Abstract
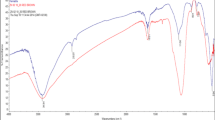
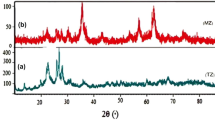
The most important effect of natural organic materials in water is reacting with disinfectants and creating disinfectant by-products that are mostly carcinogenic. The aim of this study was to determine the optimum conditions for removal of humic acid (HA) by zeolite coated with nZVI nanoparticles (Zeolite/nZVI) from aqueous solutions. In this study, after synthesis of zeolite/nZVI, its structure and morphology were examined using FTIR, BET, XRF, and FESEM techniques. The effects of HA concentration, composite content, pH, and reaction time were evaluated. The experimental data were analyzed by Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm and pseudo-first-order and second-order kinetic models. Finally, the thermodynamic parameters of enthalpy (ΔΗ°), entropy (ΔS°), and Gibbs free energy (ΔG°) were calculated. The results of the analyses confirmed the accuracy of the composite structure. Its specific surface area by using BET method was 203.43 m2/g. The HA removal efficiency was obtained at 92.98% in optimum conditions of 50 mg/L concentration, 2 g/L composite dose, pH = 3, and reaction time of 60 min. The results of the isotherm and kinetic study showed that the HA adsorption process follows the Langmuir isotherm (R2 = 0.9707) and pseudo-second-order kinetic. The maximum adsorption capacity of the composite was determined at 23.36 mg/g by Langmuir model. Thermodynamic parameters indicate that the adsorption of HA endothermic and the reaction cannot be done spontaneously. Zeolite/nZVI composite had good removal efficiency after five times of recycling. The present study showed that zeolite/nZVI can be used as an effective adsorbent for removal of HA from aqueous solutions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdoallahzadeh, H., Alizadeh, B., Khosravi, R., & Fazlzadeh, M. (2016). Efficiency of edta modified nanoclay in removal of humic acid from aquatic solutions. Journal of Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, 26, 111–125.
Abdollahzadeh, H., Fazlzadeh, M., Afshin, S., Arfaeinia, H., Feizizadeh, A., Poureshgh, Y., & Rashtbari, Y. (2020). Efficiency of activated carbon prepared from scrap tires magnetized by Fe3O4 nanoparticles: characterisation and its application for removal of reactive blue19 from aquatic solutions. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 1, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1745199.
Allah, N. H., & Zahra, N. M. (2015). Investigation on the efficacy of activated carbon modified with zinc oxide nanoparticles to remove methylene blue dye from synthetic wastewater: kinetic and isotherm study. Health System Research, 11, 382–397.
Asgari, G., Sidmohammadi, A., Ebrahimi, A., Gholami, Z., & Hoseinzadeh, E. (2010). Study on phenol removing by using modified zolite (clinoptilolite) with FeCl3 from aqueous solutions. Health System Research, 6, 848–857.
Asgari, G., Ghanizadeh, G., & Seyd, M. A. (2011). Adsorption of humic acid from aqueous solutions onto modified pumice with hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide. Journal of Babol University of Medical Sciences, 14, 14–22.
Asilian, H., Moussavi, G., & Mahmoudi, M. (2010). Adsorption of reactive red 198 azo dye fromaqueous solution onto thewaste coagulation sludge of thewater treatment plants. Iranian Journal of Health and Environment, 3, 93–102.
Auta, M., & Hameed, B. H. (2015). Synthetic textile dye removal from aqueous solution using modified local clay adsorbent. Environmental Engineering & Management Journal, 14, 955–963.
Baghapour, M. A., Jahed, B., & Joshani, G. H. (2013). Preparation of activated carbon from waste tires and its application in gasoline removal from water. Iranian Journal of Health and Environment, 6, 377–392.
Bai, R., & Zhang, X. (2001). Polypyrrole-coated granules for humic acid removal. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 243, 52–60.
Barka, N., Abdennouri, M., & Makhfouk, M. E. (2011). Removal of methylene blue and eriochrome black t from aqueous solutions by biosorption on Scolymus hispanicus L.: kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 42, 320–326.
Bazrafshan, E., Jaafari, A. J., Mostafapour, F. K., & Biglari, H. (2012). Humic acid removal from aqueous environments by electrocoagulation process duad with adding hydrogen peroxide. Iranian Journal of Health and Environment, 5, 211–224.
Bazrafshan, E., Rahdar, S., Balarak, D., Mostafapour, F. K., & Zazouli, M. A. (2015). Equilibrium and thermodynamics studies for decolorization of reactive black 5 by adsorption onto acid modified banana leaf ash. Iranian Journal of Health Sciences, 3, 15–28.
Borna, M. O., Pirsaheb, M., Niri, M. V., Mashizie, R. K., Kakavandi, B., Zare, M. R., & Asadi, A. (2016). Batch and column studies for the adsorption of chromium (vi) on low-cost Hibiscus cannabinus kenaf, a green adsorbent. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 68, 80–89.
Chieng, H. I., Lim, L. B., & Priyantha, N. (2015). Enhancing adsorption capacity of toxic malachite green dye through chemically modified breadnut peel: equilibrium, thermodynamics, kinetics and regeneration studies. Environmental Technology, 36, 86–97.
Dehghani, M. H., Zarei, A., Mesdaghinia, A., Nabizadeh, R., Alimohammadi, M., Afsharnia, M., & McKay, G. (2018). Production and application of a treated bentonite–chitosan composite for the efficient removal of humic acid from aqueous solution. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 140, 102–115.
Derakhshani, E., & Naghizadeh, A. (2018). Optimization of humic acid removal by adsorption onto bentonite and montmorillonite nanoparticles. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 259, 76–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.03.014.
Doulia, D., Leodopoulos, C., Gimouhopoulos, K., & Rigas, F. (2009). Adsorption of humic acid on acid-activated Greek bentonite. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 340, 131–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2009.07.028.
Ehrampoush, M., Mahvi, A., Fallahzadeh, H., & Moussavi, S. (2013). The evaluation of efficiency of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in humic acid adsorption in acidic conditions from aqueous solution. Tolooebehdasht, 11, 79–90.
Fazlzadeh, M., Khosravi, R., & Zarei, A. (2017). Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using peganum harmala seed extract, and loaded on peganum harmala seed powdered activated carbon as new adsorbent for removal of Cr (vi) from aqueous solution. Ecological Engineering, 103, 180–190.
Fearing, D. A., Banks, J., Guyetand, S., Eroles, C. M., Jefferson, B., Wilson, D., Hillis, P., Campbell, A. T., & Parsons, S. A. (2004). Combination of ferric and MIEX® for the treatment of a humic rich water. Water Research, 38, 2551–2558.
Fytianos, K., Voudrias, E., & Kokkalis, E. (2000). Sorption–desorption behaviour of 2, 4-dichlorophenol by marine sediments. Chemosphere, 40, 3–6.
Giasuddin, A. B., Kanel, S. R., & Choi, H. (2007). Adsorption of humic acid onto nanoscale zerovalent iron and its effect on arsenic removal. Environmental Science & Technology, 41, 2022–2027.
Hamzehzadeh, A., Fazlzadeh, M., & Rahmani, K. (2017). Efficiency of nano/persulfate process (nzvi/ps) in removing metronidazole from aqueous solution. Journal of Environmental Health Enginering, 4, 307–320.
Hashemian, S. (2007). Study of adsorption of acid dye from aqueous solutions using bentonite. Main Group Chemistry, 6, 97–107. https://doi.org/10.1080/10241220701837462.
Hii, S. L., Yong, S. Y., & Wong, C. L. (2009). Removal of rhodamine b from aqueous solution by sorption on Turbinaria conoides (phaeophyta). Journal of Applied Phycology, 21, 625–631.
Hu, B., & Luo, H. (2010). Adsorption of hexavalent chromium onto montmorillonite modified with hydroxyaluminum and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Applied Surface Science, 257, 769–775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.07.062.
Hu, Q., Chen, N., Feng, C., & Hu, W. (2015). Nitrate adsorption from aqueous solution using granular chitosan-fe3+ complex. Applied Surface Science, 347, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.04.049.
Imyim, A., & Prapalimrungsi, E. (2010). Humic acids removal from water by aminopropyl functionalized rice husk ash. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 184, 775–781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.08.108.
Jaafari, S. J., Shokouhi, R., Zadeh, E. H., Taghavi, M., Arezoumandi, R., & Ahadi, H. (2012). Removal of reactive black 5 (rb5) dye from aqueous solution by using of adsorption onto activated red mud: kinetic and equilibrium study. Jundishapur Journal of Health Sciences, 1–11.
Jiang, J. Q., & Cooper, C. (2003). Preparation of modified clay adsorbents for the removal of humic acid. Environmental Engineering Science, 20, 581. https://doi.org/10.1089/109287503770736096.
Jorfi, S., Shooshtarian, M., & Pourfadakari, S. (2020). Decontamination of cadmium from aqueous solutions using zeolite decorated by Fe3O4 nanoparticles: adsorption modeling and thermodynamic studies. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 17, 273–286.
Kakavandi, B., Kalantary, R. R., Esrafily, A., Jafari, A. J., & Azari, A. (2013). Isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic of reactive blue 5 (rb5) dye adsorption using Fe3O4 nanoparticles and activated carbon magnetic composite. Journal of Color Science & Technology, 7, 237–248.
Ke-xin, Z., Hong-wei, R., & Shu-guang, X. (2007). Performance of combined pre-ozonation and biofiltration for the purification of water from ching yellow river. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 1, 52–61.
Khaled, A., El Nemr, A., El-Sikaily, A., & Abdelwahab, O. (2009). Removal of direct n blue-106 from artificial textile dye effluent using activated carbon from orange peel: adsorption isotherm and kinetic studies. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 165, 100–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.09.122.
Kholghi, S., Badii, K., & Ahmadi, S. (2013). Bio-sorption isotherm and kinetic study of acid red 14 from aqueous solution by using Azolla A. filiculodes. Journal of Color Science and Technology, 6, 337–346.
Kim, Y.-I., & Bae, B.-U. (2007). Design and evaluation of hydraulic baffled-channel pac contactor for taste and odor removal from drinking water supplies. Water Research, 41, 2256–2264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.02.005.
Kuźniarska-Biernacka, I., Fonseca, A. M., & Neves, I. C. (2013). Manganese complexes with triazenido ligands encapsulated in nay zeolite as heterogeneous catalysts. Inorganica Chimica Acta, 394, 591–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2012.09.027.
Lu, C., Chung, Y.-L., & Chang, K.-F. (2005). Adsorption of trihalomethanes from water with carbon nanotubes. Water Research, 39, 1183–1189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.12.033.
Magdaleno, G. B., & Coichev, N. (2005). Chemiluminescent determination of humic substances based on the oxidation by peroxymonosulfate. Analytica Chimica Acta, 552, 141–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2005.07.007.
Majid, Z., AbdulRazak, A. A., & Noori, W. A. H. (2019). Modification of zeolite by magnetic nanoparticles for organic dye removal. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 44, 5457–5474.
Maleki, A., Mahvi, A. H., Rezaee, R., & Davari, B. (2013). Removal of reactive blue 19 using natural and modified zeolites. Iranian Journal of Health and Environment, 5, 519–530.
Mansoori, F., Kalankesh, L. R., & Malakootian, M. (2014). Kinetics and isothermic behavior of sio2 nanoparticles in removal of humic acid from aqueous solutions: a case study on the Alavian Dam in Maragheh city, Iran. Journal of Health and Development, 3, 71–80.
Mekatel, E. H., Amokrane, S., Aid, A., Nibou, D., & Trari, M. (2015). Adsorption of methyl orange on nanoparticles of a synthetic zeolite NaA/CuO. Comptes Rendus Chimie, 18, 336–344.
Mohseni-Bandpi, A., Al-Musawi, T. J., Ghahramani, E., Zarrabi, M., Mohebi, S., & Vahed, S. A. (2016). Improvement of zeolite adsorption capacity for cephalexin by coating with magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 218, 615–624.
Mollahosseini, A., Toghroli, M., & Kamankesh, M. (2015). Zeolite/Fe3O4 as a new sorbent in magnetic solid-phase extraction followed by gas chromatography for determining phthalates in aqueous samples. Journal of Separation Science, 38, 3750–3757.
Naddafi, K., & Gholami, M. (2014). Removal of reactive red 120 from aqueous solutions using surface modified natural zeolite. Iranian Journal of Health and Environment, 7, 277–288.
Omri, A., Benzina, M., Trabelsi, W., & Ammar, N. (2014). Adsorptive removal of humic acid on activated carbon prepared from almond shell: approach for the treatment of industrial phosphoric acid solution. Desalination and Water Treatment, 52, 2241–2252. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.800003.
Özcan, A., Ömeroğlu, Ç., Erdoğan, Y., & Özcan, A. S. (2007). Modification of bentonite with a cationic surfactant: an adsorption study of textile dye reactive blue 19. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 140, 173–179.
Ozer, C., Imamoglu, M., Turhan, Y., & Boysan, F. (2012). Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions using phosphoric acid activated carbon produced from hazelnut husks. Toxicological & Environmental Chemistry, 94, 1283–1293. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772248.2012.707656.
Pouretedal, H., & Sadegh, N. (2014). Effective removal of amoxicillin, cephalexin, tetracycline and penicillin g from aqueous solutions using activated carbon nanoparticles prepared from vine wood. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 1, 64–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2014.03.006.
Rahdar, S., Taghavi, M., Khaksefidi, R., & Ahmadi, S. (2019). Adsorption of arsenic (V) from aqueous solution using modified saxaul ash: isotherm and thermodynamic study. Applied Water Science, 9, 1–9.
Ramezani, F., Kazemi, B., & Jebali, A. (2013). Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by leishmania sp. New Cellular and Molecular Biotechnology Journal, 3, 107–111.
Rashtbari, Y., Afshin, S., Hamzezadeh, A., Abazari, M., Poureshgh, Y., & Fazlzadeh, M. (2020). Application of powdered activated carbon coated with zinc oxide nanoparticles prepared using a green synthesis in removal of reactive blue 19 and reactive black-5: adsorption isotherm and kinetic models. Desalination and Water Treatment, 179, 354–367.
Salomão, G. R., Américo-Pinheiro, J. H. P., Isique, W. D., Torres, N. H., Cruz, I. A., & Ferreira, L. F. R. (2019). Diclofenac removal in water supply by adsorption on composite low-cost material. Environmental Technology, 1, 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2019.1692078.
Simpson, D. R. (2008). Biofilm processes in biologically active carbon water purification. Water Research, 42, 2839–2848.
Torabian, A., Kazemian, H., Seifi, L., Bidhendi, G. N., Azimi, A. A., & Ghadiri, S. K. (2010). Removal of petroleum aromatic hydrocarbons by surfactant-modified natural zeolite: the effect of surfactant. CLEAN–Soil, Air, Water, 38, 77–83. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.200900157.
Torres-Pérez, J., Gérente, C., & Andrès, Y. (2012). Sustainable activated carbons from agricultural residues dedicated to antibiotic removal by adsorption. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 20, 524–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1004-9541(11)60214-0.
Wang, S., & Zhu, Z. (2007). Humic acid adsorption on fly ash and its derived unburned carbon. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 315, 41–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2007.06.034.
Wang, G. S., Hsieh, S.-T., & Hong, C. S. (2000). Destruction of humic acid in water by UV light-catalyzed oxidation with hydrogen peroxide. Water Research, 34, 3882–3887.
Wang, Y., Zeng, D., Dai, Y., Fang, C., Han, X., Zhang, Z., Cao, X. & Liu, Y. (2020). The adsorptive ability of 3D flower-like titanium phosphate for U(VI) in aqueous solution. Water Air & Soil Pollution, 231, 464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04817-2
Weng, X., Huang, L., Chen, Z., Megharaj, M., & Naidu, R. (2013). Synthesis of iron-based nanoparticles by green tea extract and their degradation of malachite. Industrial Crops and Products, 51, 342–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.09.024.
Xie, J., Li, C., Chi, L., & Wu, D. (2013). Chitosan modified zeolite as a versatile adsorbent for the removal of different pollutants from water. Fuel, 103, 480–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2012.05.036.
Zhang, L., Hu, P., Wang, J., & Huang, R. (2016). Adsorption of amido black 10b from aqueous solutions onto zr (iv) surface-immobilized cross-linked chitosan/bentonite composite. Applied Surface Science, 369, 558–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.01.217.
Zheng, H., Wang, Y., Zheng, Y., Zhang, H., Liang, S., & Long, M. (2008). Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies on the sorption of 4-hydroxyphenol on cr-bentonite. Chemical Engineering Journal, 143, 117–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2007.12.022.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rashtbari, Y., Américo-Pinheiro, J.H.P., Bahrami, S. et al. Efficiency of Zeolite Coated with Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles for Removal of Humic Acid from Aqueous Solutions. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 514 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04872-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04872-9