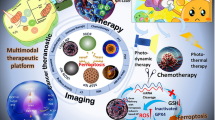
Abstract
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a new approach to destroy tumor over past decades due to its high selectivity and minimal invasiveness. Photosensitizers (PSs), plenty of oxygen, and special wavelengths of light irradiation are three indispensable basic elements in the PDT therapeutic procedure. Upon exposed to light irradiation, PSs utilized surround oxygen to produce poisonous reactive oxygen species (ROS) to kill cancer cells through apoptosis or necrosis. PDT cased cancer cells damage highly dependent on tissue oxygen concentration and DNA self-repairing inhibition. Therefore, altering ROS homeostasis in cancer cells can be exploited for tumor therapeutic. Furthermore, PDT as the highly selective therapy approach can directly ablate solid tumor at primary sites. Meanwhile, it can induce immunogenic cell death by release damage-associate molecular patterns and tumor-associated antigens to activate immune response for inhibit cancer recurrence and metastasis. However, PDT was seriously hampered due to the poor drug penetration depth and unfavorable biodistribution of PSs at the lesion tissues. As the development of nanomaterial, nanotechology-based PDT have made a huge revolution in cancer therapeutic, which can effectively overcome these drawbacks and ameliorate the complex tumor microenvironment to enhance PDT effects. In general, the size of nanoparticles between 50 and 100 nm can prolong blood circulation time and efficiently tumor accumulation through enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effects. Once inside the tumor tissues, they should be small enough to enhance penetration. Given this, we summarize the advances of PDT in tumor therapeutic.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albadari N, Deng S, Li W (2019) The transcriptional factors HIF-1 and HIF-2 and their novel inhibitors in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Drug Discov 14(7):667–682
Bao X, Yuan Y, Chen J, Zhang B, Li D, Zhou D, Jing P, Xu G, Wang Y, Holá K, Shen D, Wu C, Song L, Liu C, Zbořil R, Qu S (2018) In vivo theranostics with near-infrared-emitting carbon dots-highly efficient photothermal therapy based on passive targeting after intravenous administration. Light Sci Appl 7:91
Barker HE, Paget JTE, Khan AA, Harrington KJ (2015) The tumour microenvironment after radiotherapy: mechanisms of resistance and recurrence. Nat Rev Cancer 15(7):409–425
Boonstra J, Post JA (2004) Molecular events associated with reactive oxygen species and cell cycle progression in mammalian cells. Gene 337:1–13
Chen H, Kuo MT (2017) Improving radiotherapy in cancer treatment: promises and challenges. Oncotarget 8(37):62742–62758
Chen H, Tian J, He W, Guo Z (2015a) H2O2-activatable and O2-evolving nanoparticles for highly efficient and selective photodynamic therapy against hypoxic tumor cells. J Am Chem Soc 137(4):1539–1547
Chen Q, Liang C, Wang C, Liu Z (2015b) An imagable and photothermal “Abraxane-like” nanodrug for combination cancer therapy to treat subcutaneous and metastatic breast tumors. Adv Mater 27(5):903–910
Chen Q, Feng L, Liu J, Zhu W, Dong Z, Wu Y, Liu Z (2016) Intelligent albumin-MnO2 nanoparticles as pH-/H2O2-responsive dissociable nanocarriers to modulate tumor hypoxia for effective combination therapy. Adv Mater 28(33):7129–7136
Chen D, Zhang J, Tang Y, Huang X, Shao J, Si W, Ji J, Zhang Q, Huang W, Dong X (2018) A tumor-mitochondria dual targeted aza-BODIPY-based nanotheranostic agent for multimodal imaging-guided phototherapy. J Mater Chem B 6(27):4522–4530
Chen Q et al (2019) Nanoparticle-enhanced radiotherapy to trigger robust cancer immunotherapy. Adv Mater 31(10):e1802228
Evans SS, Repasky EA, Fisher DT (2015) Fever and the thermal regulation of immunity: the immune system feels the heat. Nat Rev Immunol 15(6):335–349
Fan W, Bu W, Shen B, He Q, Cui Z, Liu Y, Zheng X, Zhao K, Shi J (2015) Intelligent MnO2 nanosheets anchored with upconversion nanoprobes for concurrent pH-/H2O2-responsive UCL imaging and oxygen-elevated synergetic therapy. Adv Mater 27(28):4155–4161
Fang RH, Hu CMJ, Luk BT, Gao W, Copp JA, Tai Y, O’Connor DE, Zhang L (2014) Cancer cell membrane-coated nanoparticles for anticancer vaccination and drug delivery. Nano Lett 14(4):2181–2188
Farkona S, Diamandis EP, Blasutig IM (2016) Cancer immunotherapy: the beginning of the end of cancer? BMC Med 14:73
Feng B, Niu Z, Hou B, Zhou L, Li Y, Yu H (2020) Enhancing triple negative breast cancer immunotherapy by ICG-templated self-assembly of paclitaxel nanoparticles. Adv Funct Mater 30(6):1906605
Gao S, Wang G, Qin Z, Wang X, Zhao G, Ma Q, Zhu L (2017) Oxygen-generating hybrid nanoparticles to enhance fluorescent/photoacoustic/ultrasound imaging guided tumor photodynamic therapy. Biomaterials 112:324–335
Garg AD, Nowis D, Golab J, Agostinis P (2010) Photodynamic therapy: illuminating the road from cell death towards anti-tumour immunity. Apoptosis 15(9):1050–1071
Hahn AW, Gill DM, Pal SK, Agarwal N (2017) The future of immune checkpoint cancer therapy after PD-1 and CTLA-4. Immunotherapy 9(8):681–692
Hao Y, Zhang B, Zheng C, Niu M, Guo H, Zhang H, Chang J, Zhang Z, Wang L, Zhang Y (2017) Multifunctional nanoplatform for enhanced photodynamic cancer therapy and magnetic resonance imaging. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 151:384–393
Hartshorn CM, Bradbury MS, Lanza GM, Nel AE, Rao J, Wang AZ, Wiesner UB, Yang L, Grodzinski P (2018) Nanotechnology strategies to advance outcomes in clinical cancer care. ACS Nano 12(1):24–43
He C, Duan X, Guo N, Chan C, Poon C, Weichselbaum RR, Lin W (2016) Core-shell nanoscale coordination polymers combine chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy to potentiate checkpoint blockade cancer immunotherapy. Nat Commun 7:12499
Holmstrom KM, Finkel T (2014) Cellular mechanisms and physiological consequences of redox-dependent signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15(6):411–421
Huang K, Ma H, Liu J, Huo S, Kumar A, Wei T, Zhang X, Jin S, Gan Y, Wang PC, He S, Zhang X, Liang XJ (2012) Size-dependent localization and penetration of ultrasmall gold nanoparticles in cancer cells, multicellular spheroids, and tumors in vivo. ACS Nano 6(5):4483–4493
Ishihara J et al (2017) Matrix-binding checkpoint immunotherapies enhance antitumor efficacy and reduce adverse events. Sci Transl Med 9(415):eaan0401
Javeed A, Ashraf M, Riaz A, Ghafoor A, Afzal S, Mukhtar MM (2009) Paclitaxel and immune system. Eur J Pharm Sci 38(4):283–290
Ji T, Lang J, Wang J, Cai R, Zhang Y, Qi F, Zhang L, Zhao X, Wu W, Hao J, Qin Z, Zhao Y, Nie G (2017) Designing liposomes to suppress extracellular matrix expression to enhance drug penetration and pancreatic tumor therapy. ACS Nano 11(9):8668–8678
Jia Q, Ge J, Liu W, Zheng X, Chen S, Wen Y, Zhang H, Wang P (2018) A Magnetofluorescent carbon dot assembly as an acidic H2O2-driven oxygenerator to regulate tumor hypoxia for simultaneous bimodal imaging and enhanced photodynamic therapy. Adv Mater 30(13):e1706090
Kawanishi S, Hiraku Y, Pinlaor S, Ma N (2006) Oxidative and nitrative DNA damage in animals and patients with inflammatory diseases in relation to inflammation-related carcinogenesis. Biol Chem 387(4):365–372
Khalil DN, Smith EL, Brentjens RJ, Wolchok JD (2016) The future of cancer treatment: immunomodulation, CARs and combination immunotherapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 13(5):273–290
Ko YJ, Lee JW, Kim H, Cho EJ, Yang Y, Kim IS, Kim SH, Kwon IC (2020) Versatile activatable vSIRPalpha-probe for cancer-targeted imaging and macrophage-mediated phagocytosis of cancer cells. J Control Release 323:376–386
Li J, Han Y, Chen Q, Shi H, ur Rehman S, Siddiq M, Ge Z, Liu S (2014) Dual endogenous stimuli-responsive polyplex micelles as smart two-step delivery nanocarriers for deep tumor tissue penetration and combating drug resistance of cisplatin. J Mater Chem B 2(13):1813–1824
Li T, Li C, Ruan Z, Xu P, Yang X, Yuan P, Wang Q, Yan L (2019) Polypeptide-conjugated second near-infrared organic fluorophore for image-guided photothermal therapy. ACS Nano 13(3):3691–3702
Liang C, Diao S, Wang C, Gong H, Liu T, Hong G, Shi X, Dai H, Liu Z (2014) Tumor metastasis inhibition by imaging-guided photothermal therapy with single-walled carbon nanotubes. Adv Mater 26(32):5646–5652
Lin J, Wang M, Hu H, Yang X, Wen B, Wang Z, Jacobson O, Song J, Zhang G, Niu G, Huang P, Chen X (2016) Multimodal-imaging-guided cancer phototherapy by versatile biomimetic theranostics with UV and gamma-irradiation protection. Adv Mater 28(17):3273–3279
Liu C, Zhang P, Zhai X, Tian F, Li W, Yang J, Liu Y, Wang H, Wang W, Liu W (2012) Nano-carrier for gene delivery and bioimaging based on carbon dots with PEI-passivation enhanced fluorescence. Biomaterials 33(13):3604–3613
Liu Y, Ai K, Liu J, Deng M, He Y, Lu L (2013) Dopamine-melanin colloidal nanospheres: an efficient near-infrared photothermal therapeutic agent for in vivo cancer therapy. Adv Mater 25(9):1353–1359
Liu WL, Liu T, Zou MZ, Yu WY, Li CX, He ZY, Zhang MK, Liu MD, Li ZH, Feng J, Zhang XZ (2018) Aggressive man-made red blood cells for hypoxia-resistant photodynamic therapy. Adv Mater 30(35):e1802006
Lohse I, Lourenco C, Ibrahimov E, Pintilie M, Tsao MS, Hedley D (2014) Assessment of hypoxia in the stroma of patient-derived pancreatic tumor xenografts. Cancers (Basel) 6(1):459–471
Lou Y, McDonald PC, Oloumi A, Chia S, Ostlund C, Ahmadi A, Kyle A, auf dem Keller U, Leung S, Huntsman D, Clarke B, Sutherland BW, Waterhouse D, Bally M, Roskelley C, Overall CM, Minchinton A, Pacchiano F, Carta F, Scozzafava A, Touisni N, Winum JY, Supuran CT, Dedhar S (2011) Targeting tumor hypoxia: suppression of breast tumor growth and metastasis by novel carbonic anhydrase IX inhibitors. Cancer Res 71(9):3364–3376
Lu K, He C, Guo N, Chan C, Ni K, Weichselbaum RR, Lin W (2016) Chlorin-based nanoscale metal-organic framework systemically rejects colorectal cancers via synergistic photodynamic therapy and checkpoint blockade immunotherapy. J Am Chem Soc 138(38):12502–12510
Marquez-Garban DC et al (2019) Antiestrogens in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors in breast cancer immunotherapy. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 193:105415
Meng L, Cheng Y, Tong X, Gan S, Ding Y, Zhang Y, Wang C, Xu L, Zhu Y, Wu J, Hu Y, Yuan A (2018) Tumor oxygenation and hypoxia inducible factor-1 functional inhibition via a reactive oxygen species responsive nanoplatform for enhancing radiation therapy and abscopal effects. ACS Nano 12(8):8308–8322
Miao P, Han K, Tang Y, Wang B, Lin T, Cheng W (2015) Recent advances in carbon nanodots: synthesis, properties and biomedical applications. Nanoscale 7(5):1586–1595
Mikhail AS, Allen C (2009) Block copolymer micelles for delivery of cancer therapy: transport at the whole body, tissue and cellular levels. J Control Release 138(3):214–223
Min H, Wang J, Qi Y, Zhang Y, Han X, Xu Y, Xu J, Li Y, Chen L, Cheng K, Liu G, Yang N, Li Y, Nie G (2019) Biomimetic metal-organic framework nanoparticles for cooperative combination of antiangiogenesis and photodynamic therapy for enhanced efficacy. Adv Mater 31(15):e1808200
O'Neal DP, Hirsch LR, Halas NJ, Payne JD, West JL (2004) Photo-thermal tumor ablation in mice using near infrared-absorbing nanoparticles. Cancer Lett 209(2):171–176
Prasad P, Gordijo CR, Abbasi AZ, Maeda A, Ip A, Rauth AM, DaCosta RS, Wu XY (2014) Multifunctional albumin-MnO2 nanoparticles modulate solid tumor microenvironment by attenuating hypoxia, acidosis, vascular endothelial growth factor and enhance radiation response. ACS Nano 8(4):3202–3212
Rak J et al (2019) Drug delivery systems for phthalocyanines for photodynamic therapy. Anticancer Res 39(7):3323–3339
Ranji-Burachaloo H, Reyhani A, Gurr PA, Dunstan DE, Qiao GG (2019) Combined Fenton and starvation therapies using hemoglobin and glucose oxidase. Nanoscale 11(12):5705–5716
Riley RS, June CH, Langer R, Mitchell MJ (2019) Delivery technologies for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 18(3):175–196
Rosenberg SA, Yang JC, Restifo NP (2004) Cancer immunotherapy: moving beyond current vaccines. Nat Med 10(9):909–915
Schafer FQ, Buettner GR (2001) Redox environment of the cell as viewed through the redox state of the glutathione disulfide/glutathione couple. Free Radic Biol Med 30(11):1191–1212
Semenza GL (2012) Hypoxia-inducible factors: mediators of cancer progression and targets for cancer therapy. Trends Pharmacol Sci 33(4):207–214
Shao K, Singha S, Clemente-Casares X, Tsai S, Yang Y, Santamaria P (2015) Nanoparticle-based immunotherapy for cancer. ACS Nano 9(1):16–30
Sharma P, Allison JP (2015) The future of immune checkpoint therapy. Science 348(6230):56–61
Song W, Kuang J, Li CX, Zhang M, Zheng D, Zeng X, Liu C, Zhang XZ (2018) Enhanced immunotherapy based on photodynamic therapy for both primary and lung metastasis tumor eradication. ACS Nano 12(2):1978–1989
Stephan SB, Taber AM, Jileaeva I, Pegues EP, Sentman CL, Stephan MT (2015) Biopolymer implants enhance the efficacy of adoptive T-cell therapy. Nat Biotechnol 33(1):97–101
Sun Q, Sun X, Ma X, Zhou Z, Jin E, Zhang B, Shen Y, van Kirk EA, Murdoch WJ, Lott JR, Lodge TP, Radosz M, Zhao Y (2014) Integration of nanoassembly functions for an effective delivery cascade for cancer drugs. Adv Mater 26(45):7615–7621
Sun C, Zhang Y, Sun K, Reckmeier C, Zhang T, Zhang XY, Zhao J, Wu C, Yu WW, Rogach AL (2015) Combination of carbon dot and polymer dot phosphors for white light-emitting diodes. Nanoscale 7(28):12045–12050
Turley SJ, Cremasco V, Astarita JL (2015) Immunological hallmarks of stromal cells in the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Immunol 15(11):669–682
Wang LV, Hu S (2012) Photoacoustic tomography: in vivo imaging from organelles to organs. Science 335(6075):1458–1462
Wang S, Shang L, Li L, Yu Y, Chi C, Wang K, Zhang J, Shi R, Shen H, Waterhouse GIN, Liu S, Tian J, Zhang T, Liu H (2016) Metal-organic-framework-derived mesoporous carbon nanospheres containing porphyrin-like metal centers for conformal phototherapy. Adv Mater 28(38):8379–8387
Wang Y, Wei G, Zhang X, Xu F, Xiong X, Zhou S (2017) A step-by-step multiple stimuli-responsive nanoplatform for enhancing combined chemo-photodynamic therapy. Adv Mater 29(12):1605357
Wang H, Pan X, Wang X, Wang W, Huang Z, Gu K, Liu S, Zhang F, Shen H, Yuan Q, Ma J, Yuan W, Liu H (2020) Degradable carbon-silica nanocomposite with immunoadjuvant property for dual-modality photothermal/photodynamic therapy. ACS Nano 14(3):2847–2859
Wu W, Yang Q, Wu W, Yang Q, Li T, Zhang P, Zhou R, Yang C (2009) Hemoglobin-based oxygen carriers combined with anticancer drugs may enhance sensitivity of radiotherapy and chemotherapy to solid tumors. Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil Biotechnol 37(4):163–165
Xu Z, Wang Y, Zhang L, Huang L (2014) Nanoparticle-delivered transforming growth factor-beta siRNA enhances vaccination against advanced melanoma by modifying tumor microenvironment. ACS Nano 8(4):3636–3645
Xu T, Ma Y, Yuan Q, Hu H, Hu X, Qian Z, Rolle JK, Gu Y, Li S (2020) Enhanced ferroptosis by oxygen-boosted phototherapy based on a 2-in-1 nanoplatform of ferrous hemoglobin for tumor synergistic therapy. ACS Nano 14(3):3414–3425
Yang G, Xu L, Chao Y, Xu J, Sun X, Wu Y, Peng R, Liu Z (2017) Hollow MnO2 as a tumor-microenvironment-responsive biodegradable nano-platform for combination therapy favoring antitumor immune responses. Nat Commun 8(1):902
Yu X, Gao D, Gao L, Lai J, Zhang C, Zhao Y, Zhong L, Jia B, Wang F, Chen X, Liu Z (2017) Inhibiting metastasis and preventing tumor relapse by triggering host immunity with tumor-targeted photodynamic therapy using photosensitizer-loaded functional nanographenes. ACS Nano 11(10):10147–10158
Yuan Q, Wu Y, Wang J, Lu D, Zhao Z, Liu T, Zhang X, Tan W (2013) Targeted bioimaging and photodynamic therapy nanoplatform using an aptamer-guided G-quadruplex DNA carrier and near-infrared light. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 52(52):13965–13969
Zhang L, Dermawan K, Jin M, Liu R, Zheng H, Xu L, Zhang Y, Cai Y, Chu Y, Xiong S (2008) Differential impairment of regulatory T cells rather than effector T cells by paclitaxel-based chemotherapy. Clin Immunol 129(2):219–229
Zhang Z, Yao Z, Wang L, Ding H, Shao J, Chen A, Zhang F, Zheng S (2018) Activation of ferritinophagy is required for the RNA-binding protein ELAVL1/HuR to regulate ferroptosis in hepatic stellate cells. Autophagy 14(12):2083–2103
Zheng XT, Ananthanarayanan A, Luo KQ, Chen P (2015) Glowing graphene quantum dots and carbon dots: properties, syntheses, and biological applications. Small 11(14):1620–1636
Zhong H, Han B, Tourkova IL, Lokshin A, Rosenbloom A, Shurin MR, Shurin GV (2007) Low-dose paclitaxel prior to intratumoral dendritic cell vaccine modulates intratumoral cytokine network and lung cancer growth. Clin Cancer Res 13(18 Pt 1):5455–5462
Zhou F, Feng B, Yu H, Wang D, Wang T, Ma Y, Wang S, Li Y (2019) Tumor microenvironment-activatable prodrug vesicles for nanoenabled cancer chemoimmunotherapy combining immunogenic cell death induction and CD47 blockade. Adv Mater 31(14):e1805888
Funding
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province.
(BK20161317).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Z., Qin, C., Zhao, C. et al. Research progress of nanomaterial-mediated photodynamic therapy in tumor treatment. J Nanopart Res 22, 298 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-05030-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-05030-2