Abstract
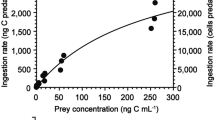
Heterotrophic dinoflagellates are major grazers of microalgae in marine food webs. The feeding of the newly described heterotrophic dinoflagellate Gyrodinium jinhaense was explored by providing 19 common microalgal prey species and the ciliate Mesodinium rubrum as prey. Furthermore, the specific growth and ingestion rates of G. jinhaense feeding on the chlorophyte Dunaliella salina were determined as a function of prey concentration. Cells of G. jinhaense were able to feed on microalgae of sizes ≤ 26 μm with the exception of the dinoflagellate Karenia mikimotoi. In contrast, G. jinhaense did not feed on microalgae > 26 μm with the exception of the dinoflagellate Lingulodinium polyedra. With increasing mean prey concentration, both the specific growth and ingestion rates of G. jinhaense feeding on D. salina rapidly increased at mean prey concentrations < 504 ng C mL−1 (6300 cells mL−1), but slowly at higher prey concentrations. The maximum growth and ingestion rates of G. jinhaense feeding on D. salina were 0.655 day−1 and 0.82 ng C predator−1 day−1 (10 cells predator−1 day−1), respectively. Gyrodinium dominans and G. moestrupii are able to feed on most microalgal prey species, including the species that G. jinhaense did not feed on. Moreover, these two Gyrodinium species have positive growth rates when feeding on the red-tide dinoflagellates Prorocentrum cordatum and Scrippsiella acuminata, which did not support growth of G. jinhaense. Therefore, G. jinhaense has an ecological niche different from that of G. dominans and G. moestrupii, and this pattern may be the result of evolution among these Gyrodinium species.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data collected and analyzed during this current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Akizawa K, Iwasaki N, Ueda H (1998) List of microplankton in Uranouchi Inlet, Kochi, Japan during the summer of 1997. Bull Mar Sci Fish 18:57–63
Brown ER, Kubanek J (2020) Harmful alga trades off growth and toxicity in response to cues from dead phytoplankton. Limnol Oceanogr 65:1723
Burkholder JM, Glibert PM, Skelton HM (2008) Mixotrophy, a major mode of nutrition for harmful algal species in eutrophic waters. Harmful Algae 8:77–93
Edwards ES, Burkill PH (1995) Abundance, biomass and distribution of microzooplankton in the Irish Sea. J Plankt Res 17:771–782
Frost BW (1972) Effects of size and concentration of food particles on the feeding behavior of the marine planktonic copepod Calanus pacificus. Limnol Oceanogr 17:805–815
Guillard RRL, Ryther JH (1962) Studies of marine planktonic diatoms: I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt, and Detonula confervacea (Cleve) Gran. Can J Microbiol 8:229–239
Guillard RRL, Hargraves PE (1993) Stichochrysis immobilis is a diatom, not a chrysophyte. Phycologia 32:234–236
Hansen PJ (1992) Prey size selection, feeding rates and growth dynamics of heterotrophic dinoflagellates with special emphasis on Gyrodinium spirale. Mar Biol 114:327–334
Hansen FC, Witte HJ, Passarge J (1996) Grazing in the heterotrophic dinoflagellate Oxyrrhis marina: size selectivity and preference for calcified Emiliania huxleyi cells. Aquat Microb Ecol 10:307–313
Harvey EL, Jeong HJ, Menden-Deuer S (2013) Avoidance and attraction: chemical cues influence predator-prey interactions of planktonic protists. Limnol Oceanogr 58:1176–1184
Harrison PJ, Furuya K, Glibert PM, Xu J, Liu HB, Yin K, Lee JHW, Anderson DM, Gowen R, AlAzri AR, Ho AYT (2011) Geographical distribution of red and green Noctiluca scintillans. Chin J Oceanol Limn 29:807–831
Heinbokel JF (1978) Studies on the functional role of tintinnids in the Southern California Bight. I. Grazing and growth rates in laboratory cultures. Mar Biol 47:177–189
Hinder SL, Hays GC, Edwards M, Roberts EC, Walne AW, Gravenor MB (2012) Changes in marine dinoflagellate and diatom abundance under climate change. Nat Clim Change 2:271–275
Hoppenrath M (2004) A revised checklist of planktonic diatoms and dinoflagellates from Helgoland (North Sea, German Bight). Helgol Mar Res 58:243–251
Jakobsen HH, Hansen PJ (1997) Prey size selection, grazing and growth response of the small heterotrophic dinoflagellate Gymnodinium sp. and the ciliate Balanion comatum–a comparative study. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 158:75–86
Jang SH, Jeong HJ, Lee MJ, Kim JH, You JH (2019) Gyrodinium jinhaense n. sp., a new heterotrophic unarmored dinoflagellate from the coastal waters of Korea. J Eukaryot Microbiol 66:821–835
Jeong HJ, Yoo YD, Kim ST, Kang NS (2004) Feeding by the heterotrophic dinoflagellate Protoperidinium bipes on the diatom Skeletonema costatum. Aquat Microb Ecol 36:171–179
Jeong HJ, Yoo YD, Kang NS, Rho JR, Seong KA, Park JW, Nam GS, Yih W (2010a) Ecology of Gymnodinium aureolum. I. Feeding in western Korean waters. Aquat Microb Ecol 59:239–255
Jeong HJ, Yoo YD, Kim JS, Seong KA, Kang NS, Kim TH (2010b) Growth, feeding and ecological roles of the mixotrophic and heterotrophic dinoflagellates in marine planktonic food webs. Ocean Sci J 45:65–91
Jeong HJ, Kim TH, Yoo YD, Yoon EY, Kim JS, Seong KA, Kim KY, Park JY (2011) Grazing impact of heterotrophic dinoflagellates and ciliates on common red-tide euglenophyte Eutreptiella gymnastica in Masan Bay, Korea. Harmful Algae 10:576–588
Jeong HJ, Lim AS, Yoo YD, Lee MJ, Lee KH, Jang TY, Lee K (2014) Feeding by heterotrophic dinoflagellates and ciliates on the free-living dinoflagellate Symbiodinium sp. (Clade E). J Eukaryot Microbiol 61:27–41
Jeong HJ, Lim AS, Franks PJS, Lee KH, Kim JH, Kang NS, Lee MJ, Jang SH, Lee SY, Yoon EY, Park JY, Yoo YD, Seong KA, Kwon JE, Jang TY (2015) A hierarchy of conceptual models of red-tide generation: nutrition, behavior, and biological interactions. Harmful Algae 47:97–115
Jeong HJ, Ok JH, Lim AS, Kwon JE, Kim SJ, Lee SY (2016) Mixotrophy in the phototrophic dinoflagellate Takayama helix (Family Kareniaceae): predator of diverse toxic and harmful dinoflagellates. Harmful Algae 60:92–106
Jeong HJ, Lim AS, Lee K, Lee MJ, Seong KA, Kang NS, Jang SH, Lee KH, Lee SY, Kim MO, Kim JH, Kwon JE, Kang HC, Kim JS, Yih W, Shin K, Jang PK, Ryu JH, Kim SY, Park JY, Kim KY, Kim JH (2017) Ichthyotoxic Cochlodinium polykrikoides red tides offshore in the South Sea, Korea in 2014: I. Temporal variations in three-dimensional distributions of red-tide organisms and environmental factors. Algae 32:101–130
Johnson MD, Rome M, Stoecker DK (2003) Microzooplankton grazing on Prorocentrum minimum and Karlodinium micrum in Chesapeake Bay. Limnol Oceanogr 48:238–248
Johnson MD (2015) Inducible mixotrophy in the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum minimum. J Eukaryot Microbiol 62:431–443
Kang NS, Jeong HJ, Yoo YD, Yoon EY, Lee KH, Lee K, Kim G (2011) Mixotrophy in the newly described phototrophic dinoflagellate Woloszynskia cincta from western Korean waters: feeding mechanism, prey species and effect of prey concentration. J Eukaryot Microbiol 58:152–170
Kang HC, Jeong HJ, Kim SJ, You JH, Ok JH (2018) Differential feeding by common heterotrophic protists on 12 different Alexandrium species. Harmful Algae 78:106–117
Kang HC, Jeong HJ, Ok JH, You JH, Jang SH, Lee SY, Lee KH, Park JY, Rho JR (2019a) Spatial and seasonal distributions of the phototrophic dinoflagellate Biecheleriopsis adriatica (Suessiaceae) in Korea: quantification using qPCR. Algae 34:111–126
Kang HC, Jeong HJ, Jang SH, Lee KH (2019b) Feeding by common heterotrophic protists on the phototrophic dinoflagellate Biecheleriopsis adriatica (Suessiaceae) compared to that of other suessioid dinoflagellates. Algae 34:127–140
Ke Z, Tan Y, Huang L, Zhang J, Lian S (2012) Relationship between phytoplankton composition and environmental factors in the surface waters of southern South China Sea in early summer of 2009. Acta Oceanol Sin 31:109–119
Kim JS, Jeong HJ (2004) Feeding by the heterotrophic dinoflagellates Gyrodinium dominans and G. spirale on the red-tide dinoflagellate Prorocentrum minimum. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 280:85–94
Kim SJ, Jeong HJ, Kang HC, You JH, Ok JH (2019) Differential feeding by common heterotrophic protists on four Scrippsiella species of similar size. J Phycol 55:868–881
Larsen J (1996) Unarmoured dinoflagellates from Australian waters II. Genus Gyrodinium (Gymnodiniales, Dinophyceae). Phycologia 35:342–349
Lee SK, Jeong HJ, Jang SH, Lee KH, Kang NS, Lee MJ, Potvin É (2014a) Mixotrophy in the newly described dinoflagellate Ansanella granifera: feeding mechanism, prey species, and effect of prey concentration. Algae 29:137
Lee KH, Jeong HJ, Jang TY, Lim AS, Kang NS, Kim JH, Kim KY, Park K, Lee K (2014b) Feeding by the newly described mixotrophic dinoflagellate Gymnodinium smaydae: feeding mechanism, prey species, and effect of prey concentration. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 459:114–125
Lee KH, Jeong HJ, Yoon EY, Jang SH, Kim HS, Yih W (2014c) Feeding by common heterotrophic dinoflagellates and a ciliate on the red-tide ciliate Mesodinium rubrum. Algae 29:153
Lessard EJ (1991) The trophic role of heterotrophic dinoflagellates in diverse marine environments. Mar Microb Food Webs 5:49–58
Li X, Yan T, Yu R, Zhou M (2019) A review of Karenia mikimotoi: Bloom events, physiology, toxicity and toxic mechanism. Harmful Algae 90:101702
Lim AS, Jeong HJ, Seong KA, Lee MJ, Kang NS, Jang SH, Lee KH, Park JY, Jang TY, Yoo YD (2017) Ichthyotoxic Cochlodinium polykrikoides red tides offshore in the South Sea, Korea in 2014: II. Heterotrophic protists and their grazing impacts on red-tide organisms. Algae 32:199–222
Marshall HG (1980) Seasonal phytoplankton composition in the lower chesapeake bay and old plantation creek, cape charles, Virginia. Estuaries 3:207–216
Menden-Deuer S, Lessard EJ, Satterberg J, Grubaum D (2005) Growth rates and starvation survival of three species of the pallium-feeding, thecate dinoflagellate genus Protoperidinium. Aquat Microb Ecol 41:145–152
Nakamura Y, Yamazaki Y, Hiromi J (1992) Growth and grazing of a heterotrophic dinoflagellate, Gyrodinium dominans, feeding on a red tide flagellate, Chattonella antiqua. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 82:275–279
Nakamura Y, Suzuki SY, Hiromi J (1995a) Growth and grazing of a naked heterotrophic dinoflagellate, Gyrodinium dominans. Aquat Microb Ecol 9:157–164
Nakamura Y, Suzuki SY, Hiromi J (1995b) Population dynamics of heterotrophic dinoflagellates during a Gymnodinium mikimotoi red tide in the Seto Inland Sea. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 125:269–277
Naustvoll LJ (2000) Prey size spectra in naked heterotrophic dinoflagellates. Phycologia 39:448–455
Ok JH, Jeong HJ, Lim AS, Lee KH (2017) Interactions between the mixotrophic dinoflagellate Takayama helix and common heterotrophic protists. Harmful Algae 68:178–191
Peter C, Krock B, Cembella A (2018) Effects of salinity variation on growth and yessotoxin composition in the marine dinoflagellate Lingulodinium polyedra from a Skagerrak fjord system (western Sweden). Harmful Algae 78:9–17
Porter KG, Sherr EB, Sherr BF, Pace M, Sanders RW (1985) Protozoa in planktonic food webs. J Eukaryot Microbiol 32:409–415
Potvin É, Hwang YJ, Yoo YD, Kim JS, Jeong HJ (2013) Feeding by heterotrophic protists and copepods on the photosynthetic dinoflagellate Azadinium cf. poporum from western Korean waters. Aquat Microb Ecol 68:143–158
Reñé A, Camp J, Garcés E (2015) Diversity and phylogeny of Gymnodiniales (Dinophyceae) from the NW Mediterranean Sea revealed by a morphological and molecular approach. Protist 166:234–263
Schmoker C, Thor P, Hernández-León S, Hansen BW (2011) Feeding, growth and metabolism of the marine heterotrophic dinoflagellate Gyrodinium dominans. Aquat Microb Ecol 65:65–73
Seong KA, Jeong HJ (2013) Interactions between marine bacteria and red tide organisms in Korean waters. Algae 28:297–305
Sherr EB, Sherr BF (2007) Heterotrophic dinoflagellates: a significant component of microzooplankton biomass and major grazers of diatoms in the sea. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 352:187–197
Shumway SE (1990) A review of the effects of algal blooms on shellfish and aquaculture. J World Aquacult Soc 21:65–104
Stern RF, Horak A, Andrew RL, Coffroth MA, Andersen RA, Küpper FC, Jameson I, Hoppenrath M, Véron B, Kasai F, Brand J, James ER, Keeling PJ (2010) Environmental barcoding reveals massive dinoflagellate diversity in marine environments. PLoS ONE 5:11
Stoecker DK (1999) Mixotrophy among Dinoflagellates 1. J Eukaryot Microbiol 46:397–401
Tillmann U (2004) Interactions between planktonic microalgae and protozoan grazers. J Eukaryot Microbiol 51:156–168
Turner JT (2010) Zooplankton community grazing impact on a bloom of Alexandrium fundyense in the Gulf of Maine. Harmful Algae 9:578–589
Yih W, Kim HS, Jeong HJ, Myung G, Kim YG (2004) Ingestion of cryptophyte cells by the marine photosynthetic ciliate Mesodinium rubrum. Aquat Microb Ecol 36:165–170
Yoo YD, Yoon EY, Jeong HJ, Lee KH, Hwang YJ, Seong KA, Kim JS, Park JY (2013a) The newly described heterotrophic dinoflagellate Gyrodinium moestrupii, an effective protistan grazer of toxic dinoflagellates. J Eukaryot Microbiol 60:13–24
Yoo YD, Yoon EY, Lee KH, Kang NS, Jeong HJ (2013b) Growth and ingestion rates of heterotrophic dinoflagellates and a ciliate on the mixotrophic dinoflagellate Biecheleria cincta. Algae 28:343–354
Yoo YD, Jeong HJ, Lee SY, Yoon EY, Kang NS, Lim AS, Lee KH, Jang SH, Park JY, Kim HS (2015) Feeding by heterotrophic protists on the toxic dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata. Harmful Algae 49:1–9
Yoon EY, Kang NS, Jeong HJ (2012) Gyrodinium moestrupii n. sp., a new planktonic heterotrophic dinoflagellate from the coastal waters of western Korea: morphology and ribosomal DNA gene sequence. J Eukaryot Microbiol 59:571–586
You JH, Jeong HJ, Kang HC, Ok JH, Park SA, Lim AS (2020) Feeding by common heterotrophic protist predators on seven Prorocentrum species. Algae 35:61–78
Acknowledgements
We thank An Suk Lim for technical supports. This research was supported by the Useful Dinoflagellate program of Korea Institute of Marine Science and Technology Promotion (KIMST) funded by the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries (MOF) and the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (NRF-2017R1E1A1A01074419) award to HJJ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of organisms were followed.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: S. Shumway.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Reviewed by undisclosed experts.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, H.C., Jeong, H.J., Park, S.A. et al. Feeding by the newly described heterotrophic dinoflagellate Gyrodinium jinhaense: comparison with G. dominans and G. moestrupii. Mar Biol 167, 156 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-020-03769-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-020-03769-9