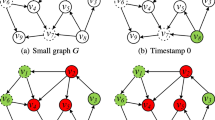
Abstract
Rumormongers spread negative information throughout the social network, which may even lead to panic or unrest. Rumor should be blocked by spreading positive information from several protector nodes in the network. Users will not be influenced if they receive the positive information ahead of negative one. In many cases, network manager or government may not know the exact positions where rumor will start. Meanwhile, protector nodes also need to be selected in order to prepare for rumor blocking. Given a social network G = (V,E,P), where P is the weight function on edge set E, P(u,v) is the probability that v is activated by u after u is activated. Assume there will be l rumormongers in the network while the exact positions are not clear, Robust Rumor Blocking(RRB) problem is to select k nodes as protector such that the expected eventually influenced users by rumor is minimized. RRB will be proved to be NP-hard and the objective function is neither submodular nor supermodular. We present an estimation process for the objective function of RRB based on Reverse Reachable Set(RR-Set) methods. A randomized greedy algorithm is designed for solving this problem. And this algorithm is proved to have approximation ratio \(\frac {1}{\alpha }(1-e^{-\alpha \gamma })(1+\epsilon )\) plus a constant, where γ is submodularity ratio and α is curvature.Finally, we evaluate our algorithm on real world data sets and do comparison among different strategies for protector. The results show the effectiveness and the efficiency of the proposed algorithm.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aslay, C., Lakshmanan, L.V.S., Lu, W., Xiao, X.: Influence maximization in online social networks. In: Proceedings of the Eleventh ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, pp. 775–776. ACM (2018)
Batagelj, V., Mrvar, A.: Pajek datasets. http://vlado.fmf.uni-lj.si/pub/networks/data/ (2006)
Bharathi, S., Kempe, D., Salek, M.: Competitive influence maximization in social networks. In: International Workshop on Web and Internet Economics, pp. 306–311. Springer (2007)
Bian, A.A., Buhmann, J.M, Krause, A., Tschiatschek, S.: Guarantees for greedy maximization of non-submodular functions with applications. arXiv:1703.02100 (2017)
Borgs, C., Brautbar, M., Chayes, J., Lucier, B.: Maximizing social influence in nearly optimal time. In: Proceedings of the twenty-fifth annual ACM-SIAM symposium on Discrete algorithms, pp. 946–957. SIAM (2014)
Budak, C., Agrawal, D., El Abbadi, A: Limiting the spread of misinformation in social networks. In: Proceedings of the 20th international conference on World wide web, pp. 665–674. ACM (2011)
Burkitt, L.: Fearing radiation, chinese rush to buy table salt. The Wall Street Journal (2011)
Chen, W., Lin, T., Tan, Z., Zhao, M., Zhou, X.: Robust influence maximization. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 795–804. ACM (2016)
Dagum, P., Karp, R., Luby, M., Ross, S.: An optimal algorithm for monte carlo estimation. SIAM J. Comput. 29(5), 1484–1496 (2000)
Das, A., Kempe, D.: Submodular meets spectral: Greedy algorithms for subset selection, sparse approximation and dictionary selection. arXiv:1102.3975 (2011)
Du, N., Liang, Y., Balcan, M-F, Gomez-Rodriguez, M., Zha, H., Le, S.: Scalable influence maximization for multiple products in continuous-time diffusion networks. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 18(2), 1–45 (2017)
Feige, U.: A threshold of ln n for approximating set cover. J ACM (JACM) 45(4), 634–652 (1998)
Fujishige, S.: Submodular functions and optimization, vol. 58. Elsevier (2005)
Goyal, A., Lu, W., Lakshmanan, L.VS: Simpath: An efficient algorithm for influence maximization under the linear threshold model. In: 2011 IEEE 11th International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), pp. 211–220. IEEE (2011)
Kempe, D., Kleinberg, J., Tardos, É: Maximizing the spread of influence through a social network. In: Proceedings of the ninth ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, pp. 137–146. ACM (2003)
Kimura, M., Saito, K., Motoda, H.: Blocking links to minimize contamination spread in a social network. ACM Trans Knowl Discov Data (TKDD) 3(2), 9 (2009)
Leskovec, J., Krause, A., Guestrin, C., Faloutsos, C., VanBriesen, J., Glance, N.: Cost-effective outbreak detection in networks. In: Proceedings of the 13th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, pp. 420–429. ACM (2007)
Li, S., Zhu, Y., Li, D., Kim, D., Huang, H.: Rumor restriction in online social networks. In: 2013 IEEE 32nd International Performance Computing and Communications Conference (IPCCC), pp. 1–10. IEEE (2013)
Lowalekar, M., Varakantham, P., Kumar, A.: Robust influence maximization.. In: Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Autonomous Agents & Multiagent Systems, pp. 1395–1396. International Foundation for Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems (2016)
Morozov, E.: Swine flu: Twitters power to misinform Foreign policy (2009)
Nemhauser, G.L., Wolsey, L.A.: Maximizing submodular set functions: formulations and analysis of algorithms. Stud Graph Discret Programm 11, 279–301 (1981)
Nemhauser, G.L., Wolsey, L.A., Fisher, M.L.: An analysis of approximations for maximizing submodular set functionsi. Math Programm 14(1), 265–294 (1978)
Nguyen, H.T., Thai, M y T, Dinh, T.N.: Stop-and-stare Optimal sampling algorithms for viral marketing in billion-scale networks.. In: Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Management of Data, pp. 695–710. ACM (2016)
Nguyen, H., Zheng, R.: On budgeted influence maximization in social networks. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 31(6), 1084–1094 (2013)
Ohsaka, N., Akiba, T., Yoshida, Y., Kawarabayashi, K-i: Fast and accurate influence maximization on large networks with pruned monte-carlo simulations. In: AAAI, pp. 138–144 (2014)
Opsahl, T.: Triadic closure in two-mode networks: Redefining the global and local clustering coefficients. Soc. Netw. 35(2), 159–167 (2013)
Ping, Y., Cao, Z., Zhu, H.: Sybil-aware least cost rumor blocking in social networks. In: 2014 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), pp. 692–697. IEEE (2014)
Rossi, Ryxan A. , Ahmed, NK.: The network data repository with interactive graph analytics and visualization. In: AAAI (2015)
Sviridenko, WJ., Vondrk, M.J.: Optimal approximation for submodular and supermodular optimization with bounded curvature. Math. Oper. Res. 42 (2), 1197–1218 (2017)
Tang, Y., Shi, Y., Xiao, X.: Influence maximization in near-linear time A martingale approach.. In: Proceedings of the 2015 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, pp. 1539–1554. ACM (2015)
Tang, Y., Xiao, X., Shi, Y.: Influence maximization: Near-optimal time complexity meets practical efficiency. In: Proceedings of the 2014 ACM SIGMOD international conference on Management of data, pp. 75–86. ACM (2014)
Tong, G., Wu, W., Guo, L., Li, D., Liu, C., Liu, B., Du, D-Z: An efficient randomized algorithm for rumor blocking in online social networks. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering (2017)
Tsai, J., Nguyen, T.H., Tambe, M.: Security games for controlling contagion. In: AAAI (2012)
Wang, B., Ge, C., Fu, L., Li, S., Wang, X., Liu, X.: Drimux: Dynamic rumor influence minimization with user experience in social networks. In: AAAI, vol. 16, pp. 791–797 (2016)
Watts, D.J., Strogatz, S.H.: Collective dynamics of small-worldnetworks. Nature 393(6684), 440 (1998)
Wu, W., Zhang, Z., Du, D.Z.: Set function optimization. J. Oper. Res. Soc. China (3), 1–11 (2018)
Yang, Y., Lu, Z., Li, Vi.O., Xu, K.: Noncooperative information diffusion in online social networks under the independent cascade model. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 4(3), 150–162 (2017)
Zhang, H., Zhang, H., Li, K., Thai, M.T.: Limiting the spread of misinformation while effectively raising awareness in social networks. In: International Conference on Computational Social Networks, pp. 35–47. Springer (2015)
Zhu, J., Zhu, J., Ghosh, S., Wu, W., Yuan, J.: Social influence maximization in hypergraph in social network. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, pp. 1–1 (2018)
Zhu, J., Ghosh, S., Zhu, J., Wu, W.: Near-optimal convergent approach for composed influence maximization problem in social networks. IEEE Access 7, 142488–142497 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grant no. 72074203, the US National Science Foundation (NSF) under Award no. 1747818 and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, J., Ghosh, S. & Wu, W. Robust rumor blocking problem with uncertain rumor sources in social networks. World Wide Web 24, 229–247 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-020-00841-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-020-00841-8