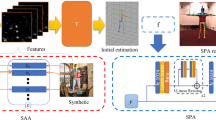
Abstract
Despite the significant improvement in the performance of monocular pose estimation approaches and their ability to generalize to unseen environments, multi-view approaches are often lagging behind in terms of accuracy and are specific to certain datasets. This is mainly due to the fact that (1) contrary to real-world single-view datasets, multi-view datasets are often captured in controlled environments to collect precise 3D annotations, which do not cover all real-world challenges, and (2) the model parameters are learned for specific camera setups. To alleviate these problems, we propose a two-stage approach to detect and estimate 3D human poses, which separates single-view pose detection from multi-view 3D pose estimation. This separation enables us to utilize each dataset for the right task, i.e. single-view datasets for constructing robust pose detection models and multi-view datasets for constructing precise multi-view 3D regression models. In addition, our 3D regression approach only requires 3D pose data and its projections to the views for building the model, hence removing the need for collecting annotated data from the test setup. Our approach can therefore be easily generalized to a new environment by simply projecting 3D poses into 2D during training according to the camera setup used at test time. As 2D poses are collected at test time using a single-view pose detector, which might generate inaccurate detections, we model its characteristics and incorporate this information during training. We demonstrate that incorporating the detector’s characteristics is important to build a robust 3D regression model and that the resulting regression model generalizes well to new multi-view environments. Our evaluation results show that our approach achieves competitive results on the Human3.6M dataset and significantly improves results on a multi-view clinical dataset that is the first multi-view dataset generated from live surgery recordings.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
We define a multi-view frame as the set of all images captured from all views at the same time step.
The MVOR dataset is publicly available at http://camma.u-strasbg.fr/datasets.
The image size is \(480 \times 640\) pixels.
Please note that for generating the qualitative images, the predicted 3D poses are transferred to the room reference frame using an offset computed as the relative difference between the neck location in the ground truth and the neck location in the predicted skeleton.
More qualitative results generated by our model on both datasets are available at https://youtu.be/Cx_kTRzqqzA.
References
Abadi, M., Agarwal, A., Barham, P., Brevdo, E., Chen, Z., Citro, C., Corrado, G.S., Davis, A., Dean, J., Devin, M., Ghemawat, S., Goodfellow, I., Harp, A., Irving, G., Isard, M., Jia Y., Jozefowicz, R., Kaiser, L., Kudlur, M., Levenberg, J., Mané, D., Monga, R., Moore, S., Murray, D., Olah, C., Schuster, M., Shlens, J., Steiner, B., Sutskever, I., Talwar, K., Tucker, P., Vanhoucke, V., Vasudevan, V., Viégas, F., Vinyals, O., Warden, P., Wattenberg, M., Wicke, M., Yu, Y., Zheng, X.: TensorFlow: large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous systems, 2015. URL https://www.tensorflow.org/. Software available from tensorflow.org
Amin, S., Andriluka, M., Rohrbach, M., Schiele, B.: Multi-view pictorial structures for 3d human pose estimation. In: British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), September (2013)
Amin, S., Müller, P., Bulling, A., Andriluka, M.: Test-time adaptation for 3d human pose estimation. Pattern Recogn. 8753, 253–264 (2014)
Andriluka, M., Pishchulin, L., Gehler, P., Schiele, B.: 2D human pose estimation: New benchmark and state of the art analysis. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3686–3693, (2014)
Belagiannis, V., Amin, S., Andriluka, M., Schiele, B., Navab, N., Ilic, S.: 3d pictorial structures for multiple human pose estimation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1669–1676, (2014)
Belagiannis, V., Wang, X., Schiele, B., Fua, P., Ilic, S., Navab, N.: Multiple human pose estimation with temporally consistent 3D pictorial structures. In: ChaLearn Looking at People Workshop, European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV2014), pp. 742–754, September (2014)
Belagiannis, V., Wang, X., Shitrit, H.B.B., Hashimoto, K., Stauder, R., Aoki, Y., Kranzfelder, M., Schneider, A., Fua, P., Ilic, S., Feussner, H., Navab, N.: Parsing human skeletons in an operating room. Machine Vision and Applications, pp. 1–12, (2016)
Biswas, P., Liang, T.C., Toh, K.C., Ye, Y., Wang, T.C.: Semidefinite programming approaches for sensor network localization with noisy distance measurements. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 3(4), 360–371 (2006)
Burenius, M., Sullivan, J., Carlsson, S.: 3d pictorial structures for multiple view articulated pose estimation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3618–3625, (2013)
Cao, Z., Simon, T., Wei, S.-E., Sheikh, Y.: Realtime multi-person 2D pose estimation using part affinity fields. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1302–1310, (2017)
Chen, C.-H., Ramanan, D.: 3D human pose estimation = 2D pose estimation + matching. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 5759–5767, July (2017)
Chen, D., Chou, P.-C., Fookes, C.B., Sridharan, S.: Multi-view human pose estimation using modified five-point skeleton model. In: International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication Systems, pp. 17–19 (2008)
Dogan, E., Eren, G., Wolf, C., Lombardi, E., Baskurt, A.: Multi-view pose estimation with mixtures-of-parts and adaptive viewpoint selection. In: IET Computer Vision (2017)
Fang, H., Xu, Y., Wang, W., Liu, X., Zhu, S.C.: Learning knowledge-guided pose grammar machine for 3d human pose estimation. CoRR, abs/1710.06513, 2017. URL http://arxiv.org/abs/1710.06513
Felzenszwalb, P.F., Huttenlocher, D.P.: Pictorial structures for object recognition. International Journal of Computer Vision 61(1), 55–79 (2005)
Felzenszwalb, P.F., Girshick, R.B., McAllester, D., Ramanan, D.: Object detection with discriminatively trained part-based models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 32(9), 1627–1645 (2010)
Fischler, M.A., Elschlager, R.A.: The representation and matching of pictorial structures. IEEE Trans. Comput. 22(1), 67–92 (1973)
Gall, J., Rosenhahn, B., Brox, T., Seidel, H.-P.: Optimization and filtering for human motion capture. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 87(1), 75–92 (2010)
Hartley, R.I., Zisserman, A.: Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Hofmann, M., Gavrila, D.M.: Multi-view 3D human pose estimation in complex environment. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 96(1), 103–124 (2011)
Huang, F., Zeng, A., Liu, M., Lai, Q., Xu, Q.: Deepfuse: an IMU-aware network for real-time 3d human pose estimation from multi-view image. In: The IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV) (2020)
Ioffe, S., Szegedy, C.: Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 448–456, (2015)
Ionescu, C., Papava, D., Olaru, V., Sminchisescu, C.: Human3.6m: Large scale datasets and predictive methods for 3d human sensing in natural environments. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 36(7), 1325–1339 (2014)
Jiang, H.: 3d human pose reconstruction using millions of exemplars. In: International Conference on Pattern Recognition, pp. 1674–1677, (Aug 2010)
Jiang, M., Zhuliang, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, Q., Li, C., Lei, Y.: Reweighted sparse representation with residual compensation for 3d human pose estimation from a single rgb image. Neurocomputing 358, 332–343 (2019)
Kadkhodamohammadi, A., Gangi, A., de Mathelin, M., Padoy, N.: A multi-view RGB-D approach for human pose estimation in operating rooms. In: Proceedings of IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pp. 363–372, (2017)
Lin, T.-Y., Maire, M., Belongie, S., Hays, J., Perona, P., Ramanan, D., Dollár, P., Zitnick, C.L.: Microsoft COCO: CommonLawrence: Microsoft COCO: Context, pp. 740–755. Springer (2014)
Luo, X., Berendsen, B., Tan, R.T., Veltkamp, R.C.: Human pose estimation for multiple persons based on volume reconstruction. In: International Conference on Pattern Recognition, pp. 3591–3594 (2010)
Luvizon, D., Picard, D., Tabia, H.: Multi-task deep learning for real-time 3d human pose estimation and action recognition. In: IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (2020)
Luvizon, Diogo C., Picard, David, Tabia, Hedi: 2D/3D pose estimation and action recognition using multitask deep learning. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), (2018)
Martinez, J., Hossain, R., Romero, J., Little, J.J.: A simple yet effective baseline for 3d human pose estimation. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 2659–2668, (2017)
Moreno-N.: Francesc: 3d human pose estimation from a single image via distance matrix regression. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, (CVPR), pp. 1561–1570, (2017)
Nair, V., Hinton, G.E.: Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 807–814, (2010)
Newell, A., Yang, K., Deng, J.: Stacked Hourglass Networks for Human Pose Estimation, pp. 483–499. (2016)
Newell, A., Huang, Z., Deng, J.: Associative embedding: End-to-end learning for joint detection and grouping. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30, 2277–2287 (2017)
Pavlakos, G., Zhou, X., Derpanis, K.G, Daniilidis, K.: Coarse-to-fine volumetric prediction for single-image 3D human pose. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1263–1272, (2017)
Pavlakos, G., Zhou, X., Derpanis, K.G., Daniilidis, K.: Harvesting multiple views for marker-less 3d human pose annotations. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1253–1262, (2017)
Radwan, I., Dhall, A., Goecke, R.: Monocular image 3D human pose estimation under self-occlusion. In: International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 1888–1895, (2013)
Rogez, G., Weinzaepfel, P., Schmid, C.: LCR-Net: Localization-classification-regression for human pose. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1216–1224, (2017)
Sigal, L., Balan, A.O., Black, M.J.: Humaneva: Synchronized video and motion capture dataset and baseline algorithm for evaluation of articulated human motion. International Journal of Computer Vision 87(1), 4–27 (2009)
Sigal, L., Isard, M., Haussecker, H., Black, M.J.: Loose-limbed people: Estimating 3D human pose and motion using non-parametric belief propagation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 98(1), 15–48 (2012)
Slembrouck, M., Luong, H., Gerlo, J., Schütte, K., Van Cauwelaert, D., De Clercq, D., Vanwanseele, B., Veelaert, P., Philips, W.: Multiview 3d markerless human pose estimation from openpose skeletons. In: Jacques B.-T., Patrice D., Wilfried P., Dan P., Paul S. (eds), Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems, pp. 166–178. Springer (2020)
Srivastav, V., Issenhuth, T., Kadkhodamohammadi, A., de Mathelin, M., Gangi, A., Padoy, N.: MVOR: a multi-view RGB-D operating room dataset for 2D and 3D human pose estimation. CoRR (2018). URL http://arxiv.org/abs/1808.08180
Srivastava, N., Hinton, G., Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Salakhutdinov, R.: Dropout: a simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res., 15(1):1929–1958 (2014). ISSN 1532-4435
Sundaresan, A., Chellappa, R.: Multicamera tracking of articulated human motion using shape and motion cues. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 18(9), 2114–2126 (2009)
Tekin, B., Rozantsev, A., Lepetit, V., Fua, P.: Direct prediction of 3d body poses from motion compensated sequences. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 991–1000 (2016)
Tekin, B., Katircioglu, I., Salzmann, M., Lepetit, V., Fua, P.: Structured prediction of 3d human pose with deep neural networks. In: Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference BMVC (2016)
Vondrak, M., Sigal, L., Jenkins, O.C.: Physical simulation for probabilistic motion tracking. In: 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1–8 (2008)
Wan, Q., Zhang, W., Xue, X.: Deepskeleton: skeleton map for 3D human pose regression. CoRR, arXiv:1711.10796 (2017). URL http://arxiv.org/abs/1711.10796
Wei, S.-E., Ramakrishna, V., Kanade, T., Sheikh, Y.: Convolutional pose machines. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 4724–4732 (2016)
Yu, J., Hong, C.: Exemplar-based 3d human pose estimation with sparse spectral embedding. Neurocomputing 269, 82–89 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by French state funds managed within the Investissements d’Avenir program by BPI France (project CONDOR) and by the ANR (references ANR-11-LABX- 0004, ANR-10-IAHU-02 and ANR-16-CE33-0009). The authors would also like to acknowledge the support of NVIDIA with the donation of a GPU used in this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kadkhodamohammadi, A., Padoy, N. A generalizable approach for multi-view 3D human pose regression. Machine Vision and Applications 32, 6 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-020-01120-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-020-01120-2