Abstract
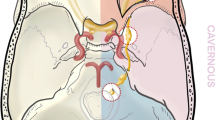
Most studies reported that cystic vestibular schwannoma (CVS) surgery has a less favourable prognosis than solid vestibular schwannoma (SVS) surgery. However, some studies report that it is unclear whether surgical outcomes for these conditions exhibit significant differences. The aim of this meta-analysis was to pool the current literature and describe and analyse any differences in the clinical symptoms and surgical outcomes among CVS and SVS. PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane databases were searched following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines through April 22, 2020. Outcomes were analysed using a meta-analysis of the proportions. The results of the search yielded 17 studies that met the criteria for inclusion and analysis, involving 3074 participants (including 821 patients with CVSs and 2253 patients with SVSs). No significant differences in the extent of tumour resection (gross-total resection versus non-gross-total resection; RR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.86–1.01; p = 0.096) and most other outcomes were noted between CVS and SVS cohorts. However, facial nerve function (House-Brackmann Grade I or II versus III or more) of CVS patients was worse (RR, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.78–0.93; p < 0.001) compared with SVS patients with more than 1 year of follow-up after surgery. The criteria of cystic acoustic neuroma needs to be further unified, and prospective cohort studies with larger sample sizes should be performed for further verification of these results in the future.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benech F, Perez R, Fontanella MM, Morra B, Albera R, Ducati A (2005) Cystic versus solid vestibular schwannomas: a series of 80 grade III-IV patients. Neurosurg Rev 28:209–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-005-0380-y
Bowden G, Cavaleri J, Monaco E III, Niranjan A, Flickinger J, Lunsford LD (2017) Cystic vestibular schwannomas respond best to radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 81:490–497. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyx027
Breun M, Nickl R, Perez J, Hagen R, Lohr M, Vince G, Trautner H, Ernestus RI, Matthies C (2019) Vestibular schwannoma resection in a consecutive series of 502 cases via the retrosigmoid approach: technical aspects, complications, and functional outcome. World Neurosurg 129:e114–e127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2019.05.056
Charabi S, Mantoni M, Tos M, Thomsen J (1994) Cystic vestibular schwannomas: neuroimaging and growth rate. J Laryngol Otol 108:375–379. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0022215100126854
Charabi S, Tos M, Borgesen SE, Thomsen J (1994) Cystic acoustic neuromas. Results of translabyrinthine surgery. Archives of otolaryngology--head & neck surgery 120:1333–1338. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.1994.01880360031006
Efthimiou O (2018) Practical guide to the meta-analysis of rare events. Evid Based Mental Health 21:72–76. https://doi.org/10.1136/eb-2018-102911
Eser Ocak P, Dogan I, Ocak U, Dinc C, Baskaya MK (2018) Facial nerve outcome and extent of resection in cystic versus solid vestibular schwannomas in radiosurgery era. Neurosurg Focus 44:E3. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.12.Focus17667
Frisch CD, Jacob JT, Carlson ML, Foote RL, Driscoll CL, Neff BA, Pollock BE, Link MJ (2017) Stereotactic radiosurgery for cystic vestibular schwannomas. Neurosurgery 80:112–118. https://doi.org/10.1227/neu.0000000000001376
Fundova P, Charabi S, Tos M, Thomsen J (2000) Cystic vestibular schwannoma: surgical outcome. The Journal of laryngology and otology 114:935–939. https://doi.org/10.1258/0022215001904653
Ganslandt O, Fahrig A, Strauss C (2008) Hemorrhage into cystic vestibular schwannoma following stereotactic radiation therapy. Zentralbl Neurochir 69:204–206. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2008-1077074
Gerganov VM, Klinge PM, Nouri M, Stieglitz L, Samii M, Samii A (2009) Prognostic clinical and radiological parameters for immediate facial nerve function following vestibular schwannoma surgery. Acta Neurochir 151:581–587; discussion 587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-009-0288-3
Han JH, Baek KH, Lee YW, Hur YK, Kim HJ, Moon IS (2018) Comparison of clinical characteristics and surgical outcomes of cystic and solid vestibular schwannomas. Otol Neurotol 39:e381–e386. https://doi.org/10.1097/mao.0000000000001813
Higgins JP, Thompson SG (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 21:1539–1558. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.1186
Hirato M, Inoue H, Zama A, Ohye C, Shibazaki T, Andou Y (1996) Gamma knife radiosurgery for acoustic schwannoma: effects of low radiation dose and functional prognosis. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 66(Suppl 1):134–141. https://doi.org/10.1159/000099803
House JW, Brackmann DE (1985) Facial nerve grading system. Otolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery 93:146–147. https://doi.org/10.1177/019459988509300202
Jian BJ, Sughrue ME, Kaur R, Rutkowski MJ, Kane AJ, Kaur G, Yang I, Pitts LH, Parsa AT (2011) Implications of cystic features in vestibular schwannomas of patients undergoing microsurgical resection. Neurosurgery 68:874–880; discussion 879-880. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e318208f614
Jones SE, Baguley DM, Moffat DA (2007) Are facial nerve outcomes worse following surgery for cystic vestibular schwannoma? Skull Base 17:281–284. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-986436
JulianPTHiggins TSG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ (Clinical research ed) 327:557–560. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
Jung S, Kang SS, Kim TS, Kim HJ, Jeong SK, Kim SC, Lee JK, Kim JH, Kim SH, Lee JH (2000) Current surgical results of retrosigmoid approach in extralarge vestibular schwannomas. Surg Neurol 53:370–377; discussion 377-378. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0090-3019(00)00196-8
Kameyama S, Tanaka R, Honda Y, Hasegawa A, Yamazaki H, Kawaguchi T (1994) The long-term growth rate of residual acoustic neurinomas. Acta Neurochir 129:127–130. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01406491
Kameyama S, Tanaka R, Kawaguchi T, Fukuda M, Oyanagi K (1996) Cystic acoustic neurinomas: studies of 14 cases. Acta Neurochir 138:695–699. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01411474
Matthies C, Samii M (1997) Management of 1000 vestibular schwannomas (acoustic neuromas): clinical presentation. Neurosurgery 40:1–9; discussion 9-10. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-199701000-00001
Mehrotra N, Behari S, Pal L, Banerji D, Sahu RN, Jain VK (2008) Giant vestibular schwannomas: focusing on the differences between the solid and the cystic variants. Br J Neurosurg 22:550–556. https://doi.org/10.1080/02688690802159031
Metwali H, Samii M, Samii A, Gerganov V (2014) The peculiar cystic vestibular schwannoma: a single-center experience. World Neurosurg 82:1271–1275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2014.07.011
Miki S, Ishikawa E, Yamamoto T, Akutsu H, Matsuda M, Sakamoto N, Matsumura A (2015) Extreme volume expansion of a vestibular schwannoma due to intratumoral hemorrhage after gamma knife radiosurgery. J Clin Neurosci 22:1196–1199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2014.12.019
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group P (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6:e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Moon KS, Jung S, Seo SK, Jung TY, Kim IY, Ryu HH, Jin YH, Jin SG, Jeong YI, Kim KK, Kang SS (2007) Cystic vestibular schwannomas: a possible role of matrix metalloproteinase-2 in cyst development and unfavorable surgical outcome. J Neurosurg 106:866–871. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2007.106.5.866
Nair S, Baldawa SS, Gopalakrishnan CV, Menon G, Vikas V, Sudhir JB (2016) Surgical outcome in cystic vestibular schwannomas. Asian J Neurosurg 11:219–225. https://doi.org/10.4103/1793-5482.145359
Nedzelski JM, Canter RJ, Kassel EE, Rowed DW, Tator CH (1986) Is no treatment good treatment in the management of acoustic neuromas in the elderly? Laryngoscope 96:825–829. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.1986.96.8.825
Pendl G, Ganz JC, Kitz K, Eustacchio S (1996) Acoustic neurinomas with macrocysts treated with gamma knife radiosurgery. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 66(Suppl 1):103–111. https://doi.org/10.1159/000099775
Piccirillo E, Wiet MR, Flanagan S, Dispenza F, Giannuzzi A, Mancini F, Sanna M (2009) Cystic vestibular schwannoma: classification, management, and facial nerve outcomes. Otol Neurotol 30:826–834. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0b013e3181b04e18
SAMII M, GERGANOV V, SAMII A (2006) Improved preservation of hearing and facial nerve function in vestibular schwanno a surgery via the retrosigmoid approach in a series of 200 patients. J Neurosurg 105:527–535. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2006.105.4.527
Samii M, Matthies C (1997) Management of 1000 vestibular schwannomas (acoustic neuromas): surgical management and results with an emphasis on complications and how to avoid them. Neurosurgery 40:11–21; discussion 21-13. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-199701000-00002
Sedgwick P (2015) Meta-analyses: what is heterogeneity? BMJ (Clinical research ed) 350:h1435. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.h1435
Selesnick SH, Johnson G (1998) Radiologic surveillance of acoustic neuromas. Am J Otology 19:846–849
Shirato H, Sakamoto T, Takeichi N, Aoyama H, Suzuki K, Kagei K, Nishioka T, Fukuda S, Sawamura Y, Miyasaka K (2000) Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for vestibular schwannoma (VS): comparison between cystic-type and solid-type VS. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 48:1395–1401. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0360-3016(00)00731-8
Sinha S, Sharma B (2008) Cystic acoustic neuromas: surgical outcome in a series of 58 patients. J Clin Neurosci 15(5):511–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2007.01.007
Tang IP, Freeman SR, Rutherford SA, King AT, Ramsden RT, Lloyd SK (2014) Surgical outcomes in cystic vestibular schwannoma versus solid vestibular schwannoma. Otol Neurotol 35:1266–1270. https://doi.org/10.1097/mao.0000000000000435
Thakur JD, Khan IS, Shorter CD, Sonig A, Gardner GL, Guthikonda B, Nanda A (2012) Do cystic vestibular schwannomas have worse surgical outcomes? Systematic analysis of the literature. Neurosurg Focus 33:E12. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.6.Focus12200
Unger F, Walch C, Haselsberger K, Papaefthymiou G, Trummer M, Eustacchio S, Pendl G (1999) Radiosurgery of vestibular schwannomas: a minimally invasive alternative to microsurgery. Acta Neurochir 141:1281–1285; discussion 1285-1286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s007010050431
Wang M, Jia D, Shen J, Zhang J, Li G (2013) Facial nerve function after large cystic vestibular schwannomas surgery via the retrosigmoid approach. Turk Neurosurg 23:161–169. https://doi.org/10.5137/1019-5149.Jtn.5910-12.1
Wazen J, Silverstein H, Norrell H, Besse B (1985) Preoperative and postoperative growth rates in acoustic neuromas documented with CT scanning. Otolaryngology--head Neck Surg 93:151–155. https://doi.org/10.1177/019459988509300204
Wells G, Shea B, O'Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, Tugwell P (2016) The Newcastle-Ottawa sScale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in metaanalyses. Ottawa (ON): Ottawa Hospital Research Institute; 2009 Available in March
Xia L, Zhang H, Yu C, Zhang M, Ren M, Qu Y, Wang H, Zhu M, Zhao D, Qi X, Yao K (2014) Fluid-fluid level in cystic vestibular schwannoma: a predictor of peritumoral adhesion. J Neurosurg 120:197–206. https://doi.org/10.3171/2013.6.Jns121630
Yashar P, Zada G, Harris B, Giannotta SL (2012) Extent of resection and early postoperative outcomes following removal of cystic vestibular schwannomas: surgical experience over a decade and review of the literature. Neurosurg Focus 33:E13. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.7.Focus12206
Zhang Z, Wang Z, Huang Q, Yang J, Wu H (2012) Removal of large or giant sporadic vestibular schwannomas via translabyrinthine approach: a report of 115 cases. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 74:271–277. https://doi.org/10.1159/000343791
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely thank all colleagues of neurosurgery department in Xuan Wu Hospital. We thank Jiantao Liang, MD, for his critical review of the manuscript.
Funding
Beijing Medical Authority’s “Sailing” Plan (XMLX201821).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Literature search: Xiaolong Wu, Gang Song, and Jiantao Liang.
Extraction of data: Xiaolong Wu, Gang Song, and Xu Wang.
Quality assessment: Xiaolong Wu, Gang Song, and Jiantao Liang.
Statistical analysis and Writing original draft: Xiaolong Wu.
Review and Editing: Mingchu Li, Ge Chen, Hongchuan Guo, Yuhai Bao, and Jiantao Liang.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. Only published studies were used for our analysis, and no patient medical records were accessed in completing this article. Thus, patients’ consent was not required.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 16 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, X., Song, G., Wang, X. et al. Comparison of surgical outcomes in cystic and solid vestibular schwannomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg Rev 44, 1889–1902 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-020-01400-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-020-01400-5