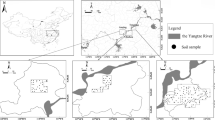
Abstract
Tanning industry has been identified as a significant source of heavy metals; however, heavy metals contamination in farmland soil due to small-scale tanning activities remains unstudied. Here, samples from topsoil, profile soil, water and sediments in the vicinity of a small-scale tanning area in Nanning, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, southern China, were collected to explore the contamination characteristics and source apportionment of Cd, Cr, Hg, As, Cu, Pb, Ni and Zn. The results show that the farmland soil was mainly contaminated by Cr and its content was 33.40–3830.00 mg kg−1. The highest level of Cr, Cd and Hg was above their thresholds, while the average contents of Cd, Cr, Pb and Hg exceeded the corresponding background levels. Moreover, enrichment of Cr in soil profiles and stream sediments were also observed, whose concentrations varied from 11.50 to 2590.00 mg kg−1 and 738.00 to 11,200.00 mg kg−1, respectively. Concentrations of Cr in top soils and soil profiles from farmland surrounding the stream were significantly higher than those from other areas, and the soils surrounding the stream were moderately to heavily polluted. The multivariate statistical analysis indicated that the heavy metals originated from traffic (Cu, Ni, Zn, Hg, and Pb), agriculture (Cr and Cd) and nature (As). Source apportionment with PMF model results showed that the relative contribution rates of heavy metals by traffic, tanning, agriculture, other industrial activities and natural sources were 16.00%, 18.88%, 20.88%, 22.04% and 22.20%, respectively. These findings indicate that small-scale tanning activities could also lead to heavy metal accumulation in the surrounding environment, which requires decision-makers to pay more attention and to develop effective remediation procedures.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi, K., & Tainosho, Y. (2004). Characterization of heavy metal particles embedded in tire dust. Environment International, 30(8), 1009–1017.
Afzal, M., Shabir, G., Iqbal, S., Mustafa, T., Khan, Q. M., & Khalid, Z. M. (2014). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soil and groundwater at leather industrial area of Kasur, Pakistan. CLEAN – Soil, Air, Water, 42(8), 1133–1139.
Ahmed, E., Abdulla, H. M., Mohamed, A. H., & El-Bassuony, A. D. (2016). Remediation and recycling of chromium from tannery wastewater using combined chemical–biological treatment system. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 104, 1–10.
Alam, M. S., Han, B., Al, M., & Pichtel, J. (2020). Assessment of soil and groundwater contamination at a former Tannery district in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 42, 1905–1920. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00457-6.
Alemu, T., Mekonnen, A., & Leta, S. (2017). Integrated tannery wastewater treatment for effluent reuse for irrigation: Encouraging water efficiency and sustainable development in developing countries. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 5, 1–20.
Ali, Z., Malik, R. N., Shinwari, Z. K., & Qadir, A. (2015). Enrichment, risk assessment, and statistical apportionment of heavy metals in tannery-affected areas. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 12(2), 537–550.
Amaral, D. F., Montalvão, M. F., Mendes, B. O., de Souza, J. M., Chagas, T. Q., Rodrigues, A. S. L., et al. (2018). Insights about the toxic effects of tannery effluent on Lithobates catesbeianus tadpoles. Science of the Total Environment, 621, 791–801.
Andleeb, S., Mahmood, T., Khalid, A., Akrim, F., & Fatima, H. (2018). Hexavalent chromium induces testicular dysfunction in small Indian mongoose (Herpestes javanicus) inhabiting tanneries area of Kasur District, Pakistan. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 148, 1001–1009.
Balkhair, K. S., & Ashraf, M. A. (2016). Field accumulation risks of heavy metals in soil and vegetable crop irrigated with sewage water in western region of Saudi Arabia. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 23(1), S32–S44.
Bareen, F.-E., & Tahira, S. A. (2011). Metal accumulation potential of wild plants in tannery effluent contaminated soil of Kasur, Pakistan: Field trials for toxic metal cleanup using Suaeda fruticosa. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 186(1), 443–450.
Chen, X., & Lu, X. (2018). Contamination characteristics and source apportionment of heavy metals in topsoil from an area in Xi’an City, China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 151, 153–160.
Chen, H., Arocena, J. M., Li, J., Thring, R. W., & Zhou, J. (2012). Mobility and storage sinks for chromium and other metals in soils impacted by leather tannery wastes. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 14(12), 3240–3248.
Cheng, J. L., Zhou, S. H., & Zhu, Y. W. (2007). Assessment and mapping of environmental quality in agricultural soils of Zhejiang Province, China. Chinesse Journal of Environmental Sciences, 19(1), 50–54.
Cho, I.-G., Park, M.-K., Cho, H.-K., Jeon, J.-W., Lee, S.-E., & Choi, S.-D. (2019). Characteristics of metal contamination in paddy soils from three industrial cities in South Korea. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 41(5), 1895–1907.
Choppala, G., Bolan, N., & Park, J. H. (2013). Chapter two: chromium contamination and its risk assessment in complex environmental settings. Advances in Agronomy, 120, 129–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-407686-0.00002-6.
Cruz, A. C. F., Gusso-Choueri, P., de Araujo, G. S., Campos, B. G., & Abessa, D. M. S. (2019). Levels of metals and toxicity in sediments from a Ramsar site influenced by former mining activities. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 171, 162–172.
Deng, Y., Jiang, L., Xu, L., Hao, X., Zhang, S., Xu, M., et al. (2019). Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in contaminated paddy fields—A case study in Xiangtan City, southern China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 171, 281–289.
Dotaniya, M. L., Das, H., & Meena, V. D. (2014). Assessment of chromium efficacy on germination, root elongation, and coleoptile growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) at different growth periods. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186(5), 2957–2963.
Dotaniya, M. L., Meena, V. D., Rajendiran, S., Coumar, M. V., Saha, J. K., Kundu, S., et al. (2017a). Geo-accumulation indices of heavy metals in soil and groundwater of Kanpur, India under long term irrigation of tannery effluent. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 98(5), 706–711.
Dotaniya, M. L., Rajendiran, S., Meena, V. D., Saha, J. K., Coumar, M. V., Kundu, S., et al. (2017b). Influence of chromium contamination on carbon mineralization and enzymatic activities in vertisol. Agricultural Research, 6(1), 91–96.
Duzgoren-Aydin, N. S., Li, X. D., & Wong, S. C. (2004). Lead contamination and isotope signatures in the urban environment of Hong Kong. Environment International, 30(2), 209–217.
Ertani, A., Mietto, A., Borin, M., & Nardi, S. (2017). Chromium in agricultural soils and crops: A review. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 228(5), 190.
Fahim, N. F., Barsoum, B. N., Eid, A. E., & Khalil, M. S. (2006). Removal of chromium(III) from tannery wastewater using activated carbon from sugar industrial waste. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 136(2), 303–309.
Guan, Q., Wang, F., Xu, C., Pan, N., Lin, J., Zhao, R., et al. (2018). Source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soil based on PMF: A case study in Hexi Corridor, northwest China. Chemosphere, 193, 189–197.
Haroun, M., Idris, A., & Syed Omar, S. R. (2007). A study of heavy metals and their fate in the composting of tannery sludge. Waste Management, 27(11), 1541–1550.
Hasan, M. M., Hosain, S., Poddar, P., Chowdhury, A. B. M. A., Katengeza, E. W., & Roy, U. K. (2019). Heavy metal toxicity from the leather industry in Bangladesh: A case study of human exposure in Dhaka industrial area. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(9), 530.
Jiang, Y., Chao, S., Liu, J., Yang, Y., Chen, Y., Zhang, A., et al. (2017). Source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil for a township in Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere, 168, 1658–1668.
Johnston, C. P., & Chrysochoou, M. (2015). Mechanisms of chromate adsorption on boehmite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 281, 56–63.
Junaid, M., Hashmi, M. Z., Tang, Y.-M., Malik, R. N., & Pei, D.-S. (2017). Potential health risk of heavy metals in the leather manufacturing industries in Sialkot, Pakistan. Scitific Reports-UK, 7(1), 8848.
Kotaś, J., & Stasicka, Z. (2000). Chromium occurrence in the environment and methods of its speciation. Environmental Pollution, 107(3), 263–283.
Kumar, A., Usmani, Z., Ahirwal, J., & Rani, P. (2019). Phytomanagement of polluted sites. In V. C. Pandey & K. Bauddh (Eds.), Phytomanagement of chromium contaminated brown fields (pp. 447–469). New York: Elsevier.
Lee, C. S., Li, X. D., Shi, W. Z., Cheung, S. C., & Thornton, I. (2006). Metal contamination in urban, suburban, and country park soils of Hong Kong: A study based on GIS and multivariate statistics. Science of the Total Environment, 356(1), 45–61.
Liu, J., Liu, Y. J., Liu, Y., Liu, Z., & Zhang, A. N. (2018). Quantitative contributions of the major sources of heavy metals in soils to ecosystem and human health risks: A case study of Yulin, China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 164, 261–269.
Lofrano, G., Meriç, S., Zengin, G. E., & Orhon, D. (2013). Chemical and biological treatment technologies for leather tannery chemicals and wastewaters: A review. Science of the Total Environment, 461–462, 265–281.
Luo, L., Ma, Y., Zhang, S., Wei, D., & Zhu, Y.-G. (2009). An inventory of trace element inputs to agricultural soils in China. Journal of Environmental Management, 90(8), 2524–2530.
Ma, H., Wang, X., & Zhang, C. (2003a). Cr(III) accumulation and phytoavailability in alkaline soils contaminated by tannery sludge. Chemical Speciation & Bioavailability, 15(1), 15–22.
Majeed, S., Rashid, S., Qadir, A., Mackay, C., & Hayat, F. (2018). Spatial patterns of pollutants in water of metropolitan drain in Lahore, Pakistan, using multivariate statistical techniques. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190(3), 128.
McBride, M. B., Richards, B. K., Steenhuis, T., Russo, J. J., & Sauvé, S. (1997). Mobility and solubility of toxic metals and nutrients in soil fifteen years after sludge application. Soil Science, 162(7), 487–500.
Men, C., Liu, R., Xu, F., Wang, Q., Guo, L., & Shen, Z. (2018). Pollution characteristics, risk assessment, and source apportionment of heavy metals in road dust in Beijing, China. Science of the Total Environment, 612, 138–147.
MEPRC. (2004). The technical specification for soil environmental monitoring. HJ/T166-2004) (in Chinese).
MEPRC. (2005). Standards for irrigation water quality (GB 5084-2005) (in Chinese). Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China.
MEPRC. (2018). Soil environmental quality risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land (GB 15618-2018) (in Chinese). Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China.
Mondol, M., Asia, A., Chamon, A., & Faiz, S. (2017). Contamination of soil and plant by the Hazaribagh tannery industries. Journal of the Asiatic Society of Bangladesh, Science, 43(2), 207–222.
Ogunlaja, A., Ogunlaja, O. O., Okewole, D. M., & Morenikeji, O. A. (2019). Risk assessment and source identification of heavy metal contamination by multivariate and hazard index analyses of a pipeline vandalised area in Lagos State, Nigeria. Science of the Total Environment, 651, 2943–2952.
Paatero, P., & Tapper, U. (1994). Positive matrix factorization: A non-negative factor model with optimal utilization of error estimates of data values. Environmetrics, 5(2), 111–126.
Paul, D., Choudhary, B., Gupta, T., & Jose, M. T. (2015). Spatial distribution and the extent of heavy metal and hexavalent chromium pollution in agricultural soils from Jajmau, India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73(7), 3565–3577.
Qing, X., Yutong, Z., & Shenggao, L. (2015). Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risk in urban soils of steel industrial city (Anshan), Liaoning, Northeast China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 120, 377–385.
Rahaman, A., Afroze, J. S., Bashar, K., Ali, M. F., & Hosen, M. R. (2016). A comparative study of heavy metal concentration in different layers of tannery vicinity soil and near agricultural soil. American Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 12, 880–889.
Rani, P., Kumar, A., & Arya, R. C. (2017). Stabilization of tannery sludge amended soil using Ricinus communis, Brassica juncea and Nerium oleander. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 17(5), 1449–1458.
Sadeghi, H., Fazlzadeh, M., Zarei, A., Mahvi, A.H., Nazmara, S. (2020). Spatial distribution and contamination of heavy metals in surface water, groundwater and topsoil surrounding Moghan’s tannery site in Ardabil, Iran. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 1–11.
Sadiq, M., Alam, I., El-Mubarek, A., & Al-Mohdhar, H. M. (1989). Preliminary evaluation of metal pollution from wear of auto tires. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 42(5), 743–748.
Saxena, G., Chandra, R., & Bharagava, R. N. (2017). Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology, volume 240. In P. de Voogt (Ed.), Environmental pollution, toxicity profile and treatment approaches for tannery wastewater and its chemical pollutants (pp. 31–69). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Sekabira, K., Origa, H. O., Basamba, T. A., Mutumba, G., & Kakudidi, E. (2010). Assessment of heavy metal pollution in the urban stream sediments and its tributaries. International Journal of Environmental Science & Technology, 7(3), 435–446.
Shafiq, M., Shaukat, T., Nazir, A., & Bareen, F.-E. (2017). Modeling of Cr contamination in the agricultural lands of three villages near the leather industry in Kasur, Pakistan, using statistical and GIS techniques. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(8), 423.
Sharma, I., & Goyal, D. (2009). Chromium (III) removal from tannery effluent by Streptomyces sp. (MB2) waste biomass of fermentation process. International Journal of Integrative Biology, 6, 148.
Shi, P., Xiao, J., Wang, Y., & Chen, L. (2014). Assessment of ecological and human health risks of heavy metal contamination in agriculture soils disturbed by pipeline construction. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 11(3), 2504–2520.
Shi, J., Chen, H., Arocena, J. M., Whitcombe, T., Thring, R. W., & Memiaghe, J. N. (2016). Elemental sulfur amendment decreases bio-available Cr-VI in soils impacted by leather tanneries. Environmental Pollution, 212, 57–64.
Sun, Z. H., Xie, X. D., Wang, P., Hu, Y. A., & Cheng, H. F. (2018). Heavy metal pollution caused by small-scale metal ore mining activities: A case study from a polymetallic mine in South China. Science of the Total Environment, 639, 217–227.
Tariq, S. R., Shah, M. H., Shaheen, N., Khalique, A., Manzoor, S., & Jaffar, M. (2005). Multivariate analysis of selected metals in tannery effluents and related soil. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 122(1), 17–22.
USEPA. (1996). Method 3052: Microwave assisted acid digestion of siliceous and organically based matrices. Test methods for evaluating solid waste. USEPA, Washington, DC, USA.
USEPA. (2007). Method 6020A: Inductively coupled plasma-mass spectroscopy. USEPA, Washington, DC, USA.
Wei, F. S., Chen, J. S., Wu, Y. Y., & Zheng, C. J. (1991). Background contents of elements in China soils. Publishing House of Chinese Environment Sciences, Beijing, 04, 12–19.
Wu, W., Wu, P., Yang, F., Sun, D.-L., Zhang, D.-X., & Zhou, Y.-K. (2018). Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risks in urban soils around an electronics manufacturing facility. Science of the Total Environment, 630, 53–61.
Xiao, R., Guo, D., Ali, A., Mi, S., Liu, T., Ren, C., et al. (2019). Accumulation, ecological-health risks assessment, and source apportionment of heavy metals in paddy soils: A case study in Hanzhong, Shaanxi, China. Environmental Pollution, 248, 349–357.
Yang, Z., Lu, W., Long, Y., Bao, X., & Yang, Q. (2011). Assessment of heavy metals contamination in urban topsoil from Changchun City. China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 108(1), 27–38.
Zhang, C. X., Lin, J., Jia, X. J., & Peng, B. Y. (2016). A salt-free and chromium discharge minimizing tanning technology: the novel cleaner integrated chrome tanning process. J Clean Prod, 112, 1055–1063.
Zhang, X., Wei, S., Sun, Q., Wadood, S. A., & Guo, B. (2018). Source identification and spatial distribution of arsenic and heavy metals in agricultural soil around Hunan industrial estate by positive matrix factorization model, principle components analysis and geo statistical analysis. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 159, 354–362.
Zhou, F., Guo, H., & Hao, Z. (2007). Spatial distribution of heavy metals in Hong Kong’s marine sediments and their human impacts: A GIS-based chemometric approach. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 54(9), 1372–1384.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Plan of China (2018YFC1802201).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Cai, X., Xia, Z. et al. Contamination characteristics of heavy metals in a small-scale tanning area of southern China and their source analysis. Environ Geochem Health 45, 5655–5668 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00732-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00732-x