Abstract—
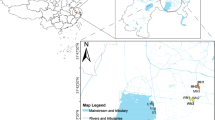
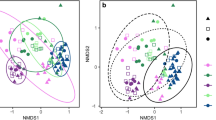
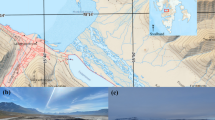
The composition of the microbiome of acid drainage water of a quarry used for the mining of brown coal was studied. The water had a pH of 5.15 and contained 1.4 g/L of sulfate. Unlike acid mine drainage associated with mining of sulfide ores, the content of iron and heavy metals was low. Molecular analysis of the microbial community was performed by high-throughput sequencing of the 18S and 16S rRNA gene fragments. Most eukaryotic sequences belonged to the fungal phylum Basidiomycota; members of the Chytridiomycota were also found. Basidiomycetes of the family Sporidiobolaceae were the predominant group, as was previously reported for acid mine drainage waters. Among the minor groups, protozoa (Alveolata and Amoebozoa) and green algae (Chlamydomonas) were found. The dominant group of prokaryotes was the genus Acidiphilium (Alphaproteobacteria); betaproteobacteria of the genera Sulfuriferula and Thiomonas were also found.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Aguilera, A., Eukaryotic organisms in extreme acidic environments, the Río Tinto case, Life (Basel), 2013, vol. 3, pp. 363‒374.
Amaral Zettler, L.A., Gómez, F., Zettler, E., Keenan, B.G., Amils, R., and Sogin, M.L., Microbiology: eukaryotic diversity in Spain’s River of Fire, Nature, 2002, vol. 417, p. 137.
Baker, B.J., Lutz, M.A., Dawson, S.C., Bond, P.L., and Banfield, J.F., Metabolically active eukaryotic communities in extremely acidic mine drainage, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2004, vol. 70, pp. 6264‒6271.
Baker, B.J., Tyson, G.W., Goosherst, L., and Banfield, J.F., Insights into the diversity of eukaryotes in acid mine drainage biofilm communities, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2009, vol. 75, pp. 2192‒2199.
Banks, D., Parnachev, V.P., Frengstad, B., Holden, W., Vedernikov, A.A., and Karnachuk, O.V., Alkaline mine drainage from metal sulphide and coal mines: examples from Svalbard and Siberia, in Mine Water Hydrogeology and Geochemistry, Younger, P.L. and Robins, N.S., Eds., London: Geological Society, 2002, pp. 287–296.
Bass, D., Silberman, J.D., Brown, M.W., Pearce, R.A., Tice, A.K., Jousset, A., Geisen, S., and Hartikainen, H., Coprophilic amoebae and flagellates, including Guttulinopsis, Rosculus and Helkesimastix, characterise a divergent and diverse rhizarian radiation and contribute to a large diversity of faecal-associated protists, Environ. Microbiol., 2016, vol. 18, pp. 1604‒1619.
Brantner, J.S. and Senko, J.M., Response of soil-associated microbial communities to intrusion of coal mine-derived acid mine drainage, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2014, vol. 48, pp. 8556‒8563.
Burow, K., Grawunder, A., Harpke, M., Pietschmann, S., Ehrhardt, R., Wagner, L., Voigt, K., Merten, D., Büchel, G., and Kothe, E., Microbiomes in an acidic rock-water cave system, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 2019, vol. 366, fnz167. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnz167
Das, B.K., Roy, A., Koschorreck, M., Mandal, S.M., Wendt-Potthoff, K., and Bhattacharya, J., Occurrence and role of algae and fungi in acid mine drainage environment with special reference to metals and sulfate immobilization, Water Res., 2009, vol. 43, pp. 883‒894.
Gadanho, M., Libkind, D., and Sampaio, J.P., Yeast diversity in the extreme acidic environments of the Iberian Pyrite Belt, Microb. Ecol., 2006, vol. 52, pp. 552‒563.
Glukhova, L.B., Frank, Y.A., Danilova, E.V. Avakyan, M.R., Tuovinen, O.H., and Karnachuk, O.V., Isolation, characterization, and metal response of novel, acid tolerant Penicillium spp. from extremely metal-rich waters at a mining site in Transbaikal (Siberia, Russia), Microb. Ecol., 2018, vol. 76, pp. 911‒924.
Hao, Ch., Wang, L., Gao, Ya., Zhang, L., and Dong, H., Microbial diversity in acid mine drainage of Xiang Mountain sulfide mine, Anhui Province, China, Extremophiles, 2010, vol. 14, pp. 465‒474.
Kadnikov, V.V., Gruzdev, E.V., Beletsky, A.V., Mardanov, A.V., Ravin, N.V., Ivasenko, D.A., Karnachuk, O.V., and Danilova, E.V., Selection of a microbial community in the course of formation of acid mine drainage, Microbiology (Moscow), 2019, vol. 88, pp. 292–299.
Kadnikov, V.V., Mardanov, A.V., Ivasenko, D.A., Antsiferov, D.V., Beletsky, A.V., Karnachuk, O.V., and Ravin, N.V., Lignite coal burning seam in the remote Altai Mountains harbors a hydrogen-driven thermophilic microbial community, Sci. Rep., 2018, vol. 8, art. 6730. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-25146-9
Kaksonen, A.H., Dopson, M., Karnachuk, O., Tuovinen, O.H., and Puhakka, J.A., Biological iron oxidation and sulfate reduction in the treatment of acid mine drainage at low temperatures, in Psychrophiles: From Biodiversity to Biotechnology, Margesin, R., Schinner, F., Marx, J.C., and Gerday, C., Eds., Berlin: Springer, 2008, pp. 429‒454.
Magoč, T. and Salzberg, S.L., FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies, Bioinformatics, 2011, vol. 27, pp. 2957‒2963.
Mardanov, A.V., Panova, I.A., Beletsky, A.V., Avakyan, M.R., Kadnikov, V.V., Antsiferov, D.V., Banks, D., Frank, Y.A., Pimenov, N.V., Ravin, N.V., and Karnachuk, O.V., Genomic insights into a new acidophilic, copper-resistant Desulfosporosinus isolate from the oxidized tailings area of an abandoned gold mine, FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 2016, vol. 92, fiw111.
Martorell, M.M., Ruberto, L.A.M., de Castellanos, L.I.F., and Mac Cormack, W.P., Bioremediation abilities of Antarctic fungi, in Fungi in Extreme Environments: Ecological Role and Biotechnological Significance, Tiquia-Arashiro, S.M. and Grube, M., Eds., Cham, Switzerland: Springer, 2019, pp. 517‒534.
Mendez-Garcia, C., Pelaez, A.I., Mesa, V., Sanchez, J., Golyshina, O.V., and Ferrer, M., Microbial diversity and metabolic networks in acid mine drainage habitats, Front. Microbiol., 2015, vol. 29, art. 475.
Mesa, V., Gallego, J.L.R., González-Gil, R., Lauga, B., Sánchez, J., Méndez-García, C., and Peláez, A.I., Bacterial, archaeal, and eukaryotic diversity across distinct microhabitats in an acid mine drainage, Front. Microbiol., 2017, vol. 8, art. 1756.
Nicomrat, D., Dick, W.A., and Tuovinen, O.H., Microbial populations identified by fluorescence in situ hybridization in a constructed wetland treating acid coal mine drainage, J. Environ. Qual., 2006, vol. 35, pp. 1329‒1337.
Okamura, K., Kawai, A., Wakao, N., Yamada, T., and Hiraishi, A., Acidiphilium iwatense sp. nov., isolated from an acid mine drainage treatment plant, and emendation of the genus Acidiphilium,Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2015, vol. 65, pp. 42‒48.
Pruesse, E., Peplies, J., and Glöckner, F.O., SINA: accurate high-throughput multiple sequence alignment of ribosomal RNA genes, Bioinformatics, 2012, vol. 28, pp. 1823‒1829.
Roşca, M., Hlihor, R.M., Cozma, P., Drăgoi, E.N., Diaconu, M., Silva, B., Tavares, T., and Gavrilescu, M., Comparison of Rhodotorula sp. and Bacillus megaterium in the removal of cadmium ions from liquid effluents, Green Process. Synth., 2018, vol. 7, pp. 74‒88.
Sokolyanskaya, L.O., Ivanov, M.V., Ikkert, O.P, Kalinina, A.E., Evseev, V.A., Glukhova, L.B., and Karnachuk, O.V., Copper precipitation as insoluble oxalates by thermotolerant Aspergillus spp. from burning wastes of coal mining, Microbiology (Moscow), 2020, vol. 89, pp. 498–501.
Su, X., Zhou, M., Hu, P., Xiao, Y., Wang, Z., Mei, R., Hashmi, M.Z., Lin, H., Chen, J., and Sun, F., Whole-genome sequencing of an acidophilic Rhodotorula sp. ZM1 and its phenol-degrading capability under acidic conditions, Chemosphere, 2019, vol. 232, pp. 76‒86.
Verma, N. and Sharma, R., Bioremediation of toxic heavy metals: a patent review, Recent Pat. Biotechnol., 2017, vol. 1, pp. 171‒187.
Zirnstein, I., Arnold, T., Krawczyk-Barsch, E., Jenk, U., Bernhard, G., and Roske, I., Eukaryotic life in biofilms formed in a uranium mine, MicrobiologyOpen, 2012, vol. 1, pp. 83–94. https://doi.org/10.1002/mbo3.17
Funding
The work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, projects nos. 18-34-00356 (molecular analysis of the microbial community) and 19-04-00981 (physicochemical analysis of the water).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EVG and AVB carried out analysis of the 18S rRNA gene sequences and manuscript preparation. VVK and AVM carried out sampling, isolation of metagenomic DNA, and sequencing. MVI carried out physicochemical analysis of the samples. OVK carried out sampling and data analysis. NVR carried out data analysis and manuscript preparation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Translated by P. Sigalevich
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gruzdev, E.V., Beletsky, A.V., Kadnikov, V.V. et al. Diversity of Eukaryotic Microorganisms in the Drainage Waters of a Coal Open-Cast Mine. Microbiology 89, 641–646 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261720050100
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261720050100