Abstract
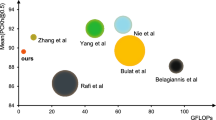
Most existing methods pay much attention to how to improve the accuracy of human pose estimation results. They usually ignore what the size of their model is. However, besides accuracy, real-time and speed are also important. In this paper, a new module named Densely Connected Residual Module is presented to effectively decrease the number of parameters in our network. We introduce our module into the backbone of High-Resolution Net. In addition, we change direct addition fusion into pyramid fusion at the end of the network. No need for ImageNet pre-training sharply decreases the total time of our training processes. We do our experiments over two benchmark datasets: the COCO keypoint detection dataset and the MPII Human Pose dataset. As a result, we achieve a decrease on number of parameters and calculated amount, respectively by around 72% and 14%, making our network more lightweight than High-Resolution Net. During testing process, our model can predict an image at a speed of 25 ms per image, which also achieves real-time fundamentally. The code has been available at https://github.com/consistent1997/LDCRN.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A: Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 568–576 (2014)
Feichtenhofer, C., Pinz, A., Zisserman, A.: Convolutional two-stream network fusion for video action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1933–1941 (2016)
Wang, L., Xiong, Y., Wang, Z., Qiao, Y., Lin, D., Tang, X., Van Gool, L.: Temporal segment networks: Towards good practices for deep action recognition. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, pp. 20–36 (2016)
Lan, Z., Zhu, Y., Hauptmann, A.G., Newsam, S.: Deep local video feature for action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 1–7 (2017)
Sun, L., Jia, K., Yeung, D.Y., Shi, B.E.: Human action recognition using factorized spatio-temporal convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4597–4605 (2015)
Cao, Z., Simon, T., Wei, S.E., Sheikh, Y.: Realtime multi-person 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7291–7299 (2017)
Cao, Z., Hidalgo, G., Simon, T., Wei, S.E., Sheikh, Y.: Openpose: realtime multi-person 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields (2018). arXiv:1812.08008
Insafutdinov, E., Pishchulin, L., Andres, B., Andriluka, M., Schiele, B.: Deepercut: A deeper, stronger, and faster multi-person pose estimation model. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, pp. 34–50 (2016)
Kocabas, M., Karagoz, S., Akbas, E.: Multiposenet: fast multi-person pose estimation using pose residual network. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 417–43 (2018)
Papandreou, G., Zhu, T., Kanazawa, N., Toshev, A., Tompson, J., Bregler, C., Murphy, K.: Towards accurate multi-person pose estimation in the wild. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4903–4911 (2017)
Fang, H.S., Xie, S., Tai, Y.W., Lu, C.: Rmpe: Regional multi-person pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2334–2343 (2017)
Newell, A., Huang, Z., Deng, J.: Associative embedding: End-to-end learning for joint detection and grouping. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 2277–2287 (2017)
Chen, Y., Wang, Z., Peng, Y., Zhang, Z., Yu, G., Sun, J.: Cascaded pyramid network for multi-person pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7103–7112 (2018)
Xia, F., Wang, P., Chen, X., Yuille, A.L.: Joint multi-person pose estimation and semantic part segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6769–6778 (2017)
Pfister, T., Charles, J., Zisserman, A.: Flowing convnets for human pose estimation in videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1913–1921 (2015)
Xiao, B., Wu, H., Wei, Y.: Simple baselines for human pose estimation and tracking. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 466–481 (2018)
Iqbal, U., Milan, A., Gall, J.: Posetrack: Joint multi-person pose estimation and tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2011–2020 (2017)
Felzenszwalb, P.F., Huttenlocher, D.P.: Pictorial structures for object recognition. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 61(1), 55–79 (2005)
Andriluka, M., Roth, S., Schiele, B.: Pictorial structures revisited: People detection and articulated pose estimation. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, pp. 1014–1021 (2009)
Yang , Y., Ramanan, D.: Articulated pose estimation with flexible mixtures-of-parts. In: CVPR 2011. IEEE, pp. 1385–1392 (2011)
Pishchulin, L., Andriluka, M., Gehler, P., Schiele, B.: Poselet conditioned pictorial structures. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 588–595 (2013)
Wei, S.E., Ramakrishna, V., Kanade, T., Sheikh, Y.: Convolutional pose machines. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4724–4732 (2016)
Newell, A., Yang, K., Deng, J.: Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, pp. 483–499 (2016)
Sun, K., Xiao, B., Liu, D., Wang, J.: Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation (2019). arXiv:1902.09212
Lin, T.Y., Dollár, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Hariharan, B., Belongie, S.: Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2117–2125 (2017)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Identity mappings in deep residual networks. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, pp. 630–645 (2016)
Huang, G., Liu, Z., Van Der Maaten, L., Weinberger, K.Q.: Densely connected convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4700–4708 (2017)
Gkioxari, G., Toshev, A., Jaitly, N.: Chained predictions using convolutional neural networks. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, pp. 728–743 (2016)
Tang, W., Yu, P., Wu, Y.: Deeply learned compositional models for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp 190–206 (2018)
Ke Sun, Cuiling Lan, Junliang Xing, Wenjun Zeng, Dong Liu, and Jingdong Wang. Human pose estimation using global and local normalization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pages 5599–5607, 2017
Fan, X., Zheng, K., Lin, Y., Wang, S.: Combining local appearance and holistic view: Dual-source deep neural networks for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1347–1355 (2015)
Peng, X., Tang, Z., Yang, F., Feris, R.S., Metaxas, D.: Jointly optimize data augmentation and network training: Adversarial data augmentation in human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2226–2234 (2018)
Toshev, A., Szegedy, C.: Deeppose: hhuman pose estimation via deep neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1653–1660 (2014)
Carreira, J., Agrawal, P., Fragkiadaki, K., Malik, J.: Human pose estimation with iterative error feedback. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4733–4742 (2016)
Chu, X., Ouyang, W., Li, H., Wang, X.: Structured feature learning for pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4715–4723 (2016)
Chu, X., Yang, W., Ouyang, W., Ma, C., Yuille, A.L., Wang, X.: Multi-context attention for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1831–1840 (2017)
Yang, W., Ouyang, W., Li, H., Wang, X.: End-to-end learning of deformable mixture of parts and deep convolutional neural networks for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3073–3082 (2016)
Wang, R., Huang, C., Wang, X.: Global relation reasoning graph convolutional networks for human pose estimation. IEEE Access 8, 38472–38480 (2020)
Yang, W., Li, S., Ouyang, W., Li, H., Wang, X.: Learning feature pyramids for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1281–1290 (2017)
Ke, L., Chang, M.C., Qi, H., Lyu, S.: Multi-scale structure-aware network for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 713–728 (2018)
Gao, B., Ma, K., Bi, H., Wang, L.: A lightweight network based on pyramid residual module for human pose estimation. Pattern Recogn. Image Anal. 29(4), 668–675 (2019)
Zhang, F., Zhu, X., Ye, M.: Efficient human pose estimation in hierarchical context. IEEE Access 7, 29365–29373 (2019)
Wang, R., Cao, Z., Wang, X., Liu, Z., Zhu, X.: Human pose estimation with deeply learned multi-scale compositional models. IEEE Access 7, 71158–71166 (2019)
Lee, C.Y., Xie, S., Gallagher, P., Zhang, Z., Tu, Z.: Deeply-supervised nets. In: Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, pp. 562–570 (2015)
Szegedy, C., Liu, W., Jia, Y., Sermanet, P., Reed, S., Anguelov, D., Erhan, D., Vanhoucke, V., Rabinovich, A.: Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1–9 (2015)
Yun, K., Park, J., Cho, J.: Robust human pose estimation for rotation via self-supervised learning. IEEE Access 8, 32502–32517 (2020)
Zhang, K., Guo, Y., Wang, X., Yuan, J., Ding, Q.: Multiple feature reweight densenet for image classification. IEEE Access 7, 9872–9880 (2019)
Zhang, K., Sun, M., Han, T.X., Yuan, X., Guo, L., Liu, T.: Residual networks of residual networks: Multilevel residual networks. IEEE Tran. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 28(6), 1303–1314 (2017)
Wang, Z., Li, W., Yin, B., Peng, Q., Xiao, T., Yuming, D., Li, Z., Zhang, X., Gang, Yu., Sun, J.: Mscoco keypoints challenge 2018. Joint Recogn. Chall. Worksh. ECCV 2018, 4 (2018)
He, K., Girshick, R., Dollár, P.: Rethinking imagenet pre-training. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4918–4927 (2019)
Bulat, A., Tzimiropoulos, G.: Human pose estimation via convolutional part heatmap regression. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, pp. 717–732 (2016)
Oved, D., Alvarado, I., Gallo, A.: Real-time human pose estimation in the browser with tensorflow. In: TensorFlow Medium, May (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFF0300502), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant no. N160504007) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 31301086).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Qin, Y. & Zhang, X. Lightweight densely connected residual network for human pose estimation. J Real-Time Image Proc 18, 825–837 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-020-01025-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-020-01025-3