Abstract
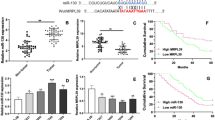
Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is one of the most aggressive and lethal malignancies. Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are being found to play crucial roles in CCA progression. This work aims to investigate the roles of long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 667 (LINC00667) in progression of CCA. RT-qPCR and western blot were applied to detect gene expression. Clinical correlation and survival were analyzed by statistical methods. Overexpression and RNA interference approaches were used to investigate the effects of LINC00667 on CCA cells. Tumor xenograft assay was performed to detect the function of LINC00667 in vivo. Transcriptional regulation and competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) mechanism were predicted via bioinformatics analysis. ChIP, luciferase reporter, and Ago2 RIP assays further confirmed the predicted results. Our data indicated that LINC00667 was highly expressed in CCA tissues and cells, and transcription factor Yin Yang 1 (YY1) induced LINC00667 expression in CCA cells. Up-regulated LINC00667 was significantly associated with lymph node metastasis, advanced TNM stage, and poor prognosis. Knockdown of LINC00667 suppressed the proliferation, migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of CCA cells, while overexpression of LINC00667 acquired opposite effects. Moreover, knockdown of LINC00667 inhibited tumor growth in vivo. In addition, LINC00667 was demonstrated to function as a ceRNA for miR-200c-3p, and then LINC00667 up-regulated pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 (PDK1) to promote CCA development by inhibiting miR-200c-3p. These findings identified a pivotal role of LINC00667 in tumorigenesis and development of CCA. Targeting the YY1/LINC00667/miR-200c-3p/PDK1 axis may provide a new therapeutic strategy for CCA treatment.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Razumilava N, Gores GJ. Cholangiocarcinoma. Lancet. 2014;383(9935):2168–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61903-0.
Hoyos S, Navas MC, Restrepo JC, Botero RC. Current controversies in cholangiocarcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018;1864(4 Pt B):1461–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.07.027.
Wang L, Cao L, Wen C, Li J, Yu G, Liu C. LncRNA LINC00857 regulates lung adenocarcinoma progression, apoptosis and glycolysis by targeting miR-1179/SPAG5 axis. Hum Cell. 2020;33(1):195–204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-019-00296-8.
Molist C, Navarro N, Giralt I, et al. miRNA-7 and miRNA-324-5p regulate alpha9-Integrin expression and exert anti-oncogenic effects in rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Lett. 2020;477:49–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2020.02.035.
Li J, Huang L, Li Z, et al. Functions and roles of long noncoding RNA in cholangiocarcinoma. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(10):17113–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28470.
Ma Q, Qi X, Lin X, Li L, Chen L, Hu W. LncRNA SNHG3 promotes cell proliferation and invasion through the miR-384/hepatoma-derived growth factor axis in breast cancer. Hum Cell. 2020;33(1):232–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-019-00287-9.
Chen W, Zhou ZQ, Ren YQ, et al. Effects of long non-coding RNA LINC00667 on renal tubular epithelial cell proliferation, apoptosis and renal fibrosis via the miR-19b-3p/LINC00667/CTGF signaling pathway in chronic renal failure. Cell Signal. 2019;54:102–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2018.10.016.
Wang D, Zheng J, Liu X, et al. Knockdown of USF1 inhibits the vasculogenic mimicry of glioma cells via stimulating SNHG16/miR-212-3p and linc00667/miR-429 axis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019;14:465–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2018.12.017.
Yang Y, Li S, Cao J, Li Y, Hu H, Wu Z. RRM2 regulated by LINC00667/miR-143-3p signal is responsible for non-small cell lung cancer cell progression. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:9927–39. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S221339.
Liu P, Chen S, Huang Y, et al. LINC00667 promotes Wilms’ tumor metastasis and stemness by sponging miR-200b/c/429 family to regulate IKK-β. Cell Biol Int. 2020;44(6):1382–93. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.11334.
Jiang Y, Yang Y, Wang H, Darko GM, Sun D, Gao Y. Identification of miR-200c-3p as a major regulator of SaoS2 cells activation induced by fluoride. Chemosphere. 2018;199:694–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.01.095.
Maolakuerban N, Azhati B, Tusong H, Abula A, Yasheng A, Xireyazidan A. MiR-200c-3p inhibits cell migration and invasion of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via regulating SLC6A1. Cancer Biol Ther. 2018;19(4):282–91. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2017.1394551.
Danarto R, Astuti I, Umbas R, Haryana SM. Urine miR-21-5p and miR-200c-3p as potential non-invasive biomarkers in patients with prostate cancer. Turk J Urol. 2019;46(1):26–30. https://doi.org/10.5152/tud.2019.19163.
Dupuy F, Tabariès S, Andrzejewski S, et al. PDK1-dependent metabolic reprogramming dictates metastatic potential in breast cancer. Cell Metab. 2015;22(4):577–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2015.08.007.
Siu MKY, Jiang YX, Wang JJ, et al. PDK1 promotes ovarian cancer metastasis by modulating tumor-mesothelial adhesion, invasion, and angiogenesis via α5β1 integrin and JNK/IL-8 signaling. Oncogenesis. 2020;9(2):24. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41389-020-0209-0.
Hsu JY, Chang JY, Chang KY, Chang WC, Chen BK. Epidermal growth factor-induced pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 expression enhances head and neck squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via up-regulation of fibronectin. FASEB J. 2017;31(10):4265–76. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201700156R.
Chen X, Zeng K, Xu M, et al. SP1-induced lncRNA-ZFAS1 contributes to colorectal cancer progression via the miR-150-5p/VEGFA axis. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(10):982. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0962-6.
Li J, Jiang X, Li C, et al. LncRNA-MEG3 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion by modulating Bmi1/RNF2 in cholangiocarcinoma. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(12):22947–59. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28856.
Shen Y, Xu J, Pan X, et al. LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 sponges miR-34c-5p to promote osteosarcoma growth via ALDOA enhanced aerobic glycolysis. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(4):278. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2485-1.
Wu M, Huang Y, Chen T, et al. LncRNA MEG3 inhibits the progression of prostate cancer by modulating miR-9-5p/QKI-5 axis. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(1):29–38. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13658.
Bai J, Xu J, Zhao J, Zhang R. LncRNA NBR2 suppresses migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by downregulating miRNA-21. Hum Cell. 2020;33(1):98–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-019-00265-1.
Shen S, Li K, Liu Y, et al. Silencing lncRNA AGAP2-AS1 upregulates miR-195-5p to repress migration and invasion of EC cells via the decrease of FOSL1 expression. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;20:331–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2019.12.036.
Shen Y, Gao X, Tan W, Xu T. STAT1-mediated upregulation of lncRNA LINC00174 functions a ceRNA for miR-1910-3p to facilitate colorectal carcinoma progression through regulation of TAZ. Gene. 2018;666:64–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.05.001.
Yang F, Shen Y, Zhang W, et al. An androgen receptor negatively induced long non-coding RNA ARNILA binding to miR-204 promotes the invasion and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25(12):2209–20. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-018-0123-6.
Li C, Liu H, Yang J, et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC00511 induced by SP1 accelerates the glioma progression through targeting miR-124-3p/CCND2 axis. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(6):4386–94. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14331.
Tang W, Zhou W, Xiang L, et al. The p300/YY1/miR-500a-5p/HDAC2 signalling axis regulates cell proliferation in human colorectal cancer. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):663. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-08225-3.
Qiao K, Ning S, Wan L, et al. LINC00673 is activated by YY1 and promotes the proliferation of breast cancer cells via the miR-515-5p/MARK4/Hippo signaling pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38(1):418. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1421-7.
Li P, Zhou B, Lv Y, Qian Q. LncRNA HEIH regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis through miR-4458/SOCS1 axis in triple-negative breast cancer. Hum Cell. 2019;32(4):522–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-019-00273-1.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81602088).
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81602088).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL: conceptualization; JL and XJ: experimental design and execution; ZH and LL: data curation and analysis; YC: experimental resources; CG and ZS: writing-original draft; PK: writing-review and editing; YC: supervision. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Ethics Committee of The 2nd Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University (KY2018-301), and patient consent was acquired prior to the initiation of experiment. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Animal Care and Use Committee of The 2nd Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University (SYDW2018-114).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Guan, C., Hu, Z. et al. Yin Yang 1-induced LINC00667 up-regulates pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 to promote proliferation, migration and invasion of cholangiocarcinoma cells by sponging miR-200c-3p. Human Cell 34, 187–200 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-020-00448-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-020-00448-1