Abstract
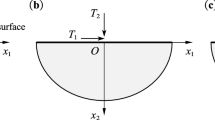
This paper proposes a numerical solution method for upper bound shakedown analysis of perfectly elasto-plastic thin plates by employing the C\(^{1}\) natural element method. Based on the Koiter’s theorem and von Mises yield criterion, the nonlinear mathematical programming formulation for upper bound shakedown analysis of thin plates is established. In this formulation, the trail function of residual displacement increment is approximated by using the C\(^{1}\) shape functions, the plastic incompressibility condition is satisfied by introducing a constant matrix in the objective function, and the time integration is resolved by using the König’s technique. Meanwhile, the objective function is linearized by distinguishing the non-plastic integral points from the plastic integral points and revising the objective function and associated equality constraints at each iteration. Finally, the upper bound shakedown load multipliers of thin plates are obtained by direct iterative and monotone convergence processes. Several benchmark examples verify the good precision and fast convergence of this proposed method.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen G, Liu YH. Numerical theories and engineering methods for structural limit and shakedown analyses. Beijing, 2006.
Melan E. Zur Plastizität des räumlichen Kontinuums. Ing-Arch. 1938;9:115–26.
Koiter WT. A new general theorem on shakedown of elastic-plasitc structures. Proc Konink Nederl Akad Wetensch B. 1956;59:24–34.
Zhou ST, Liu YH, Wang DD, Wang K, Yu SY. Upper bound shakedown analysis with the nodal natural element method. Comput Mech. 2014;54(5):1111–28.
Li KY, Liu XS, Xu BY. An experimental shakedown investigation of built-in circular plates. Chin J Appl Mech. 1989;6(3):1989.
Giambanco F, Palizzolo L, Polizzotto C. Optimal shakedown design of circular plates. J Eng Mech-ASCE. 1994;120(12):2535–56.
Chinh PD. Plastic collapse of a circular plate under cyclic loads. Int J Plast. 2003;19(4):547–59.
Yu MH, Ma GW, Li JC. Structural plasticity limit, shakedown and dynamic plastic analyses of structures. New York: Springer; 2009.
Alwis WAM, Grundy P. Shakedown analysis of plates. Int J Mech Sci. 1985;27(1–2):71–82.
Qian LX, Wang ZB. Limit analysis and shakedown analysis of bending plates and rotational shell-method of temperature parameters Acta Mechanica Sinica. 1989;21(sup):1989.
Atkociunas J, Rimkus L, Skarlzauskas V, Jarmolajeva E. Optimal shakedown design of plates. Mechanika. 2007;5:14–23.
Tran TN. A dual algorithm for shakedown analysis of plate bending. Int J Numer Meth Eng. 2011;86(7):862–75.
Hasbroucq S, Oueslati A, de Saxce G. Analytical study of the asymptotic behavior of a thin plate with temperature-dependent elastic modulus under cyclic thermomechanical loadings. Int J Mech Sci. 2012;54:95–104.
Zheng H, Peng X, Hu N. Optimal analysis for shakedown of functionally graded (FG) bree plate with genetic algorithm. Comput Mater Contin. 2014;41(1):55–84.
Blazevicius G, Rimkus L, Merkevicute D, Atkociunas J. Shakedown analysis of circular plates using a yield criterion of the mean. Struct Multidiscip Optim. 2017;55:25–36.
Zhang X, Liu Y, Ma S. Meshfree methods and their applications. Adv Mech. 2009;39(1):1–36 (in Chinese).
Le CV, Gilbert M, Askes H. Limit analysis of plates using the EFG method and second-order cone programming. Int J Numer Meth Eng. 2009;78(13):1532–52.
Le CV, Askes H, Gilbert M. Adaptive element-free Galerkin method applied to the limit analysis of plates. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2010;199(37–40):2487–96.
Zhou ST, Liu YH, Chen SS. Upper bound limit analysis of plates utilizing the C1 natural element method. Comput Mech. 2012;50(5):543–61.
Cueto E, Sukumar N, Calvo B, Martinez MA, Cegonino J, Doblare M. Overview and recent advances in natural neighbour Galerkin methods. Arch Comput Methods Eng. 2003;10(4):307–84.
Dinis LMJS, Jorge RMN, Belinha J. Analysis of plates and laminates using the natural neighbor radial point interpolation method. Eng Anal Bound Elem. 2008;32(3):267–79.
Dinis LMJS, Jorge RMN, Belinha J. A natural neighbour meshless method with a 3D shell-like approach in the dynamic analysis of thin 3D structures. Thin-Walled Struct. 2011;49:185–96.
Belinha J, Dinis LMJS, Natal Jorge RM. Analysis of thick plates by natural radial element method. Int J Mech Sci. 2013;76:33–48.
Belinha J, Dinis LMJS, Natal Jorge RM. Composite laminated plate analysis using natural radial element method. Compos Struct. 2013;103:50–67.
Li S, Liu K, Long S, Li G. The natural neighbor Petrov–Galerkin method for thick plates. Eng Anal Bound Elem. 2011;35(4):616–22.
Somireddy M, Rajagopal A. Meshless natural neighbor Galerkin method for the bending and vibration analysis of composite plates. Compos Struct. 2014;111:138–46.
Kumar B, Somireddy M, Rajagopal A. Adaptive analysis of plates and laminates using natural neighbor Galerkin meshless method. Eng Comput. 2019;35:201–14.
Sukumar N, Moran B. C-1 natural neighbor interpolant for partial differential equations. Numer Methods Partial Differ Equ. 1999;15(4):417–47.
Braun J, Sambridge M. A numerical method for solving partial differential equations on highly irregular evolving grids. Nature. 1995;376:655–60.
Zhou ST, Liu YH. Upper bound limit analysis based on the natural element method. Acta Mech Sin. 2012;28(5):1398–415.
Zhou ST, Li Y, Zhou HB, Liu YH, Yu SY. A numerical estimate method for limit analysis of plane structures by adopting the natural element method. In: SMiRT-22 proceeding. San Francisco, California, USA, 2013.8.18-23:1279-1286.
Zhou ST, Liu YH, Chen SS. Upper-bound limit analysis method of thin plates based on the nonconforming rectangular bending element. J Tsinghua Univ (Sci Technol). 2011;51(12):1887–93 (in Chinese).
Acknowledgements
S. Zhou is supported by the Chinese Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2013M540934). Y. Liu is supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0801905, 2017YFF0210704).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, S., Liu, Y., Ma, B. et al. Upper Bound Shakedown Analysis of Plates Utilizing the C\(^{1}\) Natural Element Method. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 34, 221–236 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10338-020-00193-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10338-020-00193-w