Abstract
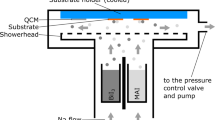
We suggest a combination of morphological control and the introduction of an additive as a strategy to completely convert thermally grown a PbI2 layer into the perovskite structure for inverted organic–inorganic hybrid perovskite solar cells (PSCs). For 2-step PSCs based on thermal evaporation, the complete conversion of PbI2 into the perovskite structure is a key parameter for device performance. To achieve complete conversion, we regulated the morphology of the PbI2 layer by controlling the growth rate. Compared to rapidly grown PbI2 layers, a PbI2 layer grown at a slow rate contained pinholes that enhanced the diffusion of methyl ammonium iodide (MAI) from the PbI2 surface. Despite the assistance of the pinholes, the conversion of the PbI2 was incomplete due to the limited interaction between the MAI and PbI2. Complete conversion of the pinhole-rich PbI2 occurred by introducing an additive into the MAI solution. The conversion of PbI2 was measured by grazing-incidence wide-angle X-ray scattering using synchrotron X-rays. By controlling the incidence angle of the X-rays, we quantitatively compared the amount of PbI2 as a function of the X-ray penetration depth. Using a completely converted 50 nm-thick PbI2 layer, we obtained a power conversion efficiency of 9.44%.
Graphic Absract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Wolf, S., Holovsky, J., Moon, S.J., Loper, P., Niesen, B., Ledinsky, M., Haug, F.J., Yum, J.H., Ballif, C.: Organometallic halide perovskites: sharp optical absorption edge and its relation to photovoltaic performance. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 5(6), 1035–1039 (2014)
Lin, Q., Armin, A., Nagiri, R.C.R., Burn, P.L., Meredith, P.: Electro-optics of perovskite solar cells. Nat. Photonics 9(2), 106–112 (2014)
Green, M.A., Ho-Baillie, A., Snaith, H.J.: The emergence of perovskite solar cells. Nat. Photonics 8(7), 506–514 (2014)
Yin, W.-J., Yang, J.-H., Kang, J., Yan, Y., Wei, S.-H.: Halide perovskite materials for solar cells: a theoretical review. J. Mater. Chem. A 3(17), 8926–8942 (2015)
Kim, Y.H., Cho, H., Lee, T.W.: Metal halide perovskite light emitters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 113(42), 11694–11702 (2016)
Veldhuis, S.A., Boix, P.P., Yantara, N., Li, M., Sum, T.C., Mathews, N., Mhaisalkar, S.G.: Perovskite materials for light-emitting diodes and lasers. Adv. Mater. 28(32), 6804–6834 (2016)
Jo, J.W., Yoo, Y., Jeong, T., Ahn, S., Ko, M.J.: Low-temperature processable charge transporting materials for the flexible perovskite solar cells. Electron. Mater. Lett. 14(6), 657–668 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-018-0073-7
Gil, B., Yun, A.J., Lee, Y., Kim, J., Lee, B., Park, B.: Recent progress in inorganic hole transport materials for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. Electron. Mater. Lett. 15(5), 505–524 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-019-00163-6
NREL. Efciency chart. https://www.nrel.gov/pv/cell-efficiency.html
Song, Z., Watthage, S.C., Phillips, A.B., Heben, M.J.: Pathways toward high-performance perovskite solar cells: review of recent advances in organo-metal halide perovskites for photovoltaic applications. J. Photonics Energy 6(2), 022001 (2016)
Song, T.-B., Chen, Q., Zhou, H., Jiang, C., Wang, H.-H., Yang, Y., Liu, Y., You, J., Yang, Y.: Perovskite solar cells: film formation and properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 3(17), 9032–9050 (2015)
Lal, N.N., Dkhissi, Y., Li, W., Hou, Q., Cheng, Y.-B., Bach, U.: Perovskite Tandem Solar Cells. Adv. Energy Mater. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201602761
Cui, P., Wei, D., Ji, J., Huang, H., Jia, E., Dou, S., Wang, T., Wang, W., Li, M.: Planar p–n homojunction perovskite solar cells with efficiency exceeding 21.3%. Nat. Energy 4(2), 150–159 (2019)
Wang, L., McCleese, C., Kovalsky, A., Zhao, Y., Burda, C.: Femtosecond time-resolved transient absorption spectroscopy of CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite films: evidence for passivation effect of PbI2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136(35), 12205–12208 (2014)
Cao, D.H., Stoumpos, C.C., Malliakas, C.D., Katz, M.J., Farha, O.K., Hupp, J.T., Kanatzidis, M.G.: Remnant PbI2, an unforeseen necessity in high-efficiency hybrid perovskite-based solar cells? APL Mater. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4895038
Shi, B., Yao, X., Hou, F., Guo, S., Li, Y., Wei, C., Ding, Y., Li, Y., Zhao, Y., Zhang, X.: Unraveling the passivation process of PbI2 to enhance the efficiency of planar perovskite solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 122(37), 21269–21276 (2018)
Lai, W.-C., Hsieh, W.-M., Yu, H.-C., Yang, S.-H., Guo, T.-F., Chen, P.: Conversion efficiency enhancement of methyl ammonium lead triiodide perovskite solar cells converted from thermally deposited lead iodide via thin methyl ammonium iodide interlayer. Org. Electron (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orgel.2020.105713
Liu, A., Liu, K., Zhou, H., Li, H., Qiu, X., Yang, Y., Liu, M.: Solution evaporation processed high quality perovskite films. Sci. Bull. 63(23), 1591–1596 (2018)
Fu, Y., Meng, F., Rowley, M.B., Thompson, B.J., Shearer, M.J., Ma, D., Hamers, R.J., Wright, J.C., Jin, S.: Solution growth of single crystal methylammonium lead halide perovskite nanostructures for optoelectronic and photovoltaic applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137(17), 5810–5818 (2015)
Tu, Y., Wu, J., He, X., Guo, P., Wu, T., Luo, H., Liu, Q., Wang, K., Lin, J., Huang, M., Huang, Y., Lan, Z., Li, S.: Solvent engineering for forming stonehenge-like PbI2nano-structures towards efficient perovskite solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 5(9), 4376–4383 (2017)
Li, Y., Ding, B., Yang, G.-J., Li, C.-J., Li, C.-X.: Achieving the high phase purity of CH3NH3PbI3 film by two-step solution processable crystal engineering. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 34(8), 1405–1411 (2018)
Kim, S.-Y., Jo, H.J., Sung, S.-J., Kim, D.-H.: Perspective: understanding of ripening growth model for minimum residual PbI2 and its limitation in the planar perovskite solar cells. APL Mater. 4(10), 100901 (2016)
Fu, F., Kranz, L., Yoon, S., Löckinger, J., Jäger, T., Perrenoud, J., Feurer, T., Gretener, C., Buecheler, S., Tiwari, A.N.: Controlled growth of PbI2 nanoplates for rapid preparation of CH3NH3PbI3 in planar perovskite solar cells. Phys. Stat. Solidi (a) 212(12), 2708–2717 (2015)
Ahn, N., Son, D.Y., Jang, I.H., Kang, S.M., Choi, M., Park, N.G.: Highly reproducible perovskite solar cells with average efficiency of 18.3% and best efficiency of 19.7% fabricated via lewis base adduct of lead(II) Iodide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137(27), 8696–8699 (2015)
Birkholz, M.: Thin film analysis by X-ray scattering. WILEY-VCH, Weinheim (2006)
Index of refraction https://henke.lbl.gov/optical_constants/getdb2.html
Gujar, T.P., Unger, T., Schonleber, A., Fried, M., Panzer, F., van Smaalen, S., Kohler, A., Thelakkat, M.: The role of PbI2 in CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite stability, solar cell parameters and device degradation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20(1), 605–614 (2017)
Soucase, B.M., Pradas, I.G., Adhikari, K.R.: Numerical simulations on perovskite photovoltaic devices. In: Pan, L., Zhu, G. (eds.) Perovskite materials: synthesis, characterisation, properties, and applications, pp. 445–486. InTech, London (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Korean Government (NRF-2018R1A2B600517813, NRF-2015R1A5A1009962), the Korea Electric Power Corporation (CX72170050).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S.H., Hong, S., An, S. et al. Strategy for the Complete Conversion of Thermally Grown PbI2 Layers in Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells. Electron. Mater. Lett. 16, 588–594 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-020-00250-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-020-00250-z