Abstract
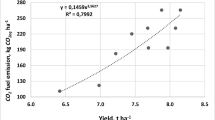
Improvement of tillage-sowing practices can be a practical way of sustainable and environmentally friendly production by decreasing fuel and CO2 emission and increasing yield in a rainfed crop rotation [Hungarian vetch (Vicia pannonica Crantz)—winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L. cv. Bezostaja)—fallow] in semi-arid conditions. Therefore, conventional (CT), reduced-1 and 2, and no-tillage (NT) practices were tested with randomized block design as three replications. The highest fuel consumption (47.8 l ha−1) and human labor requirement (8.9 h ha−1) and the lowest equipment working effectiveness (0.17 ha h−1) were determined under CT. The NT practice manifested the best results with 3.5-fold fuel saving and 2.2-fold human labor saving as well as 7.8 times more operating area per unit time compared with CT. The highest weed infestation, seedling density and the shortest emergence time were determined in this practice. Vetch forage yield also was statistically higher in the NT practice. Conservation tillage logarithmically decreased CO2 emissions and the lowest value was determined in NT with 71.4% reduction compared with the CT value (137.4 kg CO2 ha−1). Specific CO2 emissions in NT were lower by 72.1% in vetch and 60.4% in wheat than the CT values. Therefore, NT practice could be recommended as the best practice for rainfed crop rotation in semi-arid regions.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acar M, Çelik İ, Günal H (2017) Effects of long-term tillage systems on soil water content and wheat yield under Mediterranean conditions. J New Theory 17:98–108
Adewoyin AO (2013) Fuel consumption evaluation of some commonly used farm tractors for ploughing operations on the sandy-loam soil of Oyo State, Nigeria. Res J Appl Sci Eng Tech 6:2865–2871
Ahmad P, Hussain M, Ahmad S, Tabassam MAR, Shabbir I (2013) Comparison of different tillage practices among various wheat varieties. Appl Sci Rep. 4:203–209
Akbarnia A, Farhani F (2014) Study of fuel consumption in three tillage methods. Res Agr Eng 60:142–147
Alam K, Islam M, Salahin N, Hasanuzzaman M (2014) Effect of tillage practices on soil properties and crop productivity in wheat–mungbean–rice cropping system under subtropical climatic conditions. Sci World J 437283:1–15
Alamouti MY, Mohammadi P (2015) Field evaluation of tillage practices in rainfed wheat planting. Agric Eng Int J 17:45–56
Ali S, Malik MA, Ansar M, Qureshi R (2014) Weed growth dynamics associated with rainfed wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) establishment under different tillage systems in pothwar. Int J Plant Anim Environ Sci 4:146–154
Altıkat S, Çelik A (2012) Effects of different no-till seeders and tractor forward speeds on the soil physical properties and seed emergence of summer vetch and winter wheat. J Agr Sci 18:21–30
Altikat S, Kus E, Kucukerdem HK, Gozubuyuk Z (2017) The applications of no-tillage in Turkey. In: 3rd international conference on science, ecology and technology, 14–16 August 2017, Rome
Barut ZB, Ertekin C, Karaagac HA (2011) Tillage effects on energy use for corn silage in Mediterranean Coastal of Turkey. Energy 36:5466–5475
Bilandžija D, Zgorelec Ž, Kisić I (2016) Influence of tillage practices and crop type on soil CO2 emissions. Sustainability 8:90
Calado JMG, Basch G, Barros JFC, Carvalho M (2013) Weed management in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) influenced by different soil tillage systems. Afr J Agric Res 8:2551–2558
Colecchia SA, De Vita P, Rinaldi M (2015) Effects of tillage systems in durum wheat under rainfed Mediterranean conditions. Cereal Res Comm 43:704–716
Czyż EA, Dexter AR (2008) Soil physical properties under winterwheat grown with different tillage systems at selected locations. Int Agrophys 22:191–200
DATAE (2016) Hydro-meteorological observation data. Eastern Anatolia Agricultural Research Institute, Erzurum
De Vita P, Di Paolo E, Fecondo G, Di Fonzo N, Pisante M (2007) No-tillage and conventional tillage effects on durum wheat yield, grain quality and soil moisture content in southern Italy. Soil Till Res 92:69–78
Fathollahzadeh H, Mobli H, Rajabipour A, Minaee S, Jafari A, Tabatabaie SMH (2010) Average and instantaneous fuel consumption of Iranian conventional tractor with moldboard plow in tillage. J Eng Appl Sci 5:30–35
Filipovic D, Kosutic S, Gospodaric Z, Zimmer R, Banaj D (2006) The possibilities of fuel savings and the reduction of CO2 emissions in the soil tillage in Croatia. Agr Ecosyst Environ 115:290–294
Filipović D, Košutić S, Gospodarić Z (2004) Influence of different soil tillage systems on fuel consumption, labour requirement and yield in maize and winter wheat production. Poljoprivreda 10:17–23
Gozubuyuk Z, Sahin U, Ozturk I, Celik A, Adiguzel MC (2014) Tillage effects on certain physical and hydraulic properties of a loamy soil under a crop rotation in a semi-arid region with a cool climate. CATENA 118:195–205
Gozubuyuk Z, Sahin U, Adiguzel MC, Ozturk I, Celik A (2015) The influence of different tillage practices on water content of soil and crop yield in vetch–winter wheat rotation compared to fallow–winter wheat rotation in a high altitude and cool climate. Agr Water Manag 160:84–97
Gözübüyük Z, Öztürk İ, Çelik A, Evren S, Daşçı E, Adıgüzel MC (2015) Comparison of various tillage-seeding systems in terms of energy use efficiency in production of sunflower. J Agr Machin Sci 11:113–119 (In Turkish)
Gungor C, Kusek G, Kucukerdem HK, Ozturk HH, Akdemir S (2018) Carbon dioxide emissions related to fuel consumption for groundnut production in Turkey. In: Vîrsta A (ed) Scientific papers, Series E, Land reclamation, earth observation and surveying, environmental engineering, vol VII. CERES Publishing House. Bucharest, Romania, pp 1–3
Hanna M (2016) Estimating the field capacity of farm machines. Iowa State Univ., IA, USA. https://www.extension.iastate.edu/agdm/crops/html/a3-24.html. Accessed 8 May 2019
Khaledian M, Mailhol JC, Ruelle P (2014) Diesel oil consumption, work duration, and crop production of corn and durum wheat under conventional and no-tillage in southeastern France. Arch Agron Soil Sci 60:1067–1076
Kitiş YE, Kulören O, Uygur FN (2016) Allelopathic effects of common vetch (Vicia sativa L.) on germination and development of some weed species. J Cent Res Ins Field Crop 25:100–106
Koga N, Tsuruta H, Tsuji H, Nakano H (2003) Fuel consumption-derived CO2 emissions under conventional and reduced tillage cropping systems in Northern Japan. Agr Ecosyst Environ 99:213–219
Küsek G (2018) Assessment of carbon dioxide emissions due to fuel consumption in lentil production in Southeastern Anatolia Region. Harran J Agr Food Sci 22:572–584
Lal R (2004) Carbon emission from farm operations. Environ Int 30:981–990
Leghari N, Ali A, Mangrio MA (2016) Relative efficiency of different tillage practices and their effect on soil physical properties under semi-arid climate of Tandojam, Pakistan. Mehran Univ Res J Eng Tech 35:239–246
Li LL, Huang GB, Zhang RZ, Jin XJ, Li GD, Chan KY (2005) Effects of conservation tillage on soil water regimes in rainfed areas. Acta Ecol Sin 25:2326–2332
Licht MA, Al-Kaisi M (2005) Strip-tillage effect on seedbed soil temperature and other soil physical properties. Soil Till Res 80:233–249
Liu C, Cutforth H, Chai Q, Gan Y (2016) Farming tactics to reduce the carbon footprint of crop cultivation in semiarid areas. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 36:69
Mamkagh AM (2018) Effect of tillage speed, depth, ballast weight and tire inflation pressure on the fuel consumption of the agricultural tractor: a review. J Eng Res Rep 3:1–7
Meydani JA, Rahmati M, Karimi E, Aliloo AA (2014) Dryland soil water storage susceptibility to different soil tillage practices under Vetch–Wheat crop rotation. Azarian J Agr 1:18–24
Moitzi G, Weingartmann H, Boxberger J (2006) Effects of tillage systems and wheel slip on fuel consumption. In: The Union of Scientists-Rousse: energy efficiency and agricultural engineering, Rousse, 7–9 June 2006, Bulgaria, 237–242. ISSN 1311-9974
Moitzi G, Wagentristl H, Refenner K, Weingartmann H, Piringer G, Boxberger J, Gronauer A (2014) Effects of working depth and wheel slip on fuel consumption of selected tillage implements. Agric Eng Int CIGR J 16:182–190
Muazu A, Yahya A, Ishak WIW, Khairunniza-Bejo S (2015) Analysis of fuel consumption and carbon dioxide emission in direct seeding wetland rice cultivation systems in Malaysia. Res J Appl Sci Eng Tech 11:281–292
Murray G (2004) Winter wheat growth, development, and physiology of seed yield and protein level. In: Robertson LD, Guy SO, Brown BD (eds.), Southern Idaho dryland winter wheat production guide. University of Idaho College of Agricultural and Life Sciences, BUL 827, pp 9–13
Namdari M, Rafiee Sh, Jafari A (2011) CO2 emission as a result of the fuel consumption and tillage quality in different tillage conditions. Int J Environ Sci 1:1659–1669
Naujokienė V, Šarauskis E, Lekavičienė K, Adamavičienė A, Buragienė S, Kriaučiūnienė Z (2018) The influence of biopreparations on the reduction of energy consumption and CO2 emissions in shallow and deep soil tillage. Sci Total Environ 626:1402–1413
Nkakini SO, Vurasi NM (2015) Effects of moisture content, bulk density and tractor forward speeds on energy requirement of disc plough. Int J Advan Res. Eng Tech 6:69–79
Özden DM (1995) Computer programming of time study analysis and database generation in agricultural mechanization. General Directorate of Rural Services, Soil and Water Resources Research Department, Publication No: 81, Ankara (in Turkish)
Özden DM, Soğancı A (1996) The guide of Turkey agricultural tools and machinery operation value. General Directorate of Rural Services, Soil and Water Resources Research Department, Publication No: 92, Ankara (in Turkish)
Özgül M (2003) Classifying and mapping of great soil groups commonly found in Erzurum. (PhD thesis) Atatürk University, Graduate School of Natural and Applied Sciences, Erzurum (in Turkish)
Ozpinar S (2006) Effects of tillage on productivity of a winter wheat–vetch rotation under dryland Mediterranean conditions. Soil Till Res 89:258–265
Öztürk MZ, Çetinkaya G, Aydın S (2017a) Climate types of Turkey according to Köppen–Geiger climate classification. Istanbul Univ J Geography 35:17–27
Öztürk HH, Gözübüyük Z, Atay Ü (2017b) An assessment of carbon dioxide emissions related to fuel consumption for cotton production in Turkey. In: 3rd ASM international congress of agriculture and environment proceeding book, Külcü R (ed), pp 1–8, Antalya ISBN: 978-605-83551-7-0
Pittelkow CM, Linquist BA, Lundy ME, Liang X, van Groenigen KJ, Lee J, van Gestel N, Six J, Venterea RT, van Kessel C (2015) When does no-till yield more? A global meta-analysis. Field Crop Res 183:156–168
Romaneckas K, Romaneckienė R, Šarauskis E, Pilipavičius V, Sakalauskas A (2009) The effect of conservation primary and zero tillage on soil bulk density, water content, sugar beet growth and weed infestation. Agron Res 7:73–86
Rusu T (2014) Energy efficiency and soil conservation in conventional, minimum tillage and no-tillage. Int Soil Water Con Res 2:42–49
Sarauskis E, Buragiene S, Romaneckas K, Sakalauskas A, Jasinskas A, Vaiciukevicius E, Karayel D (2012) Working time, fuel consumption and economic analysis of different tillage and sowing systems in Lithuania. In: 18th international scientific conference, engineering for rural development, pp 52–59, 24–25 May 2012, Jelgava, Latvia
Šarauskis E, Vaiciukevičius E, Sakalauskas A, Romaneckas K, Jasinskas A, Lillak R (2008) Impact of sowing speed on the introduction of winter wheat seeds in differently-tilled soils. Agron Res 6:315–327
Šarauskis E, Buragienė S, Masilionytė L, Romaneckas K, Avižienytė D, Sakalauskas A (2014) Energy balance, costs and CO2 analysis of tillage technologies in maize cultivation. Energy 69:227–235
Šarauskis E, Vaitauskienė K, Romaneckas K, Jasinskas A, Butkus V, Kriaučiūnienė Z (2017) Fuel consumption and CO2 emission analysis in different strip tillage scenarios. Energy 118:957–968
Sørensen CG, Nielsen V (2005) Operational analyses and model comparison of machinery systems for reduced tillage. Biosyst Eng 92:143–155
Stajnko D, Lakota M, Vučajnk F, Bernik R (2009) Effects of different tillage systems on fuel savings and reduction of CO2 emissions in production of silage corn in Eastern Slovenia. Polish J Environ Stud 18:711–716
Strudley MW, Green TR, Ascough JC II (2008) Review: tillage effects on soil hydraulic properties in space and time: state of the science. Soil Till Res 99:4–48
Subbulakshmi S, Saravanan N, Subbian P (2009) Conventional tillage vs conservation tillage—a review. Agric Rev 30:56–63
Uzun B, Yol E, Furat Ş, Topakçı M, Çanakçı M, Karayel D (2012) The effects of different tillage methods on the post-wheat second crop sesame: seed yield, energy budget, and economic return. Turk J Agric For 36:399–407
Wuest SB, Lutcher LK (2013) Soil water potential requirement for germination of winter wheat. Soil Sci Soc Am J 77:279–283
Yalcin H, Cakir E, Aykas E (2005) Tillage parameters and economic analysis of direct seeding, minimum and conventional tillage in wheat. J Agron 4:329–332
Yu H, Peng W, Ma X, Zhang K (2011) Effects of no-tillage on soil water content and physical properties of spring corn fields in semiarid region of northern China. Chin J Appl Ecol 22:99–104
Acknowledgement
Study was funded by a Grant (TAGEM-BB-980210K1) from the “General Directorate of Agricultural Research and Policies in Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry in Turkey”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Jing Chen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gozubuyuk, Z., Sahin, U. & Celik, A. Operational and yield performances and fuel-related CO2 emissions under different tillage-sowing practices in a rainfed crop rotation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 17, 4563–4576 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02804-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02804-y