Abstract
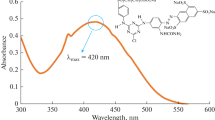
The current study aimed to investigate the removal efficiency of acid orange-7 (AO7) using synthesized Cr/TiO2 immobilized on pumice powder under visible light and UV irradiation. The characterization of synthesized nanocatalyst examined by scanning electron microscope, X-ray diffraction, and Fourier transforms infrared. The optimum of experimental parameters including catalyst dosage, dye concentration, time and pH, D-optimal Design (DOD) along with response surface methodology obtained by R software. The initial and outlet concentration was measured using a spectrophotometer. Besides, Analysis of variance results for the quadratic model showed simple linear regression with high significance and provided as a predicting model. The differences less than 0.2 between multiple and adjusted R2 in two models indicate that two examined models fitted suitably. The highest removal efficiency of AO7 was 95 and 74% under visible and UV irradiation, respectively. Therefore, the higher removal efficiency in visible light reduces the costs and energy, moreover, offers an environmentally friendly method. The results showed that the removal efficiency of AO7 increased considerably with rising catalyst dosage and time, as well as minimizing dye concentration, and pH.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Kant R. Textile dyeing industry an environmental hazard. 2011.
Bazrafshan E, Mostafapour FK, Hosseini AR, Raksh Khorshid A, Mahvi AH. Decolorisation of reactive red 120 dye by using single-walled carbon nanotubes in aqueous solutions. CHEM-NY. 2013;2013:1–8.
Stoyanova M, Slavova I, Ivanova V. Catalytic performance of supported nanosized cobalt and iron–cobalt mixed oxides on MgO in oxidative degradation of acid Orange 7 azo dye with peroxymonosulfate. Appl Catal A Gen. 2014;476:121–32.
Khoshnamvand N, Jafari A, Kamarehie B, Mohammadi A, Faraji M. Removal of malachite green dye from aqueous solutions using Zeolitic imidazole Framework-8. Environ. Process. 2019;6(3):757–72.
Martinez-Huitle CA, Ferro S. Electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants for the wastewater treatment: direct and indirect processes. Chem Soc Rev. 2006;35(12):1324–40.
Niu P. Photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange in aqueous TiO2 suspensions. Asian J Chem. 2013;25(2):1103–6.
Kao C, Chou M, Fang W, Liu B, Huang B. Regulating colored textile wastewater by 3/31 wavelength ADMI methods in Taiwan. Chemosphere. 2001;44(5):1055–63.
Barka N, Assabbane A, Nounah A, Dussaud J, Ichou YA. Photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange with immobilized TiO2 nanoparticles: effect of pH and some inorganic anions. Phys Chem News. 2008;41:85–8.
Darvishi Cheshmeh Soltani R, Rezaee A, Safari M, Khataee A, Karimi B. Photocatalytic degradation of formaldehyde in aqueous solution using ZnO nanoparticles immobilized on glass plates. Desalin Water Treat. 2015;53(6):1613–20.
Bao T, Damtie MM, Hosseinzadeh A, Wei W, Jin J, Vo HNP, et al. Bentonite-supported nano zero-valent iron composite as a green catalyst for bisphenol a degradation: preparation, performance, and mechanism of action. J Environ Manag. 2020;260:110105.
Bao T, Damtie MM, Hosseinzadeh A, Frost RL, Yu ZM, Jin J, et al. Catalytic degradation of P-chlorophenol by muscovite-supported nano zero valent iron composite: synthesis, characterization, and mechanism studies. Appl Clay Sci. 2020;195:105735.
Chen X, Mao SS. Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications. Chem Rev. 2007;107(7):2891–959.
Daghrir R, Drogui P, Robert D. Modified TiO2 for environmental photocatalytic applications: a review. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2013;52(10):3581–99.
Pelaez M, Nolan NT, Pillai SC, Seery MK, Falaras P, Kontos AG, et al. A review on the visible light active titanium dioxide photocatalysts for environmental applications. Appl Catal B Environ. 2012;125:331–49.
Dong H, Zeng G, Tang L, Fan C, Zhang C, He X, et al. An overview on limitations of TiO2-based particles for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants and the corresponding countermeasures. Water Res. 2015;79:128–46.
Alaoui OT, Nguyen QT, Rhlalou T. Preparation and characterization of a new TiO 2/SiO 2 composite catalyst for photocatalytic degradation of indigo carmin. Environ Chem Lett. 2009;7(2):175–81.
Peng Y-H, Huang G-F, Huang W-Q. Visible-light absorption and photocatalytic activity of Cr-doped TiO2 nanocrystal films. Adv Powder Technol. 2012;23(1):8–12.
Kamani H, Nasseri S, Nabizadeh R, Khoobi M, Ashrafi D, Bazrafshan E, et al. Sonocatalytic oxidation of reactive blue 29 by N-doped TiO2 from aqueous solution. JMUMS. 2018;28(166):157–69.
Jaimy KB, Ghosh S, Sankar S, Warrier K. An aqueous sol–gel synthesis of chromium (III) doped mesoporous titanium dioxide for visible light photocatalysis. Mater Res Bull. 2011;46(6):914–21.
Ould-Chikh S, Proux O, Afanasiev P, Khrouz L, Hedhili MN, Anjum DH, et al. Photocatalysis with chromium-doped TiO2: bulk and surface doping. ChemSusChem. 2014;7(5):1361–71.
Aruoja V, Dubourguier H-C, Kasemets K, Kahru A. Toxicity of nanoparticles of CuO, ZnO and TiO2 to microalgae Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. Sci Total Environ. 2009;407(4):1461–8.
Soltani RDC, Rezaee A, Khataee A, Safari M. Photocatalytic process by immobilized carbon black/ZnO nanocomposite for dye removal from aqueous medium: optimization by response surface methodology. J Ind Eng Chem. 2014;20(4):1861–8.
Xia Y, Li F, Jiang Y, Xia M, Xue B, Li Y. Interface actions between TiO2 and porous diatomite on the structure and photocatalytic activity of TiO2-diatomite. Appl Surf Sci. 2014;303:290–6.
Lu Y, Wang D, Ma C, Yang H. The effect of activated carbon adsorption on the photocatalytic removal of formaldehyde. Build Environ. 2010;45(3):615–21.
Moradi M, Mansouri AM, Azizi N, Amini J, Karimi K, Sharafi K. Adsorptive removal of phenol from aqueous solutions by copper (cu)-modified scoria powder: process modeling and kinetic evaluation. Desalin Water Treat. 2016;57(25):11820–34.
Moradi M, Hemati L, Pirsaheb M, Sharafi K. Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by powdered scoria-equilibrium isotherms and kinetic studies. World Appl Sci J. 2015;33(3):393–400.
Pirsaheb M, Hossaini H, Nasseri S, Azizi N, Shahmoradi B, Khosravi T. Optimization of photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange using immobilized scoria-Ni/TiO 2 nanoparticles. JNSC. 2020:1–17.
Kamani H, Safari GH, Asgari G, Ashrafi SD. Data on modeling of enzymatic elimination of direct red 81 using response surface methodology. Data Brief. 2018;18:80–6.
Khoshnamvand N, Jafari A, Kamarehie B, Faraji M. Optimization of adsorption and sonocatalytic degradation of fluoride by zeolitic imidazole framework-8 (ZIF-8) using RSM-CCD. Desalin Water Treat. 2019;171:270–80.
Thirugnanasambandham K, Sivakumar V, Maran JP, Kandasamy S. Chitosan based grey wastewater treatment—a statistical design approach. Carbohydr Polym. 2014;99:593–600.
Ölmez T. The optimization of Cr (VI) reduction and removal by electrocoagulation using response surface methodology. J Hazard Mater. 2009;162(2–3):1371–8.
Santhi K, Manikandan P, Rani C, Karuppuchamy S. Synthesis of nanocrystalline titanium dioxide for photodegradation treatment of remazol brown dye. Appl Nanosci. 2015;5(3):373–8.
Abdollahi B, Shakeri A, Aber S, Bonab MS. Simultaneous photodegradation of acid orange 7 and removal of Pb 2+ from polluted water using reusable clinoptilolite–TiO 2 nanocomposite. Res Chem Intermed. 2018;44(3):1505–21.
Konstantinou IK, Albanis TA. TiO2-assisted photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in aqueous solution: kinetic and mechanistic investigations: a review. Appl Catal B Environ. 2004;49(1):1–14.
Lachheb H, Puzenat E, Houas A, Ksibi M, Elaloui E, Guillard C, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of various types of dyes (alizarin S, Crocein Orange G, methyl red, Congo red, methylene blue) in water by UV-irradiated titania. Appl Catal B Environ. 2002;39(1):75–90.
Baran W, Makowski A, Wardas W. The effect of UV radiation absorption of cationic and anionic dye solutions on their photocatalytic degradation in the presence TiO2. Dyes Pigments. 2008;76(1):226–30.
Augugliaro V, Baiocchi C, Prevot AB, García-López E, Loddo V, Malato S, et al. Azo-dyes photocatalytic degradation in aqueous suspension of TiO2 under solar irradiation. Chemosphere. 2002;49(10):1223–30.
Soutsas K, Karayannis V, Poulios I, Riga A, Ntampegliotis K, Spiliotis X, et al. Decolorization and degradation of reactive azo dyes via heterogeneous photocatalytic processes. Desalination. 2010;250(1):345–50.
Behnajady M, Modirshahla N, Shokri M. Photodestruction of acid Orange 7 (AO7) in aqueous solutions by UV/H2O2: influence of operational parameters. Chemosphere. 2004;55(1):129–34.
Meena R. Photocatalytic decolorization of acid red 186 using alternative developed photocatalyst MBIR Dowex 11. Res J Chem Sci. 2012;2(9):56–62.
Song S, Xu L, He Z, Ying H, Chen J, Xiao X, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of CI direct red 23 in aqueous solutions under UV irradiation using SrTiO3/CeO2 composite as the catalyst. J Hazard Mater. 2008;152(3):1301–8.
Jain R, Shrivastava M. Photocatalytic removal of hazardous dye cyanosine from industrial waste using titanium dioxide. J Hazard Mater. 2008;152(1):216–20.
Hamadanian M, Sarabi AS, Mehra AM, Jabbari V. Photocatalyst Cr-doped titanium oxide nanoparticles: fabrication, characterization, and investigation of the effect of doping on methyl orange dye degradation. Mater Sci Semicond Process. 2014;21:161–6.
Stylidi M, Kondarides DI, Verykios XE. Visible light-induced photocatalytic degradation of acid Orange 7 in aqueous TiO2 suspensions. Appl Catal B Environ. 2004;47(3):189–201.
Hossaini H, Moussavi G, Farrokhi M. Oxidation of diazinon in cns-ZnO/LED photocatalytic process: catalyst preparation, photocatalytic examination, and toxicity bioassay of oxidation by-products. Sep Purif Technol. 2017;174:320–30.
Shirzad-Siboni M, Khataee A, Vahid B, Joo SW, Fallah S. Preparation of a green photocatalyst by immobilization of synthesized ZnO nanosheets on scallop shell for degradation of an azo dye. Curr Nanosci. 2014;10(5):684–94.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Kermanshah University of medical sciences, Iran, for financial and technical supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Not applicable.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pirsaheb, M., Hossaini, H., Azizi, N. et al. Synthesized Cr/TiO2 immobilized on pumice powder for photochemical degradation of acid orange-7 dye under UV/visible light: influential operating factors, optimization, and modeling. J Environ Health Sci Engineer 18, 1329–1341 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-020-00550-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-020-00550-4