Abstract
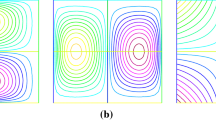
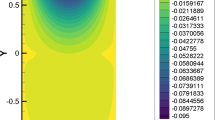
Combining the quadratic equal-order stabilized method with the approach of local and parallel finite element computations and classical iterative methods for the discretization of the steady-state Navier–Stokes equations, three parallel iterative stabilized finite element methods based on fully overlapping domain decomposition are proposed and compared in this paper. In these methods, each processor independently computes an approximate solution in its own subdomain using a global composite mesh that is fine around its own subdomain and coarse elsewhere, making the methods be easy to implement based on existing codes and have low communication complexity. Under some (strong) uniqueness conditions, stability and convergence theory of the parallel iterative stabilized methods are derived. Numerical tests are also performed to demonstrate the stability, convergence orders and high efficiency of the proposed methods.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Temam, R.: Navier–Stokes Equations: Theory and Numerical Analysis. North-Holland, Amsterdam (1984)
Girault, V., Raviart, P.A.: Finite Element Approximation of the Navier–Stokes Equations. Springer, Berlin (1979)
Girault, V., Raviart, P.A.: Finite Element Method for Navier–Stokes Equations: Theory and Algorithms. Springer, Berlin (1987)
Hughes, T.J.R., Franca, L.P., Balestra, M.: A new finite element formulation for computational fluid dynamics: V. Circumventing the Babuska–Brezzi condition: a stable Petrov–Galerkin formulation of the Stokes problem accomodating equal-order interpolations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 59, 85–99 (1986)
Brooks, A.N., Hughes, T.J.R.: Streamline upwind/Petrov–Galerkin formulations for convective dominated flows with particular emphasis on the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 32, 199–259 (1982)
Hughes, T.J.R., Franca, L.P., Hulbert, G.M.: A new finite element formulation for computational fluid dynamics: VIII. The Galerkin/least-squares method for advective–diffusive equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 73, 173–189 (1989)
Masud, A., Khurram, R.A.: A multiscale finite element method for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 195, 1750–1777 (2006)
Blasco, J., Codina, R.: Stabilization finite elements method for the transient Navier–Stokes equations based on a pressure gradient projection. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 182, 277–300 (2000)
Li, J., He, Y.N.: A stabilized finite element method based on two local Gauss integrations for the Stokes equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 214, 58–65 (2008)
He, Y.N., Li, J.: A stabilized finite element method based on local polynomial pressure projection for the stationary Navier–Stokes equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 58, 1503–1514 (2008)
Zheng, H.B., Shan L., Hou, Y.R.: A quadratic equal-order stabilized method for Stokes problem based on two local Gauss integrations. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 26, 180–1190 (2010)
Huang, P.Z., Feng, X.L., Liu, D.M.: Two-level stabilized method based on three corrections for the stationary Navier–Stokes equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 62, 988–1001 (2012)
Qiu, H.L., An, R., Mei, L.Q., Xue, C.F.: Two-step algorithms for the stationary incompressible Navier–Stokes equations with friction boundary conditions. Appl. Numer. Math. 120, 97–114 (2017)
Zhang, G.L., Su, H.Y., Feng, X.L.: A novel parallel two-step algorithm based on finite element discretization for the incompressible flow problem. Numer. Heat Transf. B Fundam. 73, 329–341 (2018)
Zheng, B., Shang, Y.Q.: A parallel quadratic equal-order stabilized finite element algorithm based on fully overlapping domain decomposition for the steady Navier–Stokes equations, Submitted for publication
Zheng, B., Shang, Y.Q.: Parallel iterative stabilized finite element algorithms based on the lowest equal-order elements for the stationary Navier–Stokes equations. Appl. Math. Comput. 357, 35–56 (2019)
Xu, J.C., Zhou, A.H.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms based on two-grid discretizations. Math. Comput. 69, 881–909 (2000)
Xu, J.C., Zhou, A.H.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms based on two-grid discretizations for nonlinear problem. Adv. Comput. Math. 14, 293–327 (2001)
He, Y.N., Xu, J.C., Zhou, A.H., Li, J.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms for the Stokes problem. Numer. Math. 109, 415–434 (2008)
Shang, Y.Q., Wang, K.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms based on two-grid discretizations for the transient Stokes equations. Numer. Algorithms 54, 195–218 (2010)
He, Y.N., Xu, J.C., Zhou, A.H.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms for the Navier–Stokes problem. J. Comput. Math. 24, 227–238 (2006)
Shang, Y.Q., He, Y.N., Kim, D.W, Zhou, X.J.: A new parallel finite element algorithm for the stationary Navier–Stokes equations. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 47, 1262–1279 (2011)
Shang, Y.Q., He, Y.N.: A parallel Oseen-linearized algorithm for the stationary Navier–Stokes equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 209, 172–183 (2012)
Du, G.Z., Hou, Y.R., Zuo, L.Y.: Local and parallel finite element method for the mixed Navier–Stokes/Darcy model. Int. J. Comput. Math. 93, 1155–1172 (2015)
Zhang, Y.H., Hou, Y.R., Shan, L., Dong, X.J.: Local and parallel finite element algorithm for stationary incompressible magnetohydrodynamics. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 33, 1513–1539 (2017)
Tang, Q.L., Huang, Y.Q.: Local and parallel finite flement algorithm based on Oseen-type iteration for the stationary incompressible MHD flow. J. Sci. Comput. 70, 1–26 (2017)
Yang, Y.D., Han, J.Y.: The multilevel mixed finite element discretizations based on local defect-correction for the Stokes eigenvalue problem. Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng. 289, 249–266 (2015)
Bi, H., Han, J.Y., Yang, Y.D.: Local and parallel finite element algorithms for the transmission eigenvalue problem. J. Sci. Comput. 78, 351–375 (2019)
Zheng, H.B., Shi, F., Hou, Y.R., et al.: New local and parallel finite element algorithm based on the partition of unity. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 435, 1–19 (2016)
Du, G.Z., Zuo, L.Y.: A parallel partition of unity scheme based on two-grid discretizations for the Navier–Stokes problem. J. Sci. Comput. 4, 1–18 (2017)
Shang, Y.Q.: A parallel subgrid stabilized finite element method based on fully overlapping domain decomposition for the Navier–Stokes equations. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 403, 667–679 (2013)
Shang, Y.Q.: Parallel defect-correction algorithms based on finite element discretization for the Navier–Stokes equations. Comput. Fluids 79, 200–212 (2013)
Shang, Y.Q., Qin, J.: Parallel finite element variational multiscale algorithms for incompressible flow at high Reyonds numbers. Appl. Numer. Math. 117, 1–21 (2017)
He, Y.N., Li, J.: Convergence of three iterative methods based on the finite element discretization for the stationary Navier–Stokes equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 198, 1351–1359 (2009)
Shang, Y.Q., He, Y.N.: Parallel iterative finite element algorithms based on full domain decomposition for the stationary Navier–Stokes equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 60, 719–737 (2010)
Adams, R.: Sobolev Spaces. Academaic Press Inc, New York (1975)
Heywood, J.G., Rannacher, R.: Finite element approximation of the nonstationary Navier–Stokes problem. Part I: regularity of solutions and second-order spatial discretization. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 19, 275–311 (1982)
Kechkar, N., Silvester, D.: Analysis of locally stabilized mixed finite element methods for the Stokes problem. Math. Comput. 58, 1–10 (1992)
Hecht, F.: New development in FreeFem++. J. Numer. Math. 20(3–4), 251–265 (2012)
Arioli, M., Loghin, D., Wathen, A.J.: Stopping criteria for iterations in finite element methods. Numer. Math. 99(3), 381–410 (2005)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11361016), the Basic and Frontier Explore Program of Chongqing Municipality, China (No. cstc2018jcyjAX0305), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. XDJK2018B032). The authors appreciate the valuable comments and suggestions made by the reviewers which led to an improvement of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, B., Shang, Y. Parallel iterative stabilized finite element methods based on the quadratic equal-order elements for incompressible flows. Calcolo 57, 34 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10092-020-00382-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10092-020-00382-6
Keywords
- Navier–Stokes equations
- Iterative stabilized method
- Finite element
- Parallel algorithm
- Domain decomposition method