Abstract
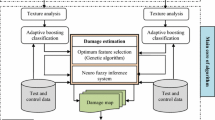
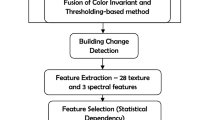
Heritage sites are vulnerable to damage due to social, anthropological and environmental factors. Major Earthquakes are followed by damage to cultural heritage buildings. The assessment of such building damage is a critical problem. Earth Observation data, owing to its property of being non-contact, cost effective, synoptic view and high repeatability, has a significant role to play in estimation of damage in the earthquake affected areas. Currently, several and varied types of remote sensing data have become available, and therefore, appropriate methods for rapid assessment and analysis of the data need to be developed. Rapid damage assessment is critical to minimize loss in terms of life and property. In case of cultural monuments, rapid assessment can minimize damage and help in the conservation of monument. This research focuses on evolving a robust method for rapid identification and extraction of damaged heritage building structures, especially those affected by disasters such as earthquakes. In this study, we propose to examine the utility of advance texture algorithms such as Gabor, fractal and semi-variogram for rapid damage detection in heritage building structures. The methodology attempts to automatically highlight damaged portions of the structure through a knowledge driven rule set. The technique was able to extract the damaged area from the heritage building structure with the use of high-resolution space borne data. It is observed that feature extraction algorithms based on fractal and variogram provide better results than the Gabor based textures and are very useful in the case of high-resolution satellite imagery. Both the methods are able to extract damaged features in both shadowed and non-shadowed regions of the image. Hence the problems posed by shadowed dead grounds on EO data can be effectively resolved. However, it is also observed that the advance texture feature extraction algorithms are useful only in case of high-spatial resolution dataset and has limited use for rapid damage assessment from medium and low resolution datasets.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akinin, M. V., & Akinina, A. V. (2017). Application of EM algorithm in problems of pattern recognition on satellite images. In 6th Mediterranean conference on embedded computing (pp. 175–178). Bar, Montenegro: IEEE.
Bhardwaj, N. (2017). Image sharpening using fuzzy logic based edge detection. International Journal of Scientific Research in Science, Engineering and Technology, 3(1), 536–542.
Dong, L., & Shan, J. (2013). A comprehensive review of earthquake-induced building damage detection with remote sensing techniques. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 84, 85–96.
Galantucci, R. A., & Fatiguso, F. (2019). Advanced damage detection techniques in historical buildings using digital photogrammetry and 3D surface anlysis. Journal of Cultural Heritage, 36, 51–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.culher.2018.09.014.
Gupta, V., Kumar, L., & Kumari, U. (2011). Color satellite image segmentation using Markov random field and multiresolutional wavelet transform. International Journal of Computer Applications in Engineering Sciences (IJCAES), 1(1), 75–79.
Jabari, S., & Zhang, Y. (2013). Very high resolution satellite image classification using fuzzy rule-based systems. Algorithms, 6, 762–781.
Dong, S., Li, H., & Sun, D. (2017). Fractal feature analysis and information extraction of woodlands based on MODIS NDVI time series. Sustainability, 9, 1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9071215.
Menderes, A., Erener, A., & Sarp, G. (2015). Automatic detection of damaged buildings after earthquake hazard by using remote sensing and information technologies. Procedia Earth and Planetary Science, 15, 257–262.
Pakdel, M., & Tajeripour, F. (2011) Texture classification using optimal Gabor filters. In 1st International eConference on computer and knowledge engineering (ICCKE) (pp. 208–213).
Perez, H., Tah, J. H. M., & Mosavi, A. (2019). Deep learning for detecting building defects using convolutional neural networks. Sensors (Switzerland), 19(16), 3556. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19163556.
Samadzadegen, F., & Rastiveisi, H. (2008). Automatic detection and classification of damaged buildings, using high resolution satellite imagery and vector data. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, XXXVII(Part B8), 415–420.
Sheet, D., Garud, H., Suveer, A., Mahadevappa, M., & Chatterjee, J. (2010). Brightness preserving dynamic fuzzy histogram equalization. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 56(4), 2475–2480.
Shi, C.-T. (2018). Signal pattern recognition based on fractal features and machine learning. Applied Sciences, 8, 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8081327.
Vafadari, A., Philip, G., & Jennings, R. (2017). Damage assessment and monitoring of cultural heritage places in a disaster and post disaster event—A case study of Syria. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, XLII-2/W5, 695–701.
Veluchamy, M., & Erode, C. R. (2013). Fuzzy logic based histogram equalization FPR image contast enhancement. Mathematical Problems in Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/891864.
Wu, X., Peng, J., Shan, J., & Cui, W. (2015). Evaluation of semivariogram features for object-based image classification. Geo-spatial Information Science, 18(4), 159–170. https://doi.org/10.1080/10095020.2015.1116206.
Zhang, X., Cui, J., Wang, W., & Lin, C. (2017). A study for texture feature extraction of high-resolution satellite images based on a direction measure and gray level co-occurrence matrix fusion algorithm. Sensors, 17, 15.
Websites accessed
Retrieved Januray 05, 2018 from https://in.mathworks.com/help/matlab/.
Retrieved February 12, 2018 from https://directory.eoportal.org/web/eoportal/satellite-missions/p/pleiades.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, N., Tiwari, P.S., Pande, H. et al. Utilizing Advance Texture Features for Rapid Damage Detection of Built Heritage Using High-Resolution Space Borne Data: A Case Study of UNESCO Heritage Site at Bagan, Myanmar. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 48, 1627–1638 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-020-01190-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-020-01190-9