Abstract
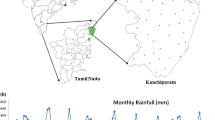
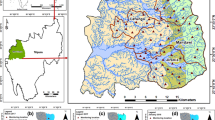
This paper elaborates the hydrochemical and environmental isotope (δ2H and δ18O) inferences obtained from Uddanam region, Andhra Pradesh, India. Groundwater samples collected during pre-monsoon (June 2019) showed that the quality is fresh (EC < 1539 µS/cm) and contaminants like fluoride (<1.6 mg/L) and nitrate (<49 mg/L) are present within permissible limits. The composite water quality indices for drinking (DWQI: 14.1–92.5) and irrigation (IWQI: 2.8–20.2) are found to be satisfactory. The major water types are found to be Ca–Na–HCO3, Na–Ca–HCO3, Na–Mg–HCO3–Cl, Ca–Mg–HCO3–Cl and Na–HCO3. Three geochemical pathways are found signifying evaporite dissolution, contribution of silicate mineral weathering and base-exchange process, which is supported by estimated chloro-alkaline indices (CAI-1: −4.3 to −0.2, CAI-2: −1.03 to −0.08). Trace metal data clearly suggest that groundwater is free from any metal pollution. Dissolved silica (SiO2) levels range from 34 to 131 mg/L and do not show any particular spatial trend. Isotope data infer that groundwater is recharged by rainwater after undergoing evaporation (δ18O: −6.0‰), which matches with that of the combined isotope signature (δ18O: −5.5‰) of SW and NE monsoon rainfall. δ18O–TDS correlations and hydrochemical facies evolution (HFE) diagram do not infer any seawater intrusion into these coastal aquifers.
Highlights
-
The composite water quality indices infer good to excellent category for drinking and agriculture.
-
Mineral weathering, evaporite dissolution and base-exchange reactions are the main geochemical processes.
-
Dissolved silica occurrence in groundwater is sporadic.
-
Isotope indicators show the signature of both SW and NE monsoons recharge to groundwater.
-
Observed brackishness in groundwater is due to water – rock interaction and not due to sea water intrusion.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anil Kumara K S, Prijub C P and Narasimha Prasad N B 2015 Study on saline water intrusion into the shallow coastal aquifers of Periyar River Basin, Kerala using hydrochemical and electrical resistivity methods; Aquatic Procedia 4 32–40.
APSAC 2018 District Survey Report-Srikakulam, 194p.
Aruna K and Mohammad T 2019 Heavy metals analysis in soil and water samples of small villages of north coastal, Uddanam mandal, Andhra Pradesh, India, causing chronic kidney disease; Asian J. Res. Chem. Pharm. Sci. 7(2) 363–366.
Bhattacharya A K, Basack S and Maity P 2008 Saline water intrusion in Bhadrak and Balasore Districts of Orissa, India; http://www.ejge.com/2008/Ppr0869.pdf.
BIS 2012 Indian standards specification for drinking water; 2nd Rev, BIS, New Delhi, IS:10500:2012.
Bhishm Kumar, Rai S P, Saravana U K, Verma S K, Garg P, Vijaya S V K, Jaiswal R, Purendra B K, Kumar S R and Pande N G 2010 Isotopic characteristics of Indian precipitation; Water Resour. Res. 46, https://doi.org/10.1029/2009wr008532.
Brown R M, McClelland N I, Deininger R A and Tozer R G 1970 Water quality index-do we dare; Water Sew. Works 117(10) 339–343.
CGWB 2013 Ground Water Brochure, Srikakulam District, Andhra Pradesh, Ministry of Water Resources, Government of India.
Chadha D K 1999 A proposed new diagram for geochemical classification of natural waters and interpretation of chemical data; Hydrogeol. J. 7(5) 431–439.
Chidambaram S, Prasad B K and Manivannan M 2013 Environmental hydrogeochemistry and genesis of fluoride in groundwaters of Dindigul district, Tamilnadu (India); Environ. Earth Sci. 68 333–342, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1741-9.
Chidambaram S, Thivya C, Ramanathan A L, Thilagavathi R and Prasanna M V 2018 Characterization of coastal aquifers in SE coast of India; In: Groundwater of South Asia (ed.) Mukherjee A, Springer Hydrogeology, Springer, Singapore.
Chowdeswararao O and Kalyani G 2018 Water quality index around Srikakulam district; Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. (IRJET) 5(5) 3914–3917.
Clark I and Fritz P 1997 Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology; Lewis Publishers, New York, 352p.
Coplen T B 1996 New guidelines for reporting stable hydrogen, carbon and oxygen isotope-ratio data; Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 60 3359–3360.
Das J 2003 Geochemistry of trace elements in the groundwater of Cuttack city, India; Water Air Soil Pollut. 147 129–140, https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024569422322.
Deshpande R D, Bhattacharya S K, Jani R A and Gupta S K 2003 Distribution of oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in shallow groundwater from Southern India: Influence of a dual monsoon system; J. Hydrol. 271(1–4) 226–239.
Deshpande R D and Gupta S K 2012 Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in hydrological cycle: New data from IWIN National Programme; Proc. Indian Nat. Sci. Acad. 78(3) 321–331.
Durfor C N and Becker E 1964 Public water supplies of the 100 largest cities in the United States; Water Supply Paper no. 1812, pp. 343–346.
Eaton E M 1950 Significance of carbonate in irrigation water; Soil Sci. 69 123–133.
Elena G F and Javier S S R 2014 An excel macro to plot the hfe-diagram to identify sea water intrusion phases; Ground Water 53(5), https://doi.org/10.1111/gwat.12280.
Gadde P G, Suresh S K, Ramesh M and Anitha A 2017 Uddanam nephropathy in India: A challenge for epidemiologists; Bull. World Health Organisation 95(12) 848–849, https://doi.org/10.2471/blt.17.196758.
Hariharan A 2007 Determination of water quality of coastal area Visakhapatnam; Curr. World Environ. 2(2) 217–220, http://dx.doi.org/10.12944/CWE.2.2.19.
Hitchon B, Perkins E H and Gunter W D 1999 Introduction to groundwater geochemistry; Alberta: Geoscience.
Hounslow A W 1995 Water quality data analysis and interpretation; CRC Press, Boca Raton.
Jankowski J, Acworth R I and Shekarforoush S 1998 Reverse ion exchange in a deeply weathered porphyriticdacite fractured aquifer system, Yass, New South Wales, Australia; In: Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium, water–rock interaction (eds) Arehart G B and Hulston J R, Rotterdam: Balkema, pp. 243–246.
Jayalakshmi D O, Ramanathan A L and Singh G 2012 Geochemical and statistical evaluation of groundwater in Imphal and Thoubal district of Manipur, India; J. Asian Earth Sci. 48 136–149.
Karanth K R 1987 Groundwater assessment, development and management; Tata-McGraw-Hill, New Delhi.
Keesari T, Shivanna K and Jalihal A A 2007 Isotope hydrochemical approach to understand fluoride release into groundwaters of Ilkal area, Bagalkot District, Karnataka, India; Hydrogeol. J. 15 589–598, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-006-0107-3.
Keesari T, Roy A and Mohokar H 2019 Characterization of mechanisms and processes controlling groundwater recharge and its quality in drought-prone region of central India (Buldhana, Maharashtra) using isotope hydrochemical and end-member mixing modelling; Nat. Resour. Res., https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-019-09550-0.
Kelley W P 1963 Use of saline irrigation; Water Soil Sci. 95(4) 355–391.
Lagudu S, Rao V V S G, Prasad P R and Sarma V S 2013 Use of geophysical and hydrochemical tools to investigate seawater intrusion in coastal alluvial aquifer, Andhra Pradesh, India; In: Groundwater in the Coastal Zones of Asia–Pacific (ed.) Wetzelhuetter C, Coastal Research Library, Springer, Dordrecht.
Lloyd J W and Heathcote J A 1985 Natural inorganic hydrochemistry in relation to groundwater; Clarendon, Oxford, 294p.
Mondal N C, Singh V S, Saxena V K and Prasad R K 2008a Improvement of groundwater quality due to fresh water ingress in Potharlanka Island, Krishna delta, India; Environ. Geol. 55(3) 595–603, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-1010-5.
Mondal N C, Saxena V and Singh S 2008b Occurrence of elevated nitrate in groundwaters of Krishna delta, India; African J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2(9) 265–271.
Mondal N C, Rao A V and Singh V P 2010a Efficacy of electrical resistivity and induced polarization methods for revealing fluoride contaminated groundwater in granite terrain; Environ. Monit. Assess. 168 103–114, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1094-3.
Mondal N C, Singh V P, Singh V S and Saxena V K 2010b Determining the interaction between groundwater and saline water through groundwater major ions chemistry; J. Hydrol. 388(1–2) 100–111, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.04.032.
Mondal N C, Singh V S, Puranik S C and Singh V P 2010c Trace element concentration in groundwater of Pesarlanka Island, Krishna Delta, India; Environ. Monit. Assess. 163 215–227, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0828-6.
Mondal N C and Singh V P 2011a Hydrochemical analysis of Stalinization for a tannery belt in southern India; J. Hydrol. 405(3–4) 235–247, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.05.058.
Mondal N C, Singh V P and Singh S 2011b Hydrochemical characteristic of coastal aquifer from Tuticorin, Tamil Nadu, India; Environ. Monit. Assess. 175 531–550, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1549-6.
Nadikatla S K, Mushini V S and Mudumba P S M 2020 Water quality index method in assessing groundwater quality of Palakondamandal in Srikakulam district, Andhra Pradesh, India; Appl. Water Sci. 10 30, https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-1110-x.
Rajendiran R T, Satyanarayana R, Prasad G, Aruna L K, Ajay K S, Vasishta S T, Krishna B, Devi M B and Hanumanth N 2019a High prevalence of CKD of unknown etiology in Uddanam, India; Kidney Int. Rep. 4(3) 380–389, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ekir.2018.10.006.
Rajendiran T, Sabarathinam C and Chandrasekar T 2019b Influence of variations in rainfall pattern on the hydrogeochemistry of coastal groundwater – An outcome of periodic observation; Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 26 29,173–29,190, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05962-w.
Ramana Rao S V 2018 District Survey Report Srikakulam District, Director of Mines and Geology, Government of Andhra Pradesh, June, 124p.
Richards L A 1954 Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils; US Department of Agriculture, Agri. Hand book 60, Washington, DC.
Roy A, Tirumalesh K and Mohokar H 2018 Assessment of groundwater quality in hard rock aquifer of central Telangana state for drinking and agriculture purposes; Appl. Water Sci. 8 124, https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0761-3.
Saha D and Ray R K 2019 Groundwater resources of India: Potential, challenges and management; Chapter 2, In: Groundwater Development and Management (ed.) Sikdar P K, Capital Publishing Company, New Delhi, India, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-75115-3_2.
Sarwade D V, Nandakumar M V, Kesari M P, Mondal N C, Singh V and Singh B 2007 Evaluation of sea water ingress into an Indian atoll; Environ. Geol. 52 1475–1483, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0592-7.
Satyanarayana G P, Ramadasu P, Padmavathi D, Prasad N V B S S and Nageswara Rao G 2017 Ground water quality Assessment in Uddanam, region, Costal Srikakulam, Andhra Pradesh, India; Int. J. Pharm. Drug Anal. 5(4) 116–128, http://ijpda.com; ISSN: 2348-8948.
Saxena V K, Mondal N C and Singh V S 2004 Identification of seawater ingress using Strontium and Boron in Krishna delta, India; Curr. Sci. 86(4) 586–590.
Schoeller H 1967 Geochemistry of groundwater. An international guide for research and practice; UNESCO 15 1–18.
Sharma D A, Keesari T, Rishi M S and Pant D 2018 A study on the role of hydrogeology on the distribution of uranium in alluvial aquifers of northwest India; Environ. Monit. Assess. 190(12) 746.
Szabolcs I and Darab C 1964 The influence of irrigation water of high sodium carbonate content of soils; Proceedings of 8th International Congress of ISSS, Trans II, pp. 803–812.
Todd D K 1960 Salt water intrusion of coastal aquifers in the United States; Int. Assoc. Sci. Hydrol. (Gent brugge Belgium) Publ. 52 452–461.
WHO 2011 Guidelines for drinking water quality; World Health Organization, Geneva.
Wilcox L V 1955 Classification and use of irrigation water; US Department of Agriculture, Washington DC, 969p.
Acknowledgements
Authors wish to thank Dr. P K Pujari, Director, RC&I Group, BARC, and Dr. H J Pant, Head, Isotope and Radiation Application Division, BARC for the constant support and encouragement. We also thank District Water Management Authority (DWMA), Srikakulam for collecting samples for trace metal and Analytical Chemistry Division, BARC for carrying out trace metal measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Tirumalesh Keesari: Planning, sampling, data interpretation, manuscript writing. Anndasankar Roy: Preparing graphs and data interpretation. Diksha Pant: Manuscript preparation and literature survey. Uday Kumar Sinha: Manuscript preparation. P V Nagendra Kumar: Sampling and providing background information. L Vaikunta Rao: Sampling and providing background information.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by N V Chalapathi Rao
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keesari, T., Roy, A., Pant, D. et al. Major ion, trace metal and environmental isotope characterization of groundwater in selected parts of Uddanam coastal region, Andhra Pradesh, India. J Earth Syst Sci 129, 205 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-020-01467-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-020-01467-0