Abstract
The Portoviejo city, located in the central part of the Ecuadorian Pacific Coast (province of Manabí), was severely affected during the Pedernales Mw 7.8 earthquake of April 16, 2016, accompanied by coseismic liquefaction phenomena that induced processes of ground subsidence, lateral spreading, sinkhole, and sand boils. The present study proposes the detection and delimitation of the areas affected by the relief deformation, associated liquefaction processes, which occurred in the urban area of Portoviejo city and especially in the Zero Zone of greater destruction after the earthquake, through the application of Differential Interferometry Synthetic Aperture Radar (INSAR) methodology, using Sentinel 1A satellite images, plus the support of geological–geotechnical data obtained from boreholes and standard penetration tests to evaluate the liquefaction potential of the layers of the subsoil based on the Potential Liquefaction Index, considering the seismic scenario of amax 0.5 g for the urban area and the Zero Zone. This procedure allowed the delimitation of areas of high seismic risk for the proper coordination and management of the construction and reconstruction processes in the city of Portoviejo and specifically in the Ground Zero.



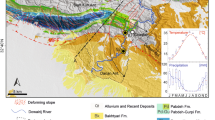
(modified from Ortiz-Hernández and Chunga 2019)










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguiar R, Mieles Bravo Y (2016) Análisis de los edificios que colapsaron en Portoviejo durante el terremoto del 16 de abril de 2016. Revista Internacional de Ingeniería de Estructuras 21(3):257–282
Cando-Jácome M, Martínez-Graña A (2018) Numerical modeling of flow patterns applied to the analysis of the susceptibility to movements of the ground. Geosciences (Switzerland) 8:340. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/327542692_Numerical_modeling_of_flow_patterns_applied_to_the_analysis_of_the_susceptibility_to_movements_of_the_ground
Carena S (2011) Subducting-plate topography and nucleation of great and giant earthquakes along the South America trench. Seismol Res Lett 82(5): 629–637. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1785/gssrl.82.5.629. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/236962482_Subducting-plate_Topography_and_Nucleation_of_Great_and_Giant_Earthquakes_along_the_South_American_Trench
Chen CJ, Juang CH (2000) Calibration of SPT-and CPT-based liquefaction evaluation methods. In: Mayne PW, Hryciw R (eds) Innovation sand application sin geotechnical site characterization, vol 97. Geotechnical Special Publication ASCE, Reston, pp 49–64. https://doi.org/10.1061/40505%28285%294
Chen L, Yuan X, Cao Z (2009) Liquefaction macrophenomena in the great Wenchuan earthquake. Earthq Eng Eng Vib 8:219–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11803-009-9033-4
Chunga K, Livio F, Mulas M, Ochoa-Cornejo F, Besenzon D, Ferrario M, Michetti AM (2018) Earthquake ground effects and intensity of the 16 April 2016, Mw 7.8 Pedernales Earthquake (Ecuador): implications for the source characterization of large subduction earthquakes. Bull Seismol Soc Am 108(6): 3384–3397. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1785/0120180051. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/ssa/bssa/article-abstract/108/6/3384/559138/Earthquake-Ground-Effects-and-Intensity-of-the-16?redirectedFrom=fulltext
Chunga K, Livio FA, Martillo C, Lara-Saavedra H, Ferrario MF, Zevallos I, Michetti AM (2019) Landslides Triggered by the 2016 Mw 7.8 Pedernales, Ecuador Earthquake: correlations 643 with ESI-07 Intensity, Lithology, Slope and PGA-h. Geosciences 9:371. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9090371. https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3263/9/9/371/htm
Eguez A, Alvarado A, Yepes H, Machette MN, Costa C, Dart RL, Bradley LA (2003) Database and map of Quaternary faults and folds of Ecuador and its offshore regions, US Geol. Surv. Open-File Rept. 3. https://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2003/ofr-03-289/
Gens R, Logan T (2003) Alaska satellite facility software tools Manual. Published by Geophysical Institute, 2003. University of Alaska Fairbanks P.O. Box 7320 Fairbanks, AK-99775 USA. https://media.asf.alaska.edu/uploads/Get%2520Started/asf_software_tools.pdf
Hey R (1977) Tectonic evolution of the Cocos-Nazca spreading center. Geol Soc Am Bull 88(12): i–vi. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/gsa/gsabulletin/article-abstract/88/10/1404/189922/Tectonic-evolution-of-the-Cocos-Nazca-spreading?redirectedFrom=PDF
INEC (2010) Base de Datos—Censo de Población y Vivienda del Ecuador 2010. Disponible en: 536 https://www.ecuadorencifras.gob.ec/base-de-datos-censo-de-poblacion-y-vivienda/
Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (2010) Missions employing formation flying. Proc IEEE (5):816–843
IOC Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (2020) Tsunami sources, hazards, risk and uncertainties associated with the Colombia-Ecuador Subduction Zone. Guayaquil, Ecuador, 27–29 January. Paris, UNESCO
Iwasaki T, Tokida K, Tatsuoka F (1981) Soil liquefaction potential evaluation with use of the simplified procedure. In: International conferences on recent advances in geotechnical earthquake engineering and soil dynamics. 12. https://scholarsmine.mst.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=2503&context=icrageesd
Iwasaki T, Tokida K, Tatsuoka F, Watanabe S, Yasuda S, Sato H (1982) Microzonation for soil liquefaction potential using simplified methods. In: Proceedings of the 3rd international conference on microzonation, Seattle
Juang CH, Chen CJ (1999) CPT-based liquefaction evaluation using artificial neural networks. Comput-Aided Civ Infrastruct Eng 14(3):221–229. https://www.nrcresearchpress.com/doi/10.1139/t99-011#.X2-4eGhKjUQ
Juang CH, Yuan H, Lee D-H, Lin PS (2003) Simplified cone penetration test-based method for evaluating liquefaction resistance of soils. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 129(1): 66–80. https://researchoutput.ncku.edu.tw/en/publications/simplified-cone-penetration-test-based-method-for-evaluating-liqu
Kelleher J (1972) Rupture zones of large South American earthquakes and some predictions. J Geophys Res 77(11):2087–2103. https://doi.org/10.1029/JB077i011p02087
Liao S, Whitman R (1986) Overburden correction factor for SPT in sand. J Geotech Eng 112(3):373–377. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Overburden-Correction-Factors-for-SPT-in-Sand-Liao-Whitman/162065f99119624ae2e1bafc465b5d384e44c36f
Martinez-Graña AM, Goy JL, Cimarra C (2015) 2D to 3D geologic map transformation using virtual globes, flight simulators, and their applications in the analysis of geodiversity in natural areas. Environ Earth Sci 73(12):8023–8034. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3959-1
Martínez-Graña AM, Goy JL, Zazo C (2016) Geomorphological applications for susceptibility mapping of landslides in natural parks. Environ Eng Manag J 15(2):1–12
Ortiz-Hernández E, Chunga K (2019) Evaluación de riesgo por licuefacción de suelos en la ciudad de Portoviejo, Manabí. II Jornadas Científicas Internacional de Ingeniería ULEAM, Manta, Ecuador. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/334596267_Evaluacion_de_riesgo_por_licuefaccion_de_suelos_en_la_ciudad_de_Portoviejo_Manabi
Pennington WD (1981) Subduction of the eastern Panama basin and seismotectonics of northwestern South America. J Geophys Res 86(B11):10753–10770. https://www.academia.edu/28780277/Subduction_of_the_Eastern_Panama_Basin_and_seismotectonics_of_northwestern_South_America
Perissin D (2011) The SARPROZ InSAR tool for urban subsidence/manmade structure stability monitoring in China. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/The-SARPROZ-InSAR-tool-for-urban-subsidence-%2F-in-Perissin-Wang/abbc4e6a0f7ea3d634bf55248a7c3a12da8b62cd
Seed HB, Idriss IM (1982) Ground motions and soil liquefaction during earthquakes. Earthquake Engineering Research Institute Monograph, Oakland. https://capitadiscovery.co.uk/brighton-ac/items/878891
Sillerico E, Marchamalo M, Rejas JG, Martínez R (2010) La técnica DInSAR: bases y aplicación a la medición de subsidencias del terreno en la construcción. Informes de la Construccion. 62. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3989/ic.09.063. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/46179345_La_tecnica_DInSAR_bases_y_aplicacion_a_la_medicion_de_subsidencias_del_terreno_en_la_construccion
Soza D (2018) Tutorial: Data processing DEM Alos-1 PalSAR RTC. https://es.scribd.com/document/392931606/Tutorial-Procesamiento-Datos-DEM-Alos-1-PalSAR-RTC
The Copernicus Open Access Hub (2018) The Open Access Hub Provides Complete, free and open access to Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, Sentinel-3 and Sentinel-5P User Products. https://scihub.copernicus.eu/userguide/
Veloza G, Styron R, Taylor M, Mora A (2012) Open-source archive of active faults for northwest South America. GSA Today 2012; 22(10): 4–10. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/235185176_Open_source_archive_of_active_faults_for_northwest_South_America
Vidal Montes R, Martínez-Graña AM, Martínez Catalán JR, Ayarza P, Sánchez San Román FJ (2016) Vulnerability to groundwater contamination, (SW Salamanca, Spain). J Maps 12:147–155. https://doi.org/10.1080/17445647.2016.1172271
Youd TL, Idriss IM, Andrus RD, Arango I, Castro G, Christian TV, Dobry R, Finn WDL, Harder LF, Hynes ME, Ishihara K, Koester JP, Liao SSC, Marcurson WF III, Marti GR, Mitchell JK, Moriwaki Y, Power MS, Robertson PK, Seed RB, Stokoe KH (2001) Liquefaction resistance of soils: summary report from the 1996 NCEER and 1998 NCEER/NSF workshops on evaluation of liquefaction resistance of soils. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng ASCE 127(10):817–833. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/242139393_Liquefaction_Resistance_of_Soils_Summary_Report_from_the_1996_NCEER_and_1998_NCEERNSF_Workshops_on_Evaluation_of_Liquefaction_Resistance_of_Soils
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the project: Junta Castilla y León SA044G18. The Geohazard Research Group of the Universidad Técnica de Manabí (UTM) supported this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cando-Jácome, M., Martínez-Graña, A., Chunga, K. et al. Satellite radar interferometry for assessing coseismic liquefaction in Portoviejo city, induced by the Mw 7.8 2016 Pedernales, Ecuador earthquake. Environ Earth Sci 79, 467 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09205-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09205-x