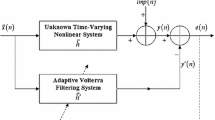
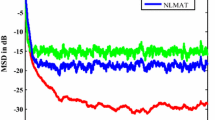
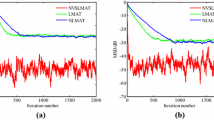
Abstract
Partial-update (PU) algorithms offer reduced computational complexity to adaptive second-order Volterra filters (SOV) in nonlinear systems while retaining acceptable performance. In this paper, a new selective partial-update technique for the normalized LMS (NLMS) SOV algorithm is proposed, which requires lesser number of comparison operations per iteration than existing methods while providing close performance to the standard M-Max NLMS-SOV algorithm. Convergence properties of the proposed algorithm are enhanced by making the algorithm step-size time varying based on the natural logarithm function. Simulation experiments compare the proposed algorithm with existing PU and variable step-size NLMS-SOV algorithms, which illustrate the advantageous properties of the new algorithm. The proposed algorithm achieves both lower steady-state misalignment and faster convergence speed when compared with the fixed step-size full-update NLMS-SOV algorithm. Simulations also show that comparison operations overhead of the proposed algorithm is reduced significantly compared to that of the standard M-Max NLMS-SOV algorithm.

























Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.S.E. Abadi, M.S. Shafiee, M. Zalaghi, A low computational complexity normalized subband adaptive filter algorithm employing signed regressor of input signal. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2018(21), 1–23 (2018)
T. Aboulnasr, K. Mayyas, Complexity reduction of the NLMS algorithm via selective coefficient update. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 47(5), 1421–1424 (1999)
T. Aboulnasr, K. Mayyas, A robust variable step-size LMS-type algorithm: analysis and simulations. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 45(3), 631–639 (1997)
T. Aboulnasr, Q. Pan, Data-dependent partial update adaptive algorithms for linear and nonlinear systems, in Signal Processing Conference 2005 13th European, pp. 1–4 (2005)
M.T. Akhtar, M. Abe, M. Kawamata, A new variable step-size LMS algorithm-based method for improved online secondary path modeling in active noise control systems. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 14(2), 720–726 (2006)
M.O. Bin Saeed, A. Zerguin, An Incremental Variable Step-size LMS Algorithm for Adaptive Networks (Circuits Syst. II Expr. Briefs, IEEE Trans, 2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSII.2019.2953199
D. Bismor, Simulations of partial update LMS algorithms in application to active noise control. Proc. Comput. Sci. 80, 1180–1190 (2016)
C. Contan, B.S. Kirei, M.D. Topa, Error-dependent step-size control of adaptive normalized least-mean-square filters used for nonlinear acoustic echo cancellation. SIViP 10(3), 511–518 (2016)
C. Contan, M. Zeller, W. Kellermann, M. Topa, Excitation-dependent step-size control of adaptive Volterra filters for acoustic echo cancellation, in Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), pp. 604–608 (2012)
P.S. Diniz, On data-selective adaptive filtering. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 66(16), 4239–4252 (2018)
P. Diniz, Adaptive Filtering Algorithms and Practical Implementation (Springer, Berlin, 2008)
S.C. Douglas, Analysis and implementation of the Max-NLMS adaptive filter. ASIMOLAR Conf. 1, 6591–6663 (1996)
K. Dogancay, Partial-Update Adaptive Signal Processing: Design Analysis and Implementation (Academic Press, London, 2008)
T. Fan, Y. Lin, A variable step-size strategy based on error function for sparse system identification. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 36(3), 1301–1310 (2017)
B. Farhang, Variable-step-size LMS algorithm: new developments and experiments. IEE Proc. Vis. Image Signal Process. 141(5), 311–317 (1994)
M. Godavarti, A.O. Hero, Partial update LMS algorithms. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 53(7), 2382–2399 (2005)
A. Guérin, G. Faucon, R. Le Bouquin-Jeannès, Nonlinear acoustic echo cancellation based on Volterra filters. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 11(6), 672–683 (2003)
S. Haykin, Adaptive Filter Theory (Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, 1996)
T. Jingfan, O. Jingzheng, A new variable step-size LMS adaptive filtering algorithm. J. Data Aequ. Process. 12(3), 171–194 (1997)
Z. Jingjing, Variable step-size LMS algorithm. Int. J. Fut. Comput. Commun. 1(4), 389–391 (2012)
S.M. Kuo, H.T. Wu, Nonlinear adaptive bilinear filters for active noise control systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 52(3), 617–624 (2005)
R.H. Kwong, E.W. Johnston, A variable Step-Size LMS algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 40(6), 864–872 (1992)
J.F. Liu, Z.Q. Jiang, X.X. Li, X. Huo, A novel variable step-size LMS adaptive filtering algorithm based on Lorentzian function. Command Control Simul. 31(2), 42–44 (2009)
Sh Liu, Y. Ma, Y. Huang, Sea clutter cancellation for passive radar sensor exploiting multi-channel adaptive filters. IEEE Sens. J. 19(3), 982–995 (2019)
Y. Ma, T. Shan, J. Lu, A multi-channel partial-update algorithm for sea clutter suppression in passive bistatic radar, in IEEE 10th Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop (SAM), pp. 252–256 (2018)
T. Ogunfunmi, Adaptive Nonlinear System Identification: The Volterra and Wiener Model Approaches (Springer, Berlin, 2007)
C. Paleologu, J. Benesty, S. L. Grant, C. Osterwise, Variable step-size NLMS algorithms designed for echo cancellation, in Signals, Systems and Computers 2009 Conference Record of the Forty-Third Asilomar Conference, pp. 633–637 (2009)
I. Pitas, Fast algorithms for running ordering and max/min calculation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 36(6), 795–804 (1989)
A. Rai, A.K. Kohli, Volterra filtering scheme using generalized variable step-size NLMS algorithm for nonlinear acoustic echo cancellation. Acta Acust. United Acust. 101(4), 821–828 (2015)
A. Rai, A.K. Kohli, Adaptive polynomial filtering using generalized variable step-size least mean pth power (LMP) algorithm. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 33(12), 3931–3947 (2014)
A.J. Redfern, G.T. Zhou, A root method for Volterra system equalization. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 5(11), 285–288 (1998)
J.B. Seo, J.H. Kim, T.H. Jung, S.W. Nam, S.W., Nonlinear acoustic echo cancellation using Volterra filtering with a modified VSS-GSPAP algorithm, in 13th International Conference on Electronics Information, and Communication (ICEIC) (2014)
T. Shan, Y. Ma, R. Tao, Sh Liu, Multi-channel NLMS-based sea clutter cancellation in passive bistatic radar. IEICE Electr. Expr. 11(20), 20140872 (2014)
K. Shi, X. Ma, T. Zhou, An efficient acoustic echo cancellation design for systems with long room impulses and nonlinear loudspeakers’. Sig. Process. 89(2), 121–132 (2009)
L. Shi, H. Zhao, H. Zeng, Y. Yu, Variable step-size widely linear complex-valued NLMS algorithm and its performance analysis. Sig. Process. 165(12), 1–6 (2019)
G.L. Sicuranza, A. Carini, Nonlinear multichannel active noise control using partial updates [acoustic noise control], in Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP’05), iii-109 (2005)
L. Tan, J. Jiang, Adaptive second-order Volterra filtered-X RLS algorithms with sequential and partial updates for nonlinear active noise control, in Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), pp. 1625–1630 (2009)
P. Wen, J. Zhang, Variable step-size diffusion normalized sign-error algorithm. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 37(11), 4993–5004 (2018)
D. Zhou, V. DeBrunner, Efficient adaptive nonlinear filters for nonlinear active noise control. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 54(3), 669–681 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mayyas, K., Afeef, L. A Variable Step-Size Partial-Update Normalized Least Mean Square Algorithm for Second-Order Adaptive Volterra Filters. Circuits Syst Signal Process 39, 6073–6097 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-020-01446-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-020-01446-2