Abstract
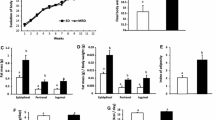
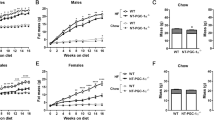
The taste receptor type I (Tas1R) family consists of three G protein-coupled receptors (T1R1, T1R2, and T1R3) that form heterodimers recognizing sweet compounds (T1R2/T1R3) or amino acids (T1R1/T1R3). These receptors are nutrient sensors that facilitate appropriate physiological responses with nutrient availability. However, their contribution to the development of pathologies associated with overnutrition (e.g., atherosclerosis) is unclear. The aim of the present study was to determine if T1R3 deletion would reduce atherosclerotic plaque development in mice. We generated atherosclerotic mice with whole-body deletion of T1R3 by crossing T1R3−/− mice with ApoE−/− mice. T1R3+/+ ApoE−/− and T1R3−/− ApoE−/− mice were maintained on an atherogenic high-fat diet for 8 weeks. Weight gain and food consumption were measured during the 8-week diet. Atherosclerotic lesion development and size were assessed by en face analysis of intact aortas and microscopic analysis of aortic roots. Our results indicate that T1R3 deletion in male and female ApoE−/− mice reduces aortic atherosclerotic plaque accumulation. Hepatic triglyceride accumulation, which was measured by quantification of oil red O staining, was also reduced in T1R3−/− mice. While the ablation of T1R3 reduced the final body weight of both males and females by approximately 12%, serum lipids, insulin, and glucose were either unchanged or slightly reduced. Immunoblot analysis of the phosphorylation of p70S6K, an effector of mTORC1, suggests T1R3 ablation reduces mTORC1 activity by approximately 50% in the male livers. Collectively, these findings suggest that the whole-body deletion of T1R3 reduces atherosclerosis and hepatic steatosis in a manner largely independent of the measured effects on whole-body glucose and lipid homeostasis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai D, Jiang H, Westerterp M, Murphy AJ, Wang M, Ganda A, Abramowicz S, Welch C, Almazan F, Zhu Y, Miller YI, Tall AR (2014) Disruption of mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 in macrophages decreases chemokine gene expression and atherosclerosis. Circ Res 114(10):1576–1584
Andres-Manzano MJ, Andres V, Dorado B (2015) Oil red O and hematoxylin and eosin staining for quantification of atherosclerosis burden in mouse aorta and aortic root. Methods Mol Biol 1339:85–99
Chang GR, Chiu YS, Wu YY, Chen WY, Liao JW, Chao TH, Mao FC (2009) Rapamycin protects against high fat diet-induced obesity in C57BL/6J mice. J Pharmacol Sci 109(4):496–503
Crowe MS et al (2018) Su1667 - expression and function of umami (T1R1/T1R3) and sweet (T1R2/T1R3) nutrient receptors in mouse gastric smooth muscle. Gastroenterology 154(6):S-568
Curtis KS, Stratford JM, Contreras RJ (2005) Estrogen increases the taste threshold for sucrose in rats. Physiol Behav 86(3):281–286
Daly K, al-Rammahi M, Moran A, Marcello M, Ninomiya Y, Shirazi-Beechey SP (2013) Sensing of amino acids by the gut-expressed taste receptor T1R1-T1R3 stimulates CCK secretion. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 304(3):G271–G282
Eaton MS, Weinstein N, Newby JB, Plattes MM, Foster HE, Arthur JW, Ward TD, Shively SR, Shor R, Nathan J, Davis HM, Plotkin LI, Wauson EM, Dewar BJ, Broege A, Lowery JW (2018) Loss of the nutrient sensor TAS1R3 leads to reduced bone resorption. J Physiol Biochem 74(1):3–8
Efeyan A, Comb WC, Sabatini DM (2015) Nutrient-sensing mechanisms and pathways. Nature 517(7534):302–310
Foster SR, Porrello ER, Purdue B, Chan HW, Voigt A, Frenzel S, Hannan RD, Moritz KM, Simmons DG, Molenaar P, Roura E, Boehm U, Meyerhof W, Thomas WG (2013) Expression, regulation and putative nutrient-sensing function of taste GPCRs in the heart. PLoS One 8(5):e64579
Geraedts MC et al (2012) Transformation of postingestive glucose responses after deletion of sweet taste receptor subunits or gastric bypass surgery. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 303(4):E464–E474
Glass CK, Witztum JL (2001) Atherosclerosis. The road ahead. Cell 104(4):503–516
Grundy SM (2004) Obesity, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(6):2595–2600
Harrington EO, Vang A, Braza J, Shil A, Chichger H (2018) Activation of the sweet taste receptor, T1R3, by the artificial sweetener sucralose regulates the pulmonary endothelium. Am J Phys Lung Cell Mol Phys 314(1):L165–l176
Hirata Y et al (2019) Kruppel-like factor 5 (Klf5) regulates expression of mouse T1R1 amino acid receptor gene (Tas1r1) in C2C12 myoblast cells. Biomed Res 40(2):67–78
Jang HJ, Kokrashvili Z, Theodorakis MJ, Carlson OD, Kim BJ, Zhou J, Kim HH, Xu X, Chan SL, Juhaszova M, Bernier M, Mosinger B, Margolskee RF, Egan JM (2007) Gut-expressed gustducin and taste receptors regulate secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(38):15069–15074
Jia G, Aroor AR, Martinez-Lemus LA, Sowers JR (2014) Overnutrition, mTOR signaling, and cardiovascular diseases. Am J Phys Regul Integr Comp Phys 307(10):R1198–R1206
Kendig DM, Hurst NR, Bradley ZL, Mahavadi S, Kuemmerle JF, Lyall V, DeSimone J, Murthy KS, Grider JR (2014) Activation of the umami taste receptor (T1R1/T1R3) initiates the peristaltic reflex and pellet propulsion in the distal colon. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 307(11):G1100–G1107
Kurdi A, De Meyer GR, Martinet W (2016) Potential therapeutic effects of mTOR inhibition in atherosclerosis. Br J Clin Pharmacol 82(5):1267–1279
Kyriazis GA, Soundarapandian MM, Tyrberg B (2012) Sweet taste receptor signaling in beta cells mediates fructose-induced potentiation of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(8):E524–E532
Laffitte A, Neiers F, Briand L (2014) Functional roles of the sweet taste receptor in oral and extraoral tissues. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 17(4):379–385
Lazutkaite G, Soldà A, Lossow K, Meyerhof W, Dale N (2017) Amino acid sensing in hypothalamic tanycytes via umami taste receptors. Mol Metab 6(11):1480–1492
Lee N, Jung YS, Lee HY, Kang NN, Park YJ, Hwang JS, Bahk YY, Koo JH, Bae YS (2014) Mouse neutrophils express functional umami taste receptor T1R1/T1R3. BMB Rep 47(11):649–654
Lin CW, Zhang H, Li M, Xiong X, Chen X, Chen X, Dong XC, Yin XM (2013) Pharmacological promotion of autophagy alleviates steatosis and injury in alcoholic and non-alcoholic fatty liver conditions in mice. J Hepatol 58(5):993–999
Liu S, Xu M, Zhu C, Zhao Q, Zhou F (2018) Taste receptor T1R1/T1R3 promotes the tumoricidal activity of hepatic CD49a(+) CD49b(-) natural killer cells. Eur J Immunol 48(12):2031–2041
Ma KL, Liu J, Wang CX, Ni J, Zhang Y, Wu Y, Lv LL, Ruan XZ, Liu BC (2013) Activation of mTOR modulates SREBP-2 to induce foam cell formation through increased retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation. Cardiovasc Res 100(3):450–460
Malki A, Fiedler J, Fricke K, Ballweg I, Pfaffl MW, Krautwurst D (2015) Class I odorant receptors, TAS1R and TAS2R taste receptors, are markers for subpopulations of circulating leukocytes. J Leukoc Biol 97(3):533–545
Margolskee RF, Dyer J, Kokrashvili Z, Salmon KSH, Ilegems E, Daly K, Maillet EL, Ninomiya Y, Mosinger B, Shirazi-Beechey SP (2007) T1R3 and gustducin in gut sense sugars to regulate expression of Na+-glucose cotransporter 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(38):15075–15080
Masubuchi Y, Nakagawa Y, Ma J, Sasaki T, Kitamura T, Yamamoto Y, Kurose H, Kojima I, Shibata H (2013) A novel regulatory function of sweet taste-sensing receptor in adipogenic differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells. PLoS One 8(1):e54500
Mauvais-Jarvis F, Clegg DJ, Hevener AL (2013) The role of estrogens in control of energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Endocr Rev 34(3):309–338
Miquilena-Colina ME, Lima-Cabello E, Sanchez-Campos S, Garcia-Mediavilla MV, Fernandez-Bermejo M, Lozano-Rodriguez T, Vargas-Castrillon J, Buque X, Ochoa B, Aspichueta P, Gonzalez-Gallego J, Garcia-Monzon C (2011) Hepatic fatty acid translocase CD36 upregulation is associated with insulin resistance, hyperinsulinaemia and increased steatosis in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and chronic hepatitis C. Gut 60(10):1394–1402
Murovets VO, Bachmanov AA, Zolotarev VA (2015) Impaired glucose metabolism in mice lacking the Tas1r3 taste receptor gene. PLoS One 10(6):e0130997
Nakagawa Y, Nagasawa M, Yamada S, Hara A, Mogami H, Nikolaev VO, Lohse MJ, Shigemura N, Ninomiya Y, Kojima I (2009) Sweet taste receptor expressed in pancreatic beta-cells activates the calcium and cyclic AMP signaling systems and stimulates insulin secretion. PLoS One 4(4):e5106
Nelson G, Chandrashekar J, Hoon MA, Feng L, Zhao G, Ryba NJP, Zuker CS (2002) An amino-acid taste receptor. Nature 416(6877):199–202
Peterson TR, Sengupta SS, Harris TE, Carmack AE, Kang SA, Balderas E, Guertin DA, Madden KL, Carpenter AE, Finck BN, Sabatini DM (2011) mTOR complex 1 regulates lipin 1 localization to control the SREBP pathway. Cell 146(3):408–420
Postic C, Girard J (2008) Contribution of de novo fatty acid synthesis to hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance: lessons from genetically engineered mice. J Clin Invest 118(3):829–838
Raka F, Farr S, Kelly J, Stoianov A, Adeli K (2019) Metabolic control via nutrient-sensing mechanisms: role of taste receptors and the gut-brain neuroendocrine axis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 317(4):E559–e572
Schierwagen R, Maybüchen L, Zimmer S, Hittatiya K, Bäck C, Klein S, Uschner FE, Reul W, Boor P, Nickenig G, Strassburg CP, Trautwein C, Plat J, Lütjohann D, Sauerbruch T, Tacke F, Trebicka J (2015) Seven weeks of Western diet in apolipoprotein-E-deficient mice induce metabolic syndrome and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis with liver fibrosis. Sci Rep 5:12931
Shirazi-Beechey SP, Daly K, al-Rammahi M, Moran AW, Bravo D (2014) Role of nutrient-sensing taste 1 receptor (T1R) family members in gastrointestinal chemosensing. Br J Nutr 111(Suppl 1):S8–S15
Simon BR, Learman BS, Parlee SD, Scheller EL, Mori H, Cawthorn WP, Ning X, Krishnan V, Ma YL, Tyrberg B, MacDougald OA (2014) Sweet taste receptor deficient mice have decreased adiposity and increased bone mass. PLoS One 9(1):e86454
Smith KR, Hussain T, Karimian Azari E, Steiner JL, Ayala JE, Pratley RE, Kyriazis GA (2016) Disruption of the sugar-sensing receptor T1R2 attenuates metabolic derangements associated with diet-induced obesity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 310(8):E688–e698
Taniguchi K (2004) Expression of the sweet receptor protein, T1R3, in the human liver and pancreas. J Vet Med Sci 66(11):1311–1314
Taya K, Hirose K, Hamada S (2009) Trehalose inhibits inflammatory cytokine production by protecting IkappaB-alpha reduction in mouse peritoneal macrophages. Arch Oral Biol 54(8):749–756
Toyoshima K, Seta Y, Toyono T, Kataoka S (2007) Immunohistochemical identification of cells expressing steroidogenic enzymes cytochrome P450scc and P450 aromatase in taste buds of rat circumvallate papillae. Arch Histol Cytol 70(4):215–224
VanderLaan PA, Reardon CA, Getz GS (2004) Site specificity of atherosclerosis: site-selective responses to atherosclerotic modulators. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 24(1):12–22
Wang Y, Liu JQ, Wu H, Fang XT, Chen H, Zhang CL (2017) Amino acids regulate mTOR pathway and milk protein synthesis in a mouse mammary epithelial cell line is partly mediated by T1R1/T1R3. Eur J Nutr 56(8):2467–2474
Wauson EM, Zaganjor E, Lee AY, Guerra ML, Ghosh AB, Bookout AL, Chambers CP, Jivan A, McGlynn K, Hutchison MR, Deberardinis RJ, Cobb MH (2012) The G protein-coupled taste receptor T1R1/T1R3 regulates mTORC1 and autophagy. Mol Cell 47(6):851–862
Wilson CG, Tran JL, Erion DM, Vera NB, Febbraio M, Weiss EJ (2016) Hepatocyte-specific disruption of CD36 attenuates fatty liver and improves insulin sensitivity in HFD-fed mice. Endocrinology 157(2):570–585
Yu J, Henske EP (2006) Estrogen-induced activation of mammalian target of rapamycin is mediated via tuberin and the small GTPase Ras homologue enriched in brain. Cancer Res 66(19):9461–9466
Zhao GQ, Zhang Y, Hoon MA, Chandrashekar J, Erlenbach I, Ryba NJP, Zuker CS (2003) The receptors for mammalian sweet and umami taste. Cell 115(3):255–266
Zhou Y, Ren J, Song T, Peng J, Wei H (2016) Methionine regulates mTORC1 via the T1R1/T1R3-PLCbeta-Ca(2+)-ERK1/2 signal transduction process in C2C12 cells. Int J Mol Sci 17(10):1684
Funding
This work was supported by Grant 15SDG25090279 from the American Heart Association (to E.M.W.) and the Iowa Osteopathic Education and Research Foundation (to E.M.W.)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Research involving animals
All animal procedures were approved by and performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the Des Moines University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC).
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shojaat, S.S., Engman, S., Hofferber, J. et al. Loss of the nutrient receptor Tas1R3 reduces atherosclerotic plaque accumulation and hepatic steatosis in ApoE−/− mice. J Physiol Biochem 76, 623–636 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-020-00768-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-020-00768-8