Abstract
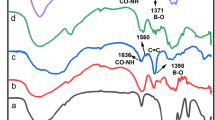
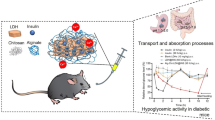
Effective delivery system for oral insulin administration is a promising way for diabetes therapy. Herein, we prepared alginate microbeads containing chitosan nanoparticles (CNP) for controlled release of insulin. CNP was developed by reaction between tripolyphosphate (TPP) and chitosan. The ratio of TPP to chitosan was optimized aiming with smaller and more unified distributed CNP. TEM and DLS analysis confirmed that CNP has size around 150 nm with low PDI value and strong surface charge. Encapsulate ability for bovine serum albumin, working as model protein, was 11.45%, and the encapsulate efficiency was 23.70%. To modify the release profile of protein suitable for oral insulin delivery, sodium alginate was applied to coat on the surface of CNP by electrostatic interaction. After that, CaCl2 was added to reinforce the alginate coating layer. FTIR analysis confirmed the interaction of alginate with chitosan and reaction with calcium ion. After reaction with Ca2+ ion, size measurement revealed that CNP was incorporated into alginate microbeads with mean diameter about 3.197 μm. Alginate microbeads presented irregular shape with small particles inside as revealed by optical microscope. Meanwhile, the release test demonstrated that protein release was pH-dependent. Acidic pH value retards protein release and neutral pH value promotes protein release. At last, insulin-loaded alginate microbeads were administrated to hyperglycemia model mice and blood glucose profile was monitored afterward. Insulin-loaded microbeads significantly lowered blood glucose level compared with mice treated with alginate microbeads without insulin. It is noted that insulin-loaded alginate microbeads could lower blood glucose level in much prolonged period of 96 h, indicating that insulin was released in controlled manner.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fonte, P., Araujo, F., Silva, C., Pereira, C., Reis, S., Santos, H. A., & Sarmento, B. (2015). Polymer-based nanoparticles for oral insulin delivery: revisited approaches. Biotechnology Advances, 33(6), 1342–1354.
Khafagy, E. S., Morishita, M., Onuki, Y., & Takayama, K. (2007). Current challenges in non-invasive insulin delivery systems: a comparative review. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 59(15), 1521–1546.
Chaturvedi, K., Ganguly, K., Nadagouda, M. N., & Aminabhavi, T. M. (2013). Polymeric hydrogels for oral insulin delivery. Journal of Controlled Release, 165(2), 129–138.
Mukhopadhyay, P., Mishra, R., Rana, D., & Kundu, P. P. (2012). Strategies for effective oral insulin delivery with modified chitosan nanoparticles: a review. Progress in Polymer Science, 37(11), 1457–1475.
Zokaei, E., Badoei-dalfrad, A., Ansari, M., Karami, Z., Eslaminejad, T., & Nematollahi-Mahani, S. N. (2019). Therapeutic potential of DNAzyme Loaded on chitosan/cyclodextrin nanoparticle to recovery of chemosensitivity in the MCF-7 cell line. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 187(3), 708–723.
Luo, Y. C., Teng, Z., Li, Y., & Wang, Q. (2015). Solid lipid nanoparticles for oral drug delivery: Chitosan coating improves stability, controlled delivery, mucoadhesion and cellular uptake. Carbohydrate Polymers, 122, 221–229.
Wang, J., Xu, M. X., Cheng, X. J., Kong, M., Liu, Y., Feng, C., & Chen, X. G. (2016). Positive/negative surface charge of chitosan based nanogels and its potential influence on oral insulin delivery. Carbohydrate Polymers, 136, 867–874.
George, M., & Abraham, T. E. (2006). Polyionic hydrocolloids for the intestinal delivery of protein drugs: alginate and chitosan - a review. Journal of Controlled Release, 114(1), 1–14.
Lopez-Hortas, L., Dominguez, H., & Torres, M. D. (2019). Valorisation of edible brown seaweeds by the recovery of bioactive compounds from aqueous phase using MHG to develop innovative hydrogels. Process Biochemistry, 78, 100–107.
Alexakis, T., Boadi, D. K., Quong, D., Groboillot, A. F., & Neufeld, R. J. (1995). Microencapsulation of DNA within alginate microspheres and crosslinked chitosan membranes for in vivo application. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 50(1), 93–106.
Li, J., Kim, S. Y., Chen, X., & Park, H. J. (2016). Calcium-alginate beads loaded with gallic acid: Preparation and characterization. LWT- Food Science and Technology, 68, 667–673.
Reis, C. P., Ribeiro, A. J., Neufeld, R. J., & Veiga, F. (2007). Alginate microparticles as novel carrier for oral insulin delivery. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 96(5), 977–989.
Silva, C. M., Ribeiro, A. J., Figueiredo, I. V., Goncalves, A. R., & Veiga, F. (2006). Alginate microspheres prepared by internal gelation: development and effect on insulin stability. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 311(1-2), 1–10.
Mukhopadhyay, P., Chakraborty, S., Bhattacharya, S., Mishra, R., & Kundu, P. P. (2015). pH-sensitive chitosan/alginate core-shell nanoparticles for efficient and safe oral insulin delivery. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 72, 640–648.
Liu, Y., Zong, S., & Li, J. (2019). Attenuation Effects of Bulk and Nanosized ZnO on Glucose, Lipid Level, and Inflammation Profile in Obese Mice. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 190, 475–486.
Wang, Y., Su, N., Hou, G., Li, J., & Ye, M. (2017). Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of a polysaccharide from Lachnum YM240 and its derivatives in mice, induced by a high fat diet and low dose STZ. Medchemcomm, 8(5), 964–974.
Liu, H., & Gao, C. Y. (2009). Preparation and properties of ionically cross-linked chitosan nanoparticles. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 20(7), 613–619.
Kalam, M. A. (2016). Development of chitosan nanoparticles coated with hyaluronic acid for topical ocular delivery of dexamethasone. International Journal Of Biological Macromolecules, 89, 127–136.
Li, J., Shin, G. H., Chen, X. G., & Park, H. J. (2015). Modified curcumin with hyaluronic acid: Combination of pro-drug and nano-micelle strategy to address the curcumin challenge. Food Research International, 69, 202–208.
Hari, P., Chandy, T., & Sharma, C. P. (1996). Chitosan/calcium–alginate beads for oral delivery of insulin. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 59(11), 1795–1801.
Zhang, H.-L., Wu, S.-h., Tao, Y., Zang, L.-q., & Su, Z.-q. (2010). Preparation and characterization of water-soluble chitosan nanoparticles as protein delivery system. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2010(1), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/898910.
Dehkordi, S. S., Alemzadeh, I., Vaziri, A. S., & Vossoughi, A. (2019). Optimization of alginate-whey protein isolate microcapsules for survivability and release behavior of probiotic bacteria. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 190, 182–196.
Zhang, N., Li, J., Jiang, W., Ren, C., Li, J., Xin, J., & Li, K. (2010). Effective protection and controlled release of insulin by cationic β-cyclodextrin polymers from alginate/chitosan nanoparticles. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 393(1-2), 213–219.
Gan, Q., & Wang, T. (2007). Chitosan nanoparticle as protein delivery carrier--systematic examination of fabrication conditions for efficient loading and release. Colloids and Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 59(1), 24–34.
Moeini, A., Cimmino, A., Dal Poggetto, G., Di Biase, M., Evidente, A., Masi, M., Lavermicocca, P., Valerio, F., Leone, A., Santagata, G., & Malinconico, M. (2018). Effect of pH and TPP concentration on chemico-physical properties, release kinetics and antifungal activity of Chitosan-TPP-Ungeremine microbeads. Carbohydrate Polymers, 195, 631–641.
Morris, G. A., Castile, J., Smith, A., Adams, G. G., & Harding, S. E. (2011). The effect of prolonged storage at different temperatures on the particle size distribution of tripolyphosphate (TPP) - chitosan nanoparticles. Carbohydrate Polymers, 84(4), 1430–1434.
Xu, Y. M., & Du, Y. M. (2003). Effect of molecular structure of chitosan on protein delivery properties of chitosan nanoparticles. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 250(1), 215–226.
Moya, M. L., Morley, M., Khanna, O., Opara, E. C., & Brey, E. M. (2012). Stability of alginate microbead properties in vitro. Journal Of Materials Science-Materials In Medicine, 23(4), 903–912.
Shah, S., Pal, A., Kaushik, V., & Devi, S. (2009). Preparation and characterization of venlafaxine hydrochloride-loaded chitosan nanoparticles and in vitro release of drug. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 112(5), 2876–2887.
Mumuni, M. A., Kenechukwu, F. C., Ofokansi, K. C., Attama, A. A., & Díaz, D. D. (2020). Insulin-loaded mucoadhesive nanoparticles based on mucin-chitosan complexes for oral delivery and diabetes treatment. Carbohydrate Polymers, 229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115506 .
Sarmento, B., Ferreira, D., Veiga, F., & Ribeiro, A. (2006). Characterization of insulin-loaded alginate nanoparticles produced by ionotropic pre-gelation through DSC and FTIR studies. Carbohydrate Polymers, 66(1), 1–7.
Sarmento, B., Ribeiro, A., Veiga, F., Sampaio, P., Neufeld, R., & Ferreira, D. (2007). Alginate/chitosan nanoparticles are effective for oral insulin delivery. Pharmaceutical Research, 24(12), 2198–2206.
Zhang, Y., Wei, W., Lv, P., Wang, L., & Ma, G. (2011). Preparation and evaluation of alginate–chitosan microspheres for oral delivery of insulin. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 77(1), 11–19.
Sarkar, S., Das, D., Dutta, P., Kalita, J., & Manna, P. (2020). Chitosan: A promising therapeutic agent and effective drug delivery system in managing diabetes mellitus. Carbohydrate Polymers, 247, 116594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116594.
Kevin, L., Huixia, W., Andrew S. N., & Julie A. C. (2019) Alginate/chitosan microparticles for gastric passage and intestinal release of therapeutic protein nanoparticles. Journal of Controlled Release, 295, 174–186.
Funding
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31700015), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (JZ2018HGTB0244) and Anhui Natural Science Foundation (1808085QC66).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Financial Interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Wu, H., Jiang, K. et al. Alginate Calcium Microbeads Containing Chitosan Nanoparticles for Controlled Insulin Release. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 193, 463–478 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-020-03420-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-020-03420-9