Abstract
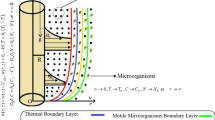
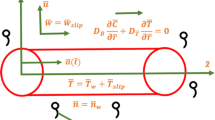
This investigation presents novel applications for bioconvection flow of non-Newtonian fluid with diverse flow features. The developed unsteady bio-nano-transport model is formulated under the influence of some novel features such as variable thermal conductivity, heat absorption/generation and activation energy. In contrast to typical investigations, the flow has been originated by accelerated porous plate which conferred the suction and injection phenomenon. The thermal aspects of magnetized nanoparticles are evaluated by employing prestigious Buongiorno’s model. The flow model is constituted via partial differential equations for which dimensionless form is availed before develop the analytical expressions. The convergent technique namely homotopy analysis procedure is followed to suggest the solution. The validation of solution has been done by comparing it with already reported investigations and finds an excellent accuracy. The rheological characteristics of Eyring Powell fluid and thermal features of nanoparticles against involved control parameters are explained through various graphs. The reported results may contribute effective role in enhancement of thermal processes, cooling phenomenon, bio-fuels etc.







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
28 September 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-023-03267-2
References
S.U.S. Choi, Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. ASME Publ. Fed. 231, 99–106 (1995)
J. Boungiorno, Convective transport in nanofluids. J. Heat Transfer 128, 240–250 (2010)
A. Wakif, L.I. Animasaun, P.V. Satya Narayana, G. Sarojamma, Meta-analysis on thermo-migration of tiny/nano-sized particles in the motion of various fluids. Chin. J. Phys. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjph.2019.12.002
T. Hayat, K. Muhammad, M. Farooq, A. Alsaedi, Melting heat transfer in stagnation point flow of carbon nanotubes towards variable thickness surface. AIP Adv. 6, 015214 (2016)
S.U. Khan, S. Al, Shehzad, Brownian movement and thermophoretic aspects in third grade nanofluid over oscillatory moving sheet. Phys. Scr. 94, 095202 (2019)
T. Hayat, M.Z. Kiyani, I. Ahmad, B. Ahmad, On analysis of magneto Maxwell nano-material by surface with variable thickness. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 131, 1016–1025 (2017)
N. Sandeep, I.L. Animasaun, Heat transfer in wall jet flow of magnetic-nanofluids with variable magnetic field. Alex. Eng. J. 56, 263–269 (2017)
H. Waqas, S.A. Shehzad, S.U. Khan, M. Imran, Novel numerical computations on flow of nanoparticles in porous rotating disk with multiple slip effects and microorganisms. J. Nanofluids 8, 1423–1432 (2019)
H. Sardar, M. Khan, M. Alghamdi, Multiple solutions for the modified Fourier and Fick’s theories for Carreau nanofluid. Indian J. Phys. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-019-01628-y
S. Manjunatha, B. Ammani Kuttan, S. Jayanthi, A. Chamkha, B.J. Gireesha, Heat transfer enhancement in the boundary layer flow of hybrid nanofluids due to variable viscosity and natural convection. Heliyon 5, e01469 (2019)
A.A. Siddiqui, M. Turkyilmazoglu, A new theoretical approach of wall transpiration in the cavity flow of the ferrofluids. Micromachines 10, 373 (2019)
S.U. Khan, H. Waqas, M.M. Bhatti, M. Imran, Bioconvection in the rheology of magnetized Couple stress nanofluid featuring activation energy and Wu’s slip. J. Non-Equilib. Thermodyn. 45, 81–95 (2020)
A. Maleki, M. Elahi, M.E.H. Assad, M.A. Nazari, M.S. Shadloo, N. Nabipour, Thermal conductivity modeling of nanofluids with ZnO particles by using approaches based on artificial neural network and MARS. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09373-9
M.I. Afridi, M. Qasim, A. Wakif, A. Hussanan, Second Law analysis of dissipative nanofluid flow over a curved surface in the presence of lorentz force: utilization of the Chebyshev–Gauss–Lobatto spectral method. Nanomaterials 9, 195 (2019)
S.A. Moshizi, I. Pop, Conjugated effect of joule heating and magnetohydrodynamic on laminar convective heat transfer of nanofluids inside a concentric annulus in the presence of slip condition. Int. J. Thermophys. 37, 72 (2016)
M.A. Taghikhani, Cu–water nanofluid MHD mixed convection in a lid-driven cavity with two sinusoidal heat sources considering joule heating effect. Int. J. Thermophys. 40, 44 (2019)
Q. Hussain, N. Alvi, T. Latif, S. Asghar, Radiative heat transfer in Powell-Eyring nanofluid with peristalsis. Int. J. Thermophys. 40, 46 (2019)
J. Ahmed, M. Khan, L. Ahmad, Joule Heating Effects in thermally radiative swirling flow of maxwell fluid over a porous rotating disk, Int. J. Thermophys., 40, Article number: 106 (2019)
K. Martin, A. Sözen, E. Çiftçi, H. Muhammad Ali, An experimental investigation on aqueous Fe–CuO hybrid nanofluid usage in a plain heat pipe, Int. J. Thermophys. 41, Article number: 135 (2020)
F.E. Berger Bioucas, M.H. Rausch, J. Schmidt, A. Bück, T.M. Koller, A.P. Fröba, Effective thermal conductivity of nanofluids: measurement and prediction, Int. J. Thermophys., 41, Article number: 55 (2020)
R. Tariq, Y. Hussain, N. A. Sheikh, K. Afaq, H. Ali, Regression-based empirical modeling of thermal conductivity of CuO–water nanofluid using data-driven techniques, Int. J. Thermophys. 41, Article number: 43 (2020)
G. López-Gamboa, J.L. Jiménez-Pérez, Z.N. Correa-Pacheco, M.L. Alvarado-Noguez, M. Amorim Lima, A. Cruz-Orea, J.G. Mendoza Alvarez, Artificial neural network for modeling thermal conductivity of biodiesels with different metallic nanoparticles for heat transfer applications, Int. J. Thermophys., 41, 10 (2020)
A.A. Minea, B. Buonomo, J. Burggraf, D. Ercole, K.R. Karpaiya, A.D. Pasqua, G. Sekrani, J. Steffens, J. Tibaut, N. Wichmann, P. Farber, A. Huminic, G. Huminic, R. Mahu, O. Manca, C. Oprea, S. Poncet, J. Ravnik, NanoRound: a benchmark study on the numerical approach in nanofluids’ simulation. Int. Commun. Heat Mass 108, 104292 (2019)
A.A. Minea, A review on electrical conductivity of nanoparticle-enhanced fluids. Nanomaterials 9, 1592 (2019)
A.V. Kuznetsov, The onset of nanofluid bioconvection in a suspension containing both nanoparticles and gyrotactic microorganisms. Int. Commun. Heat Mass 37, 1421–1425 (2010)
A.V. Kuznetsov, Nanofluid bioconvection in water-based suspensions containing nanoparticles and oxytactic microorganisms: oscillatory instability. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 6, 100 (2011)
M.J. Uddin, Y. Alginahi, O.A. Bég, M.N. Kabir, Numerical solutions for gyrotactic bioconvection in nanofluid-saturated porous media with Stefan blowing and multiple slip effects. Comput. Math. Appl. 72, 2562–2581 (2016)
S. Saini, Y.D. Sharma, Numerical study of nanofluid thermo-bioconvection containing gravitactic microorganisms in porous media: effect of vertical through flow. Adv. Powder Technol. 29, 2725–2732 (2018)
M. Zhao, Y. Xiao, S. Wang, Linear stability of thermal-bioconvection in a suspension of gyrotactic micro-organisms. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran 126, 95–102 (2018)
S.U. Khan, A. Rauf, S.A. Shehzad, Z. Abbas, T. Javed, Study of bioconvection flow in Oldroyd-B nanofluid with motile organisms and effective Prandtl approach. Phys. A 527, 121179 (2019)
D. Lu, M. Ramzan, N. Ullah, J.D. Chung, U. Farooq, A numerical treatment of radiative nanofluid 3D flow containing gyrotactic microorganism with anisotropic slip, binary chemical reaction and activation energy. Sci. Rep. 7, 17008 (2017)
A.M. Alwatban, S.U. Khan, H. Waqas, Iskander Tlili. Interaction of Wu’s slip features in bioconvection of Eyring Powell nanoparticles with activation energy, Processes 7, 859 (2019)
M. Sulaiman, A. Ali and S. Islam, Heat and mass transfer in three-dimensional flow of an Oldroyd-B nanofluid with gyrotactic micro-organisms, Math. Probl. Eng., 15, Article ID 6790420, (2018)
R.E. Powell, H. Eyring, Nature, London p. 427 (1944)
I. Khan, S. Fatima, M.Y. Malik, T. Salahuddin, Exponentially varying viscosity of magnetohydrodynamic mixed convection Eyring-Powell nanofluid flow over an inclined surface. Results Phys. 8, 1194–1203 (2018)
O.A. Abegunrin, I.L. Animasaun, N. Sandeep, Insight into the boundary layer flow of non-Newtonian Eyring-Powell fluid due to catalytic surface reaction on an upper horizontal surface of a paraboloid of revolution. Alex. Eng. J. 57, 2051–2060 (2018)
S.O. Salawu, H.A. Ogunseye, Entropy generation of a radiative hydromagnetic Powell-Eyring chemical reaction nanofluid with variable conductivity and electric field loading. Results Eng. 5, 100072 (2020)
D. Kumar, K. Ramesh, S. Chandok, Mathematical modeling and simulation for the flow of magneto-Powell-Eyring fluid in an annulus with concentric rotating cylinders. Chin. J. Phys. 65, 187–197 (2020)
S. Hadi Seyedi, B.N. Saray, A.J. Chamkha, Heat and mass transfer investigation of MHD Eyring-Powell flow in a stretching channel with chemical reactions. Physica A 544, 124109 (2020)
S.U. Khan, N. Ali, T. Hayat, Analytical and numerical study of diffusion of chemically reactive species in Eyring-Powell fluid over an oscillatory stretching surface. Bulg. Chem. Commun. 49, 320–330 (2017)
S.J. Liao, Advances in the homotopy analysis method, World Scientific Publishing, 5 Toh Tuck Link, Singapore 2014
M. Turkyilmazoglu, Analytic approximate solutions of rotating disk boundary layer flow subject to a uniform suction or injection. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 52, 1735–1744 (2010)
M. Turkyilmazoglu, The analytical solution of mixed convection heat transfer and fluid flow of a MHD viscoelastic fluid over a permeable stretching surface. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 77, 263–268 (2013)
N. Khan, M.S. Hashmi, S.U. Khan, W.A. Syed, Study of polymeric liquid between stretching disks with chemical reaction. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. 40, 102 (2018)
M. Waqas, S. Jabeen, T. Hayat, S.A. Shehzad, A. Alsaedi, Numerical simulation for nonlinear radiated Eyring-Powell nanofluid considering magnetic dipole and activation energy. Int. Commun. Heat Mass 112, 104401 (2020)
K. Al-Khaled, S.U. Khan, I. Khan, Chemically reactive bioconvection flow of tangent hyperbolic nanoliquid with gyrotactic microorganisms and nonlinear thermal radiation. Heliyon 6, e03117 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, S.U., Ali, H.M. Swimming of Gyrotactic Microorganisms in Unsteady Flow of Eyring Powell Nanofluid with Variable Thermal Features: Some Bio-technology Applications. Int J Thermophys 41, 159 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-020-02736-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-020-02736-2