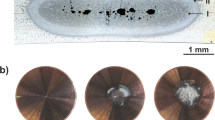
Abstract
The influence of current pulse width on electrode wear during resistance spot welding of thin sheets (1 mm, 0.04 in) of aluminum alloy 6016-T4 was studied, and an increase in sheet surface roughness and electrode erosion was evident with increasing pulse time for the same weld nugget size. Aluminum alloy 6016-T4 is an especially critical material concerning electrode wear for resistance spot welding due to rapid onset of electrode sticking and erosion of the electrode surface. Typically, welding of this material therefore requires electrode redressing operations after approximately 20 to 30 welds to maintain constant weld size and sheet surface quality. It was demonstrated that a reduction of current pulse width is a means of reducing electrode wear without affecting joint properties. The electrode wear process involved a pickup of aluminum material from the sheets followed by alloying process, leading to formation of intermetallic phases and erosion of material from the surface of the electrodes with increasing number of welds made. A reduction of current pulse width positively affected electrode wear properties by reducing temperatures at the electrode and sheet surfaces, thereby delaying electrode wear and reducing its severity.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data contained in this manuscript and associated files are approved by Mercedes-Benz A.G. for publishing by the journal.
References
Manladan SM, Yusof F, Ramesh S, Fadzil M, Luo Z, Ao S (2017) A review on resistance spot welding of aluminum alloys. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 90:605–634
Saha DC, Park Y-D (2011) A review on Al-Al/Al-steel resistance spot welding technologies for light weight vehicles. J KWJS 29(4):35–40. https://doi.org/10.5781/kwjs.2011.29.4.397
Gould JE (2012) Joining aluminum sheet in the automotive industry - a 30 year history. Weld J 91(1):23 s–34 s
Ambroziak A, Korzeniowski M (2010) Using resistance spot welding for joining aluminium elements in automotive industry. Arch Civil Mech Eng 10(1):5–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1644-9665(12)60126-5
Boomer DR, Hunter JA, Castle DR (2003) A new approach for robust high-productivity resistance spot welding of aluminium. SAE Technical Paper Series. https://doi.org/10.4271/2003-01-0575.
Fukumoto S, Lum I, Biro E, Boomer DR, Zhou Y (2003) Effects of electrode degradation on electrode life in resistance spot welding of aluminum alloy 5182. Weld J 82(11):307 s–312 s
Lum I, Biro E, Zhou Y, Fukumoto S, Boomer DR (2004) Electrode pitting in resistance spot welding of aluminum alloy 5182. Metall Mater Trans A 35A:217–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-004-0122-8
Rashid M, Fukumoto S, Medley JB, Villafuerte J, Zhou Y (2007) Influence of lubricants on electrode life in resistance spot welding of aluminum alloys. Weld J 86(3):62 s–70 s
Patil RR, Tilak CJKA, Srivastava V, De A (2011) Minimising Electrode Wear in Resistance Spot Welding of Aluminium Alloys. Sci Technol Weld Join 16(6):509–513. https://doi.org/10.1179/1362171811y.0000000036
Li Z, Hao C, Zhang J, Zhang H (2007) Effects of sheet surface conditions on electrode life in resistance welding aluminum. Weld J 86(4):81 s–89 s
Gintrowski G, Liang Z, Hibert V, Kempa S, Schiebahn A, Reisgen U (n.d.) Improvement of RSW process reliability for 6000 series Al car body sheets. Bad Nauheim, Germany
Schulz EW, Wagner M, Schubert H, Zhang W, Balasubramanian B, Brewer LN (2019) Short-pulse resistance spot welding of aluminum alloy 6016-T4 part 1: influence of welding time and current on weld quality. Manuscript submitted for publication
Schulz EW, Wagner M, Schubert H, Zhang W, Balasubramanian B, Brewer LN (2019) Short-pulse resistance spot welding of aluminum alloy 6016-T4 part 2: influence of pulse shape on weld quality. Manuscript submitted for publication.
Automobile Industry Association (Verband der Automobilindustrie e.V.) (2013) Aluminum Sheet Material (VDA 239-200). Berlin, Germany
German Institute for Standardization (Deutsches Institut für Normung) (2010) Resistance Welding – Spot welding electrode caps (ISO 5821:2009)
Reiso O, Øverlie H, Ryum N (1990) Dissolution and melting of secondary Al2Cu phase particles in an AlCu alloy. MTA 21:1689–1695. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02672585
Acknowledgments
This study has been funded and supported by the Mercedes-Benz A.G. in Sindelfingen, Germany, and is published with their permission.
Funding
This study was funded by Mercedes-Benz A.G. in Sindelfingen, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Eric Schulz and Ahmed Mahjoubi. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Eric Schulz, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Code availability
The RSW code used was SORPAS 2D Welding, a commercially available code. This code is used in cooperation with Swantec and under license with them.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Recommended for publication by Commission III - Resistance Welding, Solid State Welding, and Allied Joining Process
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schulz, E., Mahjoubi, A., Wagner, M. et al. Electrode wear in short-pulse resistance spot welding of aluminum AA 6016-T4. Weld World 65, 127–141 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-020-01003-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-020-01003-0