Abstract
The study investigates the origin, age, paleo-depositional environment and formation conditions of gypsum lithofacies deposited in northeastern Muş in Eastern Anatolia using element analysis and sulfur, oxygen and strontium isotope combinations. The correlation diagrams of major ions and trace elements plots in the gypsum lithofacies indicate that carbonates and clastics carried by terrestrial waters (streams, rivers, etc.) significantly contributed to the evaporitic phases. Furthermore, the effects of hydrothermal solutions, increased salinity of the basin and presence of biological activity were associated with high values for major ions and trace elements. While the δ18O and δ34S isotope contents of some gypsum lithofacies samples show that they are of terrestrial or marine origin, others do not indicate either origin because they are affected by other factors such as water salinity variations, bacterial sulfate reduction, new terrestrial water and detrital inputs carried into the basin. However, 87Sr/86Sr isotope concentrations analyzed in gypsum lithofacies in the study area indicate Rupelian (Lower Oligocene) time, which is compatible with the Cenozoic age curve. Based on all these data, gypsum lithofacies in this basin were deposited in a transition zone (shallow sea-lagoon-inland sabkha-mudflats) under the influence of both marine and terrestrial conditions. Therefore, we claim that this basin formed during the Rupelian (Early Oligocene), at a time when the sea connection between the Indian Ocean and the eastern Mediterranean was restricted; that is, the southern branch of the Neotethys was extremely shallow during this period and almost terminated in the study area.

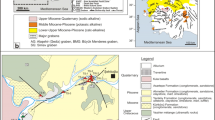
(modified from Güngör Yeşilova 2019)


(modified from Güngör Yeşilova 2019)





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdioğlu Yazar E, Arslan M, Helvacı C, Gündoğan İ, Temizel İ, Aydınçakır D (2020) Geochemistry of Miocene evaporites from the Aşkale region (Erzurum, Eastern Turkey): constraints forpaleo-environment. Bull Min Res Exp. https://doi.org/10.19111/bulletinofmre.772360
Açlan M, Altun Y (2018) Syn-collisional I-type Esenköy Pluton (Eastern Anatolia-Turkey): an indication for collision between Arabian and Eurasian plates. J African Ear Sci 142:1–11
Adamia S, Zakariadze G, Chkhotua T, Sadradze N, Tsereteli N, Chabukiani A, Gventsadze A (2011) Geology of the Caucasus: a review. Turkish J Earth Sci 20:489–544
Akay E, Bıkan E, Ünay E (1989) Muş Tersiyer havzasının stratigrafisi. MTA Der 109:59–76 (in Turkish)
Ala-aho P, Soulsby C, Pokrovsky OS, Kirpotin SN, Karlsson J, Serikova S, Vorobyev SN, Manasypov RM, Loiko S, Tetzlaff D (2018) Using stable isotopes to assess surface water source dynamics and hydrological connectivity in a high-latitude wetland and permafrost influenced landscape. J Hydrol 556:279–293
Allen AS (1969) Geologic settings of subsidence. Rev Eng Geol 2:305–342
Alsharhan AS, Nairn AEM (2003) Sedimentary basins and petroleum geology of the Middle East. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Altay T, Karakaya MÇ, Erkan Y (2007) Formation condition and properties of the various types of gypsum occurrences at Sivrihisar (Eskişehir, Turkey). J Fac Eng Arch Selçuk Univ 23:1–2
Amdouni R (2009) Behaviour of trace elements during the natural evaporation of sea water: Case of solar salt works of Sfax saline (S.E of Tunisia). Glo Nest J 11:96–105
Andreeva P (2010) Early diagenetic structures in Middle Devonian (Givetian) sabkha evaporites from the Moesian Platform (Northeastern Bulgaria). Geosciences 1113:89–90
Aref MAM, Attia OEA, Wali AMA (1997) Facies and depositional environment of the Holocene evaporites in the Ras Shukeir area, Gulf of Suez Egypt. Sed Geol 110:123–145
Arpat E, Şaroğlu F (1972) Doğu Anadolu fayı ile ilgili bazı gözlemler ve düşünceler. MTA Der 78:44–50 (in Turkish)
Averty KB, Paytan A (2003) Empirical partition coefficients for Sr and Ca in marine barite: implications for reconstructing seawater Sr and Ca concentrations. Geochem Geophy Geosys 4:1–14
Baertschi P (1976) Absolute 18O content of Standard Mean Ocean Water. Eart Planet Sci Let 31:341
Barkov NI, Nikolaev VI, Strizhov VP (1995) On the genesis of mirabilite in the McMurdo Sound region. Antarctica Lit Min Res 30:374–379
Batı Z, Sancay RH (2007) Palynostratigraphy of Rupelian sediments in the Mus Basin, Eastern Anatolia, Turkey. Micropaleontology 53:249–283
Böttcher ME, Brumsack HJ, De Lange GJ (1998) Sulfate reduction and related stable isotope (34S, 18O) variations in interstitial waters from the Eastern Mediterranean; In: Robertson AHF, Emeis KC, Richter Camerlenghi A (eds) Proceedings of Ocean Drilling Program Scientific Results. Collage Station, Germany, pp 365–373
Böttcher ME, Brumsack HJ, Dürselen CD (2007) The isotopic composition of modern seawater sulfate: I. Coastal waters with special regard to the North Sea. J Marine Sys 67:73–82
Bouroullec J (1979) Etude sequentielle du toit de la serie evaporitique du Lias inferiur dans un puits du bassin Aquitain, France du sud-Quest. Dans: “Depots evaporitiques”. Edit Techn 86:29–31 (in French)
Bozkurt E (2001) Neotectonics of Turkey—a synthesis. Geodin Acta 14(1–3):3–30
Butler GP (1969) Modern evaporite deposition and geochemistry of coexisting brines, the Sabkha, Trucial Coast, Arabian Gulf. J Sed Pet 39:70–89
Cendon DI, Peryt TM, Ayora C, Pueyo JJ, Taberner C (2004) The importance of recycling processes in the Middle Miocene Badenian evaporite basin (Carpathian foredeep), Palaeoenvironmental implications. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 212:141–158
Claypool GE, Holser WT, Kaplan YR, Sakai H, Zak I (1980) The age of sulpfur and oxygen isotopes in marine sulfate and their mutual interpretation. Chem Geo 28:199–260
Cody RD (1979) Lenticular gypsum: occurrences in nature, and experimental determinations of effects of soluble green plant material on its formation. J Sed Pet 49:1015–1028
Craig H (1966) Isotopic composition and origin of the Red Sea and Salton Sea geothermal brines. Science 154:1544–1548
DePaolo DJ, Ingram BL (1985) High-resolution stratigraphy with strontium isotopes. Science 227:938–941
Dewey JF, Hempton MR, Kidd WSF, Şaroğlu F, Şengör AMC (1986) Shortening of continental lithosphere: the neotectonics of Eastern Anatoliada young collision zone. In: Coward MP, Riea AC (eds) Collision tectonics. Geological Society of London Special Publication, London, pp 3–36
Eckardt FD, Spiro B (1999) The origin of sulphur in gypsum and dissolved sulphate in the Central Namib Desert. Namibia Sed Geo 123:255–273
Fontes JC, Letolle R, Nesteroff WD, Ryan WDF (1973) Oxygen, carbon, sulfur and hydrogen stables isotopes in carbonate and sulfate mineral phases of Neogene evaporites sediments and in interstitial waters. Init Rep Deep Sea Drill Proj 13:788–796
Gaillardet J, Millot R, Dupréi B (2003) Chemical denudation rates of the Western Canadian orogenic belt: the Stikine terrane. Chem Geol 201:257–279
García-Veigas J, Cendon DI, Rosell L, Orti F, Torres-Ruiz J, Martin JM, Sanz E (2013) Salt deposition and brine evolution in the Granada Basin (Late Tortonian, SE Spain). Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 369:452–465
García-Veigas J, Rosell L, Cendon DI, Gibert L, Martín JM, Torres-Ruiz J, Orti F (2015) Large celestine orebodies formed by early-diagenetic replacement of gypsified stromatolites (Upper Miocene, Montevive-Escúzar deposit, Granada Basin, Spain). Ore Geol Rev 64:187–199
Garcia-Veigas J, Cendon DI, Gibert L, Lowenstein TK, Artiga A (2018) Geochemical indicators in Western Mediterranean Messinian evaporites: implications for the salinity crisis. Marine Geol 403:197–214
Göncüoğlu C, Turhan N (1984) Geology of the Bitlis Metamorfic Belt. In: Tekeli O, Göncüoğlu MC (eds) Geology of the Taurus Belt. MTA, Ankara, pp 237–244
Güngör Yeşilova P (2019) Diagenetic history and petrographic-mineralogical examination of the Tertiary evaporites in the Bulanık (Muş). Bull Min Res Exp. https://doi.org/10.19111/bulletinofmre.569619
Güngör Yeşilova P, Helvacı C (2017) Petrographic study and geochemical investigation of the evaporites associated with the Germik Formation (Siirt Basin, Turkey). 32:177–194
Guo P, Chiyang L, Peng W, Ke W, Haili Y, Li B (2017) Geochemical behavior of rare elements in Paleogene saline lake sediments of the Qaidam Basin NE Tibetan Plateau. Carb Evap. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-017-0394
Gürer ÖF, Gürer A (1999) Development of evaporites and the counterclockwise rotation of Anatolia, Turkey. Int Geol Rev 41:607–622
Gürsoy H, Temiz H, Poisson AM (1992) Recent faulting in the Sivas area (Sivas Basin), Central Anatolia- Tükiye. Bull. Fac Eng Cumhuriyet Univ Ser A: Earth Sci 9:11–17
Hardie LA (1984) Evaporites: Marine or non-marine. Am J Sci 284:193–240
Herrero MJ, Marfil R, Escavy Climate JI, Scherer M, Arroyo X, Martín-Crespo T, López S (2019) Hydrothermal activity within a sedimentary succession: aragonites as indicators of Mesozoic Rifting (Iberian Basin Spain). Int Geo Rev. https://doi.org/10.1080/00206814.2019.1636317
Hüsing SK, Zachariasse WJ, Van Hinsbergen DJ, Krijgsman W, Inceöz M, Harzhauser M, Mandic O, Kroh A (2009) Oligocene Miocene basin evolution in SE Anatolia, Turkey: constraints on the closure of the eastern Tethys gateway. Geo Soc Lon Spec Pub 311:107–132
Hussain M, Warren JK (1989) Nodular and enterolithic gypsum; the “sabkha-tization” of Salt Flat Playa, West Texas. Sed Geol 64:13–24
Huvaz Ö (2009) Comparative petroleum systems analysis of the interior basins of Turkey: implications for petroleum potential. Marine Pet Geo 26:1656–1676
İlker S (1966) Erzurum-Muş bölgesinde Karaköse J 48 a4 ve J48 d1 paftalarının l:25 000 ölçekli detay petrol etüdü. MTA, Ankara
Karaoğlan F, Parlak O, Hejl E, Neubauer F, Klötzli U (2016) The temporal evolution of the active margin along the Sooutheast Anatolian orogenic belt (SE Turkey): evidence from U-PB, Ar-Ar and fission track chronology. Gond Res 33:190–208
Kasprzyk A (1994) Distribution of strontium in the Badenian (Middle Miocene) gypsum deposits of the Nida area, south Poland. Geol Quar 38:497–517
Kasprzyk A (1997) Oxygen and sulphur isotope composition of Badenian (Middle Miocene) gypsum deposits in southern Poland: a preliminary study. Geol Quar 41:53–60
Kasprzyk A (2005) Diagenetic alteration of Badenian sulphate deposits in the Carpathian Foredeep Basin, Southern Poland: Processes and their successionGeological Quarterly 49:305–316
Kaymakçı N, İnceöz M, Ertepınar P, Koç A (2010) Late Cretaceous to Recent kinematics of SE Anatolia (Turkey). Geol Soc 340:409–435
Kelling G, Gökçen SL, Floyd PA, Şengör N (1987) Neogene tectonics and plate convergence in the eastern Mediterranean: new data from southern Turkey. Geology 15:425–429
Kıral K, Çağlayan A (1980) Kağızman (Kars)-Ağrı-Taşlıçay (Ağrı) dolayının jeolojisi. MTA, Ankara
Köksal S, Göncüoğlu MC (2008) Sr and Nd Isotopic Characteristics of Some S-, I- and A-type Granitoids from Central Anatolia. Turk J Earth Sci 17:111–127
Krupka KM, Serne RJ (2002) Geochemical factors affecting thebehavior of antimony, cobalt, europium, technetium, and uranium in vadose sediments. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Washington
Kubica B (1992) Rozwo´j litofacjalny osado´w chemicznych badenu w po´łnocnej cze¸s´ci zapadliska przedkarpackiego. Panstwowy Instytut Geologiczny, Prace
Land LS (1983) Stable isotopes in sedimentary geology. Soc Eco Paleont Min Short Cour 10:1–151
Lloyd R (1968) Oxygen isotope behavior in the sulfate-water system. J Geophys Res 73:6099–6110
Longinelli A, Craig H (1967) Oxygen–18 variations in sulfate ions in sea-water and saline lakes. Science 156:56–59
Lu FH, Meyers WJ (2003) Sr, S and O (SO4) Isotopes and the depositional environments of the Upper Miocene evaporites Spain. J Sed Res 73:444–450
MacNamara J, Thode HG (1950) Comparison of the isotopic composition of terrestrial and meteoritic sulfur. Phys Rev 78:307–308
McArthur JM, Howarth RJ, Bailey TR (2001) Strontium isotope stratigraphy: Lowess version 3: best fit to the marine Sr-isotope curve for 0–509 Ma and accompanying look-up table for deriving numerical age. J Geol 109:155–170
McArthur JM, Howarth RJ, Shields GA (2012) Strontium isotope stratigraphy. In: Gradstein FM, Ogg JG, Schmotz MD, Ogg GM (eds) The geologic time scale. Elsevier Science Limited, Amsterdam, pp 127–144
McKenzie JA, Ricchiuto TE (1978) Stable isotopic investigation of carbonate samples related to the Messinian salinity crisis from DSDP Leg 42 A Mediterranean sea. Init Rep Deep Sea Drill Proj 42:650–655
McKibben MA, Eldridge CS (1989) Sulfur isotopic variations among minerals and aqueous species in the Salton Sea geothermal system; a SHRIMP ion microprobe and conventional study of active ore genesis in a sediment-hosted environment. Am J Sci J 1:1661–1707
Michard A, Whitechurch H, Ricou LE, Montigny R, Yazgan E (1984) Tauric subduction (Malatya-Elazığ provinces) and its bearing on tectonics of the Tethyan realm in Turkey. In: Dixon JE, Robertson AHF (eds) The geological evolution of the Eastern Mediterranean. Geological Society, London, pp 362–373
Miller KG, Wright JD, Katz ME, Wade BS, Browning JV, Cramer BS, Rosenthal Y (2009) Climate threshold at the Eocene-Oligocene transition: Antarctic ice sheet influence on ocean circulation. In: Koeberl C, Montanari A (eds) The Late Eocene Earth-hothouse, icehouse, and impacts. Geol Soc Amer Spec Pap, London, pp 169–178
Moores EM, Fairbridge RW (1997) Encyclopedia of European and Asian regional geology. Springer, Netherlands
Moragas M, Martínez C, Baqués V, Playa E, Trave A, Alias G, Cantarero I (2013) Diagenetic evolution of a fractured evaporite deposit (Vilobí Gypsum Unit, Miocene, NE Spain). Geofluids 13:180–193
Nesbitt HW, Young GM (1982) Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites. Nature 299:715–717
Nielsen H, Rambow D (1969) S-Isotopenuntersuchungen an sulfaten hessischer mineralwässer. Notizbl Hess Land Amt Boden 97:352–366 (in German)
Norrish K, Chappel BW (1977) X-ray fluorescence spectrometry. In: Zussman J (ed) Physical methods in determinative mineralogy. Academic Press, Londan, pp 201–272
Okay AI, Zattin M, Cavazza W (2010) Apatite fission-track data for the Miocene Arabiae Eurasia collision. Geology 38:35–38
Orti F, Rosell L (2000) Evaporite systems and diagenetic patterns in the Calatayud Basin (Miocene, central Spain). Sedimentology 47:665–685
Orti F, Rosell L, Utrilla R, Inglrs M, Pueyo JJ, Pierre C (1988) Reciclaje de las evaporitas en la Peninsula Ibrrica durante el Ciclo Alpino. Cong Geol Espafia 5:421–424 (in Spanish)
Orti F, Gündoğan İ, Helvacı C (2002) Sodium sulphate deposits of Neogene age: the Kirmir Formation, Beypazari Basin. Turkey Sed Geol 146:305–333
Ortí F, Rosell L, Anadón P (2010) Diagenetic gypsum related to sulfur deposits in evaporites (Libros Gypsum, Miocene, NE Spain). Sed Geol 228:304–331
Oyan V (2017) Petrogenesis and Ar-Ar dating of Early Miocene Mecitli granitoid in Eastern Anatolian Region, Turkey: evidence for lower crust-mantle interaction and fractionation from mmes to host rocks on the basis of petrological modelling. In: Azzam R (ed) Bulletin of engineering geology and the environment. Czech Republic, WMESS, pp 11–15
Palmer MR, Helvacı C, Fallick AE (2004) Sulphur, sulphate oxygen and strontium isotope composition of Cenozoic Turkish evaporites. Chem Geol 209:341–356
Paytan A, Kastner M, Campbell D, Thiemens MH (2004) Seawater sulfur isotope fluctuations in the Cretaceous. Science 304:1663–1665
Peryt TM, Orti F, Rosell L (1993) Sulfate platform-basin transition of the Lower Werra Anhydrite (Zechstein, Upper Per- mian), Western Poland: facies and petrography. J Sediment Petrol 63:646–658
Pierre C (1988) Applications ofstable isotope geochemistry to the study of evaporates. In: Schreiber BC (ed) Evaporites and hydrocarbons. Columbia University Press, New York, pp 300–344
Playa E, Rosell L (2005) The celestite problem in gypsum Sr geochemistry: an evaluation of the purifying methods of gypsiferous samples. Chem Geol 221:102–116
Playa E, Orti F, Rosell L (2000) Marine to non-marine sediementation in the upper Miocene evaporites of the Eastern Betics, SE Spain: sedimentological and geochemical evidences. Sed Geol 133:135–166
Robertson AHF, Clift PD, Degnan P, Jones G (1991) Palaeogeographic and palaeotectonic evolution of the Eastern Mediterranean Neotethys. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 87:289–343
Robertson AHF, Ustaömer T, Pıckett E, Collins A, Andrew T, Dıxon JE (2004) Testing models of Late Palaeozoic-Early Mesozoic orogeny in Western Turkey: support for an evolving open-Tethys model. J Geol Soc 161:501–511
Rögl F (1998) Palaeogographic considerations for Mediterranean and Paratethys seaways (Oligocene to Miocene). Ann Natur Mus Wien 99A:279–310
Rosell L, Orti F, Kasprzyk A, Playa E, Peryt TM (1998) Strontium geochemistry of primary gypsum: Messinian of southeastern Spain and Sicily and Badenian of Poland. J Sed Res 68:63–79
Rosen R, Warren JK (1990) The origin and significance of groundwater-seepage gypsum from Bristol Dry Lake California, USA. Sedimentology 37:3–9
Roy PD, Smykatz-Kloss W, Sinha R (2006) Late Holocene geochemical history inferred from Sambhar and Didwana playa sediments, Thar Desert, India: comparison and synthesis. Quat Int 144:84–98
Şahintürk Ö, Erdem K (2002) Muş baseni hidrokarbon potansiyeli hakkında rapor. TPAO, Ankara
Şahintürk Ö, Kasar S (1979) Tekman-Pasinler-Kağızman-Tuzluca basenlerinin stratigrafik ve tektonik analizleri ile hidrokarbon olanakları. TPAO, Ankara
Sakınç M (1982) Mollababa-Uruman (Muş İli) yöresinin jeolojisi biostratigrafisi ve paleontolojisi. Yerbilimleri 3:1–2 (in Turkish)
Salvany IM, Orti F (1997) Glauberite deposits of the Lerin formation (Lower Miocene: Alcanadre Zone, La Rioja Navarra). In: Busson G, Schreiber BC (eds) Sedimentary deposition in rift and foreland basins in France and Spain (Paleogene and Lower Neogene). Colombia University, New York, pp 412–419
Sancay RH (2005) Palynostratigraphic and palynofacies investigation of the Oligocene-Miocene units in the Kars-Erzurum-Muş subbasins (Eastern Anatolia). Dissertation, Middle East Technical University
Sancay RH, Batı Z, Işık U, Kırıcı S, Akça N (2006) Palynomorph, foraminifera, and calcareous nanoplankton biostratigraphy of Oligo-Miocene sediments in the Muş Basin, Eastern Anatolia. Turkey Turk J Earth Sci 15:259–319
Şaroğlu F (1986) Doğu Anadolu'nun neotektonik dönemde jeolojik ve yapısal evrimi. MTA, Ankara
Şaroğlu F, Güner Y (1981) Doğu Anadolu'nun jeomorfolojik gelişimine etki eden öğeler: jeomorfoloji, tektonik, volkanizma ilişkileri. Türkiye Jeol Kur Bül 24:39–50 (in Turkish)
Şaroğlu F, Yılmaz Y (1986) Doğu Anadolu'da neotektonik dönemdeki jeolojik evrim ve havza modelleri. MTA, Ankara
Şaroğlu F, Yılmaz Y (1990) Geology of Karliova region: intersection of the North Anatolian and East Anatolian transform faults. Bull İst Tech Univ l 44:475–497
Schreiber BC, El Tabakh M (2000) Deposition and early alteration of evaporites. Sedimentology 47:215–238
Schreiber BC, Freidman GM, Decima A, Schreiber E (1976) Depositional environments of Upper Miocene (Messinian) evaporite deposits of the Sicilian Basin. Sedimentology 23:729–760
Şen S, Antoine PO, Varol B, Ayyıldız T, Sözeri K (2011) Giant rhinoceros Paraceratherium and other vertebrates from Oligocene and Middle Miocene deposits of the Kağızman-Tuzluca Basin Eastern Turkey. Naturwissenschaften 98:407–423
Şengör AMC (1979) Mid-Mesozoic closure of Permo-Triassic: Tethys and its implications. Nature 279:590–593
Şengör AMC (1980) Türkiye'nin neotektoniğinin esasları. TJK Yayını, Ankara
Şengör AMC, Kidd WSF (1979) Post-collisional tectonics of the Turkish-Iranian Plateau and a comparison with Tibet. Tectonophysics 55:361–376
Şengör AMC, Yılmaz Y (1981) Tethyan evolution of Turkey: a plate tectonic approach. Tectonophysics 75:181–241
Şengör AMC, Zeren S, Genç T, Zor E (2003) East Anatolian high plateau as a mantlesupport, north–south shortened domal structure. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003GL017858
Şengör AMC, Özeren MS, Keskin M, Sakınç M, Özbakır AD, Kayan I (2008) Eastern Turkish high plateau as a small Turkic-type orogen: implications for post-collisional crust-forming processes in Turkic-type orogens. Earth Sci Rev 90:1–48
Shearman DJ (1966) Origin of marine evaporites by diagenesis. Trans Inst Min Metall 75:208–215
Shearman DJ, Orti F (1976) Upper Miocene gypsum: San Miguel de Salinas, SE Spain. Soc Geol Ital 16:327–339
Smoot JP, Lowenstein TK (1991) Depositional environments of non-marine evaporites. In: Melvin JL (ed) Evaporites, petroleum and mineral resourches. Elsevier, USA, pp 189–347
Sonnenfeld P (1984) Brines and evaporites. Academic Press, Orlando
Sözeri TE (2007) Muş civarı (Doğu Anadolu) burdigaliyen kireçtaşlarının fasiyes ve rezervuar özelliklerinin incelenmesi. Dissertation, Ankara University
Steininger F, Rögl F (1984) Palaeogeography and palinspastic reconstruction of the Neogene of the Mediterranean Paratethys. Geol Soc London Spec Pub 17:659–668
Stenni B, Longinelli A (1990) Stable isotope study of water, gypsum and carbonate samples from the Bannock and Tyro Basins, eastern Mediterranean. Marine Chem 31:123–135
Szynkiewicz A, Moore CH, Glamoclija M, Pratt LM (2009) Sulfur isotope signatures in gypsiferous sediments of the Estancia and Tularosa Basins as indicators of sulfate sources, hydrological processes, and microbial activity. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 73:6162–6186
Tekin E (2001) Stratigraphy, geochemistry and depositional environment of the celestine-bearing gypsiferous formations of the Tertiary Ulaş-Sivas Basin, East-Central Anatolia (Turkey). Turkish J Earth Sci 10:35–49
Temel ÖR, Tokatlı K (1999) Muş Tersiyer havzasının jeolojisi ve petrol olanakları. TPAO, Ankara
Thode HG (1991) Sulphur isotopes in nature and the environment: an overview. In: Krouse HR, Grinenko VA (eds) Stable isotopes in the assessment of natural and anthropogenic sulphur in the environment. John Wiley and Sons Ltd, Chichester, pp 1–26
Thode HG, Monster J (1965) Sulfur isotope geochemistry of petroleum, evaporties and ancient seasi. AAPG 4:367–377
Torfstein A, Gavrieli I, Katz A, Kolodny Y, Stein M (2008) Gypsum as a monitor of the paleo-limnological–hydrological conditions in lake lisan and the dead sea. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 72:2491–2509
Toulkeridis T, Podwojewski P, Clauer N (1998) Tracing the source of gypsum in New Caledonian soils by REE contents and S-Sr isotopic compositions. Chem Geol 145:61–71
Türkecan A (1991) Muş yöresindeki Pliyosen yaşlı volkanitlerin petrolojisi. MTA Der 112:85–101 (in Turkish)
Utrilla R, Pierre C, Ortí F, Pueyo JJ (1992) Oxygen and sulphur isotope compositions as indicators of the origin of Mesozoic and Cenozoic evaporites from Spain. Chem Geol 102:229–244
Van Simaeys S (2004) The Rupelian-Chattian boundary in the North Sea Basin and its calibration to the international timescale. Neth J Geosci/Geol Mijnbouw 83:241–248
Warren JK (1982) Hydrologic setting, occurence and significance of gypsum in late Quaternary salt lakes, South Australia. Sedimentology 29:609–637
Warren JK (1991) Sulfate dominated sea-marginal and platform evaporative settings Sabkhas and Salinas, mudflats and salterns. In: Melvin JL (ed) Evaporites, petroleum and mineral resources. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 69–187
Warren JK (2016) Evaporites: a compendium (ISBN 978–3–319–13511–3). Springer, Berlin
Yeşilova Ç, Helvacı C, Carrillo E (2018) Evaporitic sedimentation in the southeastern anatolian foreland basin: new insights on the neotethys closure. Sed Geol 369:13–27
Yılmaz Y (1993) New evidence and model on the evaluation of the southeast Anatolian orogen. Geol Soc Amer Bull 105:251–271
Yılmaz A, Terlemez İ, Uysal Ş (1986) Erzurum güneydoğusunda yeralan Hınıs-Tekman ve Karayazı arasının jeolojisi. MTA, Ankara
Yılmaz Y, Yiğitbaş E, Genç SC (1993) Ophiolitic and metamorphic assemblages of southeast Anatolia and their significance in the geological evolution of the orogenic belt. Tectonics 12:1280–1297
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Yüzüncü Yıl University Scientific Research Project Council (YYÜ, BAP, Project No: 2014-MİM–B082). We also thank Canada Acme Labs for elemental analyses; National Isotope Centre Laboratories located in New Zealand to 18O and 34S isotope analyses; METU Central Laboratory (R&D Training and Measuring Center, Radiogenic Isotope Laboratory) for 87Sr/86Sr radiogenic isotope analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Güngör Yeşilova, P., Yeşilova, Ç., Açlan, M. et al. Geochemical characteristics of gypsum lithofacies in northeastern of Muş (Eastern Anatolia-Turkey): an indication of the Neotethys closure. Carbonates Evaporites 35, 112 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-020-00648-8
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-020-00648-8