Abstract
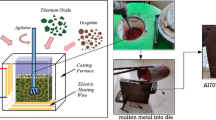
Under various electromagnetic induction heating powers, different Al3Ti/Al composites were fabricated by in-situ synthesis method from aluminum and titanium fibers. Microstructures and particles distribution of the composites were examined by XRD, SEM and EDS. The results show that no other intermetallic compounds beside Al3Ti can be in-situ synthesized. Around the titanium fibers, the reaction zones and diffusion zones can be obviously found. Due to the stirring of the electromagnetic function, the formation of the micro-cracks inside the reaction zone was conducive to the peeling off of the Al3Ti particles, and ensures the continuous reaction between liquid aluminum and titanium fibers, as well as the diffusion of Al3Ti particles. At the same time, there were secondary splits of Al3Ti particles located in diffusion zones. Two-body abrasion test shows that with the increase of induction heating power, the wear rates of the composites reduced and the number of grooves decreased.
摘要
通过施加不同的感应加热功率, 由铝和钛纤维进行原位反应, 制备出 Al3Ti/Al 复合材料. 通过 XRD,SEM 和 EDS 表征了复合材料的微观结构和颗粒分布情况. 结果表明, 反应产物仅为 Al3Ti 金属间化合物, 钛纤维周围有明显的反应区和扩散区. 反应区的微裂纹有利于 Al3Ti 颗粒的剥离, 促进了液态铝与钛纤维之间的反应. 由于电磁感应加热的搅拌功能, 促进了Al3Ti 颗粒的反应和扩散. 同时, Al3Ti 颗粒在扩散过程中存在二次分离与剥落. 两体磨损试验表明, 随着感应加热功率的加大, 磨损率和沟槽数量减少, 复合材料的耐磨性能提高.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
GUPTA P K, SRIVASTAVA R K. Fabrication of ceramic reinforcement aluminium and its alloys metal matrix composite materials: A review [J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2018, 5(9): 18761–18775. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2018.06.223.
ZHU He-guo, JIANG Ya-ling, SONG Jin-zhu, LI Jian-liang, MUNROE P, XIE Zong-han. In situ synthesis and characterization of a hierarchically structured Al2O3/Al3Ti composite [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2013, 48(2): 929–935. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6817-0.
LIU Zhi-wei, CHENG Na, ZHENG Qiao-ling, WU Jian-hua, HAN Qing-you, HUANG Zhi-fu, XING Jian-dong, LI Ye-fei, GAO Yi-ming. Processing and tensile properties of A356 composites containing in situ small-sized Al3Ti particulates [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2018, 710: 392–399. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.11.005.
ZHANG Dong-qiang, YANG Ping, WU Jian-yang, ZHAO Jing, CHEN Yan-an. Preparation of defect free ceramic/Ti composite membranes by surface modification and in situ oxidation [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(12): 3295–3304. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4253-x.
GUPTA R, DANIEL B S S. Impression creep behaviour of in-situ Al3Ti reinforced Al alloy composite fabricated by salt-melt reaction technique [J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2018, 5(9): 16936–16945. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2018.04.097.
CHIANEH V A, HOSSEINI H M, NOFAR M. Micro structural features and mechanical properties of Al-Al3Ti composite fabricated by in-situ powder metallurgy route [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 473(1, 2): 127–132. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.05.068.
GUPTA R, DANIEL B S S. Impression creep behaviour of ultrasonically processed in-situ Al3Ti reinforced aluminium composite [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2018, 733: 257–266. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.07.017.
XU Qian-gang, ZHANG Hai-feng, DING Bing-zhe, HU Zhuang-qi. Nature and growth of interaction layers formed during the reaction between solid Ni and liquid Al [J]. Journal of Materials Sciences and Technology, 2009, 18(6): 512–515. DOI: EN/Y2002/V18/I06/512.
QIN Jin, CHEN Gang, WANG Bo, HU Nan, HAN Fei, DU Zhi-ming. Formation of in-situ Al3Ti particles from globular Ti powders and Al alloy melt under ultrasonic vibration [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 653: 32–38. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.09.005.
ARJMAND S, KHAYATI G R, AKBAIR, G H. Al/Ti5Si3-Al3Ti composite prepared via in-situ surface coating of Ti using tungsten inert gas welding [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 808: 151739. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.151739.
KESANGAM N, PINITSOONTORN S, SRIMANOSAOWAPAK S. Effect of initial microstructure on induction heating of A319 aluminium alloy [J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2018, 5(3): 9615–9623. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2017.10.148.
TOCHAEE E B, HOSSEINI H M, REIHANI S S. Fabrication of high strength in-situ Al-Al3Ti nanocomposite by mechanical alloying and hot extrusion: Investigation of fracture toughness [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2016, 658: 246–254. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.02.010.
LIU Zhi-wei, HAN Qing-you, LI Jian-guo. Fabrication of in situ Al3Ti/Al composites by using ultrasound assisted direct reaction between solid Ti powders and liquid Al [J]. Powder Technology, 2013, 247: 55–59. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2013.07.005.
TOMOSHIGE R, MATSUSHITA T. Production of titanium-aluminum-carbon ternary composites with dispersed fine TiC particles by combustion synthesis and their microstructure observations [J]. Ceram Soc Jpn, 1996, 104: 94–100. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2109/jcersj.104.94.
LI Gui-rong, WANG Hong-ming, ZHAO Yu-tao, CHEN Deng-bin, CHEN Gang, CHENG Xiao-nong. Microstructure of in situ Al3Ti/6351Al composites fabricated with electromagnetic stirring and fluxes [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(4): 577–583. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(09)60181-3.
MIRJALILI M, SOLTANIEH M, MATSUURA K, OHNO M. On the kinetics of TiAl3 intermetallic layer formation in the titanium and aluminum diffusion couple [J]. Intermetallics, 2013, 32: 297–302. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2012.08.017.
SATO H, WATANABE Y. Three-dimensional microstructural analysis of fragmentation behavior of platelet Al3Ti particles in Al-Al3Ti composite deformed by equal-channel angular pressing [J]. Materials Characterization, 2018, 144: 305–315. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2018.07.005.
JIANG Shu-ying, LI Shi-chun, ZHANG Lei. Microstructure evolution of Al-Ti liquid-solid interface [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23: 3545–3552. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62899-X.
MA Si-ming, WANG Yong-shneg, WANG Xiao-ming. The in-situ formation of Al3Ti reinforcing particulates in an Al-7wt% Si alloy and their effects on mechanical properties [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 792: 365–374. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.04.064.
WANG Hong-ming, LI Gui-rong, ZHAO Yu-tao, ZHANG Zhao. Microstructure, billet surface quality and tensile property of (Al2O3+Al3Zr)p/Al composites in situ synthesized with electromagnetic field [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2011, 509(18): 5696–5700. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.02.139.
LIU Zheng, LIU Xiao-mei, HU Chun-hui, MAO Wei-min. Research on fractal characteristics of primary phase morphology in semi-solid A356 alloy [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters), 2009, 22(6): 421–428. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-7191(08)60118-0.
ZOU Qing-chuan, HAN Ning, SHEN Zhang-feng, JIE Jin-chuan, LI Ting-ju. Effects of AlB2/AlP phase and electromagnetic stirring on impurity B/P removal in the solidification process of Al-30Si alloy [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2018, 207: 151–157. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.06.052.
LI Y, ZHANG Yu, BI Jing, LUO Zhen. Impact of electromagnetic stirring upon weld quality of Al/Ti dissimilar materials resistance spot welding [J]. Materials & Design, 2015: 577–586. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.06.042.
AGRAWAL S, GHOSE A K, CHAKRABARTY I. Effect of rotary electromagnetic stirring during solidification of in-situ Al-TiB2 composites [J]. Materials & Design, 2017, 113: 195–206. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.10.007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The overarching research goals were developed by NIU Li-bin, WU Hong and MA Jun. MA Jun and NIU Li-bin provided the first draft of manuscript. GAO Chong provided the measured data. AN Yu-jiao conducted the literature review. All authors replied to reviewers’ comments and revised the final version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
MA Jun, NIU Li-bin, WU Hong, GAO Chong, AN Yu-jiao declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(2015DFR50990-01) supported by International Cooperation Project of Ministry of Science and Technology of China; Projects(18JS060, 18JS075) supported by the Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Nano-materials and Technology, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, J., Niu, Lb., Wu, H. et al. Formation and wear behaviors of in-situ Al3Ti/Al composites using aluminum and titanium fibers under electromagnetic induction heating. J. Cent. South Univ. 27, 3594–3602 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4500-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4500-1