Abstract
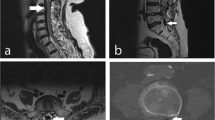
Post-operative vision loss (POVL) can be a devastating complication of neurosurgical procedures and is unusual in the pediatric population. Mechanisms of POVL include direct optic nerve injury, vascular occlusion, or indirect malperfusion resultant from surgeries with substantial blood loss or fluid shifts, with prone positioning being a major risk factor for these events. Posterior ischemic optic neuropathy (PION) is a rare cause of POVL and is associated with a poor prognosis for recovery of visual function. We present a case of PION following a supine bifrontal craniotomy for a frontal epidural abscess secondary to pan-sinusitis in a pediatric patient. This is an unusual reported case in that no additional traditional risk factors were identified. We present clinical and radiographic findings, diagnostic considerations, treatment strategies, and a literature review. The patient was managed medically and recovered substantial vision in the affected eye.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wittenborn JS, Zhang X, Feagan CW, Crouse WL, Shrestha S, Kemper AR, Hoerger TJ, Saaddine JB (2013) The economic burden of vision loss and eye disorders among the United States population younger than 40 years. Ophthalmology 120(9):1728–1735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2013.01.068
Takahashi Y, Kakizaki H, Selva D, Leibovitch I (2010) Bilateral orbital compartment syndrome and blindness after cerebral aneurysm repair surgery. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 26(4):299–301. https://doi.org/10.1097/IOP.0b013e3181c062ca
Habets JGV, Haeren RHL, Lie SAN, Bauer NJC, Dings JTA (2018) Acute monocular blindness due to orbital compartment syndrome following pterional craniotomy. World Neurosurg 114:72–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.03.013
Desai SJ, Lawton MT, McDermott MW, Horton JC (2015) Vertical diplopia and ptosis from removal of the orbital roof in pterional craniotomy. Ophthalmology. 122(3):631–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2014.09.011
Patel RS, Yousem DM, Maldjian JA, Zager EL (2000) Incidence and clinical significance of frontal sinus or orbital entry during pterional (frontotemporal) craniotomy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21(7):1327–1330
Lima V, Burt B, Leibovitch I, Prabhakaran V, Goldberg RA, Selva D (2009) Orbital compartment syndrome: the ophthalmic surgical emergency. Surv Ophthalmol 54(4):441–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.survophthal.2009.04.005
Mukherjee S, Thakur B, Tolias C (2016) Sudden-onset monocular blindness following orbito-zygomatic craniotomy for a ruptured intracranial aneurysm. BMJ Case Rep 2016:bcr2014208393. Published 2016 Oct 19. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2014-208393
Kang S, Yang Y, Kim T, Kim J (1997) Sudden unilateral blindness after intracranial aneurysm surgery. Acta Neurochir 139(3):221–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01844755
Mac Grory B, Lavin P, Kirshner H, Schrag M (2020) Thrombolytic therapy for acute central retinal artery occlusion. Stroke. 51(2):687–695. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.027478
Biousse V, Newman NJ (2015) Ischemic optic neuropathies. N Engl J Med 372(25):2428–2436. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1413352
Kim JW, Hills WL, Rizzo JF, Egan RA, Lessell S (2006) Ischemic optic neuropathy following spine surgery in a 16-year-old patient and a ten-year-old patient. J Neuroophthalmol 26(1):30–33. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.wno.0000205980.32023.2d
Shifa J, Abebe W, Bekele N, Habte D (2016) A case of bilateral visual loss after spinal cord surgery. Pan Afr Med J 23:119. https://doi.org/10.11604/pamj.2016.23.119.8443
Lee J, Crawford MW, Drake J, Buncic JR, Forrest C (2005) Anterior ischemic optic neuropathy complicating cranial vault reconstruction for sagittal synostosis in a child. J Craniofac Surg 16(4):559–562. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.scs.0000164331.73805.66
Qingli L, Orcutt JC, Seifter LS (1989) Orbital mucormycosis with retinal and ciliary artery occlusions. Br J Ophthalmol 73(8):680–683. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjo.73.8.680
Sang MN, Jong WM, Sang YL, Jung BC (2006) Acute optic neuropathy resulting from frontal mucocele with vision recovery after endoscopic sinus surgery. Neuro-Ophthalmology 30(1):29–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/01658100600599550
Mazzurco M, Pavone P, Di Luca M, Smilari P, Pustorino E, Fiumara A, Di Mauro P, Greco F, Cocuzza S (2019) Optic neuropathy, secondary to ethmoiditis, and Onodi cell inflammation during childhood: a case report and review of the literature. Neuropediatrics 50(6):341–345. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0039-1693156
Aldrees SS, Micieli JA (2020) Rapidly sequential vision from loss posterior ischemic optic neuropathy due to methicillin-susceptible staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. J Neuroophthalmol, Publish Ah. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNO.0000000000000850
Quddus A, Lawlor M, Siddiqui A, Holmes P, Plant GT (2015) Using diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging to confirm a diagnosis of posterior ischaemic optic neuropathy: two case reports and literature review. Neuroophthalmology 39(4):161–165. Published 2015 Jun 23. https://doi.org/10.3109/01658107.2015.1021054
Purvin V, Kuzma B (2005) Intraorbital optic nerve signal hyperintensity on magnetic resonance imaging sequences in perioperative hypotensive ischemic optic neuropathy. J Neuroophthalmol 25(3):202–204. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.wno.0000177295.52468.5b
Harrar DB, Solomon J, Shah AS, Vaughn J, Durbin AD, Rivkin MJ (2018) Diffusion-weighted imaging changes in a child with posterior ischemic optic neuropathy. Pediatr Neurol 84:49–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2018.03.014
Leung V, Shemesh AA, Al Shafai L, Krings T, Valiante T, Margolin E (2019) Severe intraoperative orbital venous congestion during resection of a frontal meningioma presenting with post-operative vision loss and ophthalmoplegia: a case report. Neuro-Ophthalmology 43(4):265–268. https://doi.org/10.1080/01658107.2018.1527856
Fandino W (2017) Strategies to prevent ischemic optic neuropathy following major spine surgery: a narrative review. J Clin Anesth 43:50–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinane.2017.09.009
Liu GT, Phillips PC, Molloy PT, Needle MN, Galetta SL, Balcer LJ, Schut L, Duhaime A-C, Sutton LN (1998) Visual impairment associated with mutism after posterior Fossa surgery in children. Neurosurgery 42(2):253–256. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-199802000-00027
Eli IM, Kim RB, Kilburg C, Pecha TJ, Couldwell WT, Menacho ST (2018) Postoperative posterior ischemic optic neuropathy after left far-lateral craniectomy for resection of craniocervical meningioma. World Neurosurg 114:339–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.03.204
Vahedi P, Meshkini A, Mohajernezhadfard Z, Tubbs RS (2013) Post-craniotomy blindness in the supine position: unlikely or ignored? Asian J Neurosurg 8(1):36–41. https://doi.org/10.4103/1793-5482.110278
Beck RW, Greenberg HS (1985) Post-decompression optic neuropathy. J Neurosurg 63(2):196–199. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1985.63.2.0196
Boström J, Janssen G, Messing-Jünger M et al (2000) Multiple intracranial juvenile xanthogranulomas. Case report. J Neurosurg 93(2):335–341. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2000.93.2.0335
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Consent to publish
Legal guardians signed informed consent regarding publishing the data and photographs.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oliver, J.D., Kobets, A.J., Judy, B.F. et al. Posterior ischemic optic neuropathy following supine craniotomy for epidural abscess in a child. Childs Nerv Syst 37, 2657–2660 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-020-04921-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-020-04921-y