysis. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 22 (2):199–210
Pan SJ, Yang Q (2009) A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Transactions on knowledge and data engineering 22(10):1345–1359
Patel VM, Gopalan R, Li R, Chellappa R (2015) Visual domain adaptation: A survey of recent advances. IEEE signal processing magazine 32(3):53–69
Saenko K, Kulis B, Fritz M, Darrell T (2010) Adapting visual category models to new domains. In: European conference on computer vision, Springer, pp 213–226
Shen J, Qu Y, Zhang W, Yu Y (2017) Wasserstein distance guided representation learning for domain adaptation. arXiv:1707.01217
Si S, Tao D, Geng B (2009) Bregman divergence-based regularization for transfer subspace learning. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 22(7):929–942
Sim T, Baker S, Bsat M (2002) The cmu pose, illumination, and expression (pie) database. In: Proceedings of Fifth IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face Gesture Recognition, IEEE, pp 53–58
Torralba A, Efros AA, et al. (2011) Unbiased look at dataset bias. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1521–1528
Tzeng E, Hoffman J, Saenko K, Darrell T (2017) Adversarial discriminative domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 7167–7176
Wang J, Chen Y, Hao S, Feng W, Shen Z (2017) Balanced distribution adaptation for transfer learning. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), IEEE, pp 1129–1134
Yan S, Xu D, Zhang B, Zhang H-J, Yang Q, Lin S (2006) Graph embedding and extensions: A general framework for dimensionality reduction. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 29(1):40–51
Yu F, Liu L, He B, Huang Y, Shi C, Cai S, Song Y, Du S, Wan Q (2019) Analysis and fpga realization of a novel 5d hyperchaotic four-wing memristive system, active control synchronization, and secure communication application, Complexity, 2019
Yu F, Liu L, Xiao L, Li K, Cai S (2019) A robust and fixed-time zeroing neural dynamics for computing time-variant nonlinear equation using a novel nonlinear activation function. Neurocomputing 350:108–116
Zhang J, Xie Z, Sun J, Zou X, Wang J (2020) A cascaded r-cnn with multiscale attention and imbalanced samples for traffic sign detection. IEEE Access 8:29742–29754
Zhang J, Li W, Ogunbona P (2017) Joint geometrical and statistical alignment for visual domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 1859–1867
Zhang Y, Tang H, Jia K, Tan M (2019) Domain-symmetric networks for adversarial domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 5031–5040
Acknowledgements
The work is supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC0309400), National Natural Science Foundation of China (61871188), Guangzhou city science and technology research projects(201902020008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shang, J., Niu, C., Zhou, Z. et al. Asymmetric alignment joint consistent regularization for multi-source domain adaptation. Multimed Tools Appl 80, 6041–6064 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09883-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09883-6