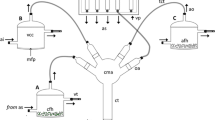
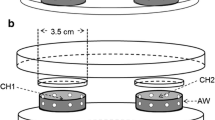
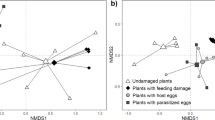
Abstract
In solitary endoparasitoids, oviposition in a host previously parasitized by a conspecific (superparasitism) leads to intraspecific competition, resulting in the elimination of all but one parasitoid offspring. Therefore, avoidance of parasitized hosts presents a strong selective advantage for such parasitoid species. Parasitoids use herbivore-induced plant volatiles (HIPVs) to find their hosts. In this study, we evaluated the ability of Microplitis croceipes (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) to discriminate between unparasitized and parasitized Heliothis virescens (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae using cotton plant odors as cues. A combination of behavioral and analytical techniques were used to test two hypotheses: (i) parasitoids will show preference for plant odors induced by unparasitized hosts over odors induced by parasitized hosts, and (ii) the parasitism status of herbivores affects HIPV emission in plants. Heliothis virescens larvae were parasitized for varying durations (0, 2 and 6-days after parasitism (DAP)). In four-choice olfactometer bioassays, female M. croceipes showed greater attraction to plant odors induced by unparasitized hosts compared to plant odors induced by parasitized hosts (2 and 6-DAP). Comparative gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analyses of cotton volatiles indicated reduced emission of 10 out of 21 identified compounds from plants infested by parasitized hosts compared with plants infested by unparasitized hosts. The results suggest that changes in plant volatile emission due to the parasitism status of infesting herbivores affect recruitment of parasitoids. Avoidance of superparasitism using plant odors optimizes host foraging in M. croceipes, and this strategy may be widespread in solitary parasitoid species.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afsheen S, Wang X, Li R et al (2008) Differential attraction of parasitoids in relation to specificity of kairomones from herbivores and their by-products. Insect Sci 15:381–397. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7917.2008.00225.x
Alborn HT, Turlings TCJ, Jones TH et al (1997) An elicitor of plant volatiles from beet armyworm oral secretion. Science 276:945–949. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.276.5314.945
Arimura G-I, Matsui K, Takabayashi J (2009) Chemical and molecular ecology of herbivore-induced plant volatiles: proximate factors and their ultimate functions. Plant Cell Physiol 50:911–923. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcp030
Bae S, Kim Y (2004) Host physiological changes due to parasitism of a braconid wasp, Cotesia plutellae, on diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 138:39–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2004.02.018
Bakker K, van Alphen JJM, van Batenburg FHD et al (1985) The function of host discrimination and superparasitization in parasitoids. Oecologia 67:572–576. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00790029
Beckage NE, Gelman DB (2004) Wasp parasitoid disruption of host development: Implications for New Biologically Based Strategies for Insect Control. Annu Rev Entomol 49:299–330. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ento.49.061802.123324
Böckmann EA, Tormos J, Beitia F, Fischer K (2012) Offspring production and self-superparasitism in the solitary ectoparasitoid Spalangia cameroni (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae) in relation to host abundance. Bull Entomol Res 102:131–137. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007485311000447
Bonaventure G, VanDoorn A, Baldwin IT (2011) Herbivore-associated elicitors: FAC signaling and metabolism. Trends Plant Sci 16:294–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2011.01.006
Caron V, Myers JH, Gillespie DR (2010) The failure to discriminate: superparasitism of Trichoplusia ni Hübner by a generalist tachinid parasitoid. Bull Entomol Res 100:255–261. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007485309990198
Charnov EL, Stephens DW (1988) On the evolution of host selection in solitary parasitoids. Am Nat 132:707–722
Colazza S, Cusumano A, Lo Giudice D, Peri E (2014) Chemo-orientation responses in hymenopteran parasitoids induced by substrate-borne semiochemicals. Biocontrol 59:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-013-9546-7
Dong K, Zhang D, Dahlman DL (1996) Down-regulation of juvenile hormone esterase and arylphorin production in Heliothis virescens larvae parasitized by Microplitis croceipes. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 32:237–248. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1520-6327(1996)32:2<237::AID-ARCH7>3.0.CO;2-V
Fathpour H, Dahlman DL (1995) Polydnavirus of Microplitis croceipes prolongs the larval period and changes hemolymph protein content of the host, Heliothis virescens. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 28:33–48. https://doi.org/10.1002/arch.940280104
Fatouros NE, Van Loon JJA, Hordijk KA et al (2005) Herbivore-induced plant volatiles mediate in-flight host discrimination by parasitoids. J Chem Ecol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-005-6076-5
Fisher RC, Ganesalingham VK (1970) Changes in the composition of host haemolymph after attack by an insect parasitoid. Nature 227:191–192. https://doi.org/10.1038/227191a0
Fitt G (1989) The ecology of Heliothis species in relation to agroecosystems. Annu Rev Entomol 34:17–53
Gandon S, Rivero A, Varaldi J (2006) Superparasitism Evolution: Adaptation or Manipulation? Am Nat 167:E1–E22. https://doi.org/10.1086/498398
Godfray H (1993) Parasitoids: Behavioral and Evolutionary Ecology. Princeton University Press
Gouinguené SP, Turlings TCJ (2002) The Effects of Abiotic Factors on Induced Volatile Emissions in Corn Plants. Plant Physiol 129:1296–1307. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.001941
Hare JD (2011) Ecological Role of Volatiles Produced by Plants in Response to Damage by Herbivorous Insects. Annu Rev Entomol 56:161–180. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ento-120709-144753
Harvey JA, Malcicka M (2016) Nutritional integration between insect hosts and koinobiont parasitoids in an evolutionary framework. Entomol Exp Appl 159:181–188. https://doi.org/10.1111/eea.12426
Hegazi EM, Vinson SB (1998) A possible mechanism for the physiological suppression of conspecific eggs and larvae following superparasitism by solitary endoparasitoids. J Insect Physiol 44:703–712. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-1910(98)00003-1
Lewis WJ (1970) Life history and anatomy of Microplitis croceipes (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), a parasite of Heliothis spp. (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 63:67–70
Lewis WJ, Burton RL (1970) Rearing Microplitis croceipes in the laboratory with Heliothis zea as hosts. J Econ Entomol 63:656–658. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/63.2.656
Li Y, Dickens JC, Steiner WWM (1992) Antennal olfactory responsiveness of Microplitis croceipes (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) to cotton plant volatiles. J Chem Ecol 18:1761–1773. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02751101
Liu X, Chen G, Zhang Y et al (2017) Virus-infected plants altered the host selection of Encarsia formosa, a parasitoid of whiteflies. Front Physiol 8:937. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00937
Loughrin JH, Manukian A, Heath RR et al (1994) Diurnal cycle of emission of induced volatile terpenoids by herbivore-injured cotton plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 5
Magdaraog PM, Tanaka T, Harvey JA (2013) Inter- and intra-specific host discrimination in gregarious and solitary endoparasitoid wasps. Biocontrol 58:745–754. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-013-9532-0
McCall PJ, Turlings TCJ, Lewis WJ, Tumlinson JH (1993) Role of plant volatiles in host location by the specialist parasitoid Microplitis croceipes cresson (Braconidae: Hymenoptera). J Insect Behav 6:625–639. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01048128
McLoud LA, Bernal J, Vinson SB (2013) Examination and revision of the larval life history of Microplitis croceipes (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Biol Control 67:39–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2013.06.016
Moraes CMD, Lewis WJ, Paré PW et al (1998) Herbivore-infested plants selectively attract parasitoids. Nature 393:570–573. https://doi.org/10.1038/31219
Morawo T, Fadamiro H (2014a) Duration of Plant Damage by Host Larvae Affects Attraction of Two Parasitoid Species (Microplitis croceipes and Cotesia marginiventris) to Cotton: Implications for Interspecific Competition. J Chem Ecol 40:1176–1185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-014-0525-y
Morawo T, Fadamiro H (2014b) Attraction of two larval parasitoids with varying degree of host specificity to single components and a binary mixture of host-related plant volatiles. Chemoecology 24:127–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00049-014-0154-5
Morawo T, Burrows M, Fadamiro H (2016) Electroantennogram response of the parasitoid, Microplitis croceipes to host-related odors: The discrepancy between relative abundance and level of antennal responses to volatile compound. F1000Res 5:2725. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.10104.2
Ngumbi EN (2011) Mechanisms of Olfaction in Parasitic Wasps: Analytical and Behavioral Studies of Response of a Specialist (Microplitis croceipes) and a Generalist (Cotesia marginiventris) Parasitoid to Host-Related Odor. Ph.D., Auburn University, Auburn
Ngumbi E, Fadamiro H (2012) Species and sexual differences in behavioural responses of a specialist and generalist parasitoid species to host-related volatiles. Bull Entomol Res 102:710–718. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007485312000326
Ngumbi E, Chen L, Fadamiro HY (2009) Comparative GC-EAD Responses of A Specialist (Microplitis croceipes) and A Generalist (Cotesia marginiventris) Parasitoid to Cotton Volatiles Induced by Two Caterpillar Species. J Chem Ecol 35:1009. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-009-9700-y
Ngumbi E, Chen L, Fadamiro H (2010) Electroantennogram (EAG) responses of Microplitis croceipes and Cotesia marginiventris and their lepidopteran hosts to a wide array of odor stimuli: Correlation between EAG response and degree of host specificity? J Insect Physiol 56:1260–1268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinsphys.2010.03.032
Nufio CR, Papaj DR (2001) Host marking behavior in phytophagous insects and parasitoids. Entomol. Exp. Appl
Park KC, Zhu J, Harris J et al (2001) Electroantennogram responses of a parasitic wasp, Microplitis croceipes, to host-related volatile and anthropogenic compounds. Physiol Entomol 26:69–77. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3032.2001.00219.x
Peiffer M, Felton GW (2009) Do caterpillars secrete “Oral Secretions”? J Chem Ecol 35:326–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-009-9604-x
Pennacchio F, Vinson SB, Tremblay E, Tanaka T (1994) Biochemical and developmental alterations of Heliothis virescens (F.) (lepidoptera, noctuidae) larvae induced by the endophagous parasitoid Cardiochiles nigriceps ngumbiviereck (Hymenoptera, braconidae). Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 26:211–233. https://doi.org/10.1002/arch.940260211
Pennacchio F, Caccia S, Digilio MC (2014) Host regulation and nutritional exploitation by parasitic wasps. Curr Opin Insect Sci 6:74–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cois.2014.09.018
Poelman EH, Gols R, Snoeren TAL et al (2011a) Indirect plant-mediated interactions among parasitoid larvae. Ecol Lett 14:670–676. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2011.01629.x
Poelman EH, Zheng S-J, Zhang Z et al (2011b) Parasitoid-specific induction of plant responses to parasitized herbivores affects colonization by subsequent herbivores. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:19647–19652. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1110748108
Poelman EH, Bruinsma M, Zhu F et al (2012) Hyperparasitoids use herbivore-induced plant volatiles to locate their parasitoid host. PLoS Biol 10:. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1001435
Potting RPJ, Snellen HM, Vet LEM (1997) Fitness consequences of superparasitism and mechanism of host discrimination in the stemborer parasitoid Cotesia flavipes. Entomol Exp Appl 82:341–348. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1570-7458.1997.00148.x
Rana RL, Dahlman DL, Webb BA (2002) Expression and characterization of a novel teratocyte protein of the braconid, Microplitis croceipes (cresson). Insect Biochem Mol Biol 32:1507–1516. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0965-1748(02)00071-1
Ruschioni S, van Loon JJA, Smid HM, van Lenteren JC (2015) Insects Can Count: Sensory Basis of Host Discrimination in Parasitoid Wasps Revealed. Plos One 10:e0138045. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0138045
Sasso R, Iodice L, Cristina Digilio M et al (2007) Host-locating response by the aphid parasitoid Aphidius ervi to tomato plant volatiles. J Plant Interact 2:175–183. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429140701591951
Shorey HH, Hale RL (1965) Mass-Rearing of the Larvae of Nine Noctuid Species on a Simple Artificial Medium12. J Econ Entomol. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/58.3.522
Steidle JLM, Loon JJAV (2003) Dietary specialization and infochemical use in carnivorous arthropods: testing a concept. Entomol Exp Appl 108:133–148. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1570-7458.2003.00080.x
Stelinski LL, Rodriguez-Saona C, Meyer WL (2009) Recognition of foreign oviposition-marking pheromone in a multi-trophic context. Naturwissenschaften 96:585–592. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-009-0507-z
Strand MR (2014) Teratocytes and their functions in parasitoids. Curr Opin Insect Sci 6:68–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cois.2014.09.005
Strand MR, Burke GR (2015) Polydnaviruses: from discovery to current insights. Virology 0:393–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2015.01.018
Tan C-W, Peiffer M, Hoover K et al (2018) Symbiotic polydnavirus of a parasite manipulates caterpillar and plant immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115:5199–5204. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1717934115
Tan C-W, Peiffer M, Hoover K et al (2019) Parasitic Wasp Mediates Plant Perception of Insect Herbivores. J Chem Ecol 45:972–981. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-019-01120-1
Thompson AC, Baker DN, Gueldner RC, Hedin PA (1971) Identification and quantitative analysis of the volatile substances emitted by maturing cotton in the field. Plant Physiol 48:50–52. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.48.1.50
Tillman PG, Powell JE (1992) Intraspecific host discrimination and larval competition in Microplitis croceipes Microplitis demolitor, Cotesia kazak (HYM.: Braconidae) and Hyposoter didymator HYM: Ichneumonidae), parasitoids of Heliothis virescens (LEP. Noctuidae) Entomophaga 37:429–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02373116
Turlings TCJ, Wäckers F (2004) Recruitment of predators and parasitoids by herbivore-injured plants. Adv Insect Chem Ecol 2:21–75. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511542664.003
Turlings TCJ, McCall PJ, Alborn HT, Tumlinson JH (1993) An elicitor in caterpillar oral secretions that induces corn seedlings to emit chemical signals attractive to parasitic wasps. J Chem Ecol 19:411–425. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00994314
van Alphen JJ, Visser ME (1990) Superparasitism as an adaptive strategy for insect parasitoids. Annu Rev Entomol 35:59–79. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.en.35.010190.000423
Vet LEM, Dicke M (1992) Ecology of infochemical use by natural enemies in a tritrophic context. Annu Rev Entomol 37:141–172. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.en.37.010192.001041
Vet LEM, Wäckers FL, Dicke M (1991) The reliability-detectability problem for foraging parasitoids: the usability of 1st and 2nd trophic level stimuli. Abstr 6th Eur Workshop Insect Parasit Tritrophic Interact Perugia
Vinson SB (1976) Host Selection by Insect Parasitoids. Annu Rev Entomol 21:109–133. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.en.21.010176.000545
Vinson SB, Barras DJ (1970) Effects of the parasitoid, Cardiochiles nigriceps, on the growth, development, and tissues of Heliothis virescens. J Insect Physiol 16:1329–1338. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1910(70)90132-0
Vinson SB, Guillot FS (1972) Host marking: Source of a substance that results in host discrimination in insect parasitoids. Entomophaga 17:241–245. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02371134
Vinson SB, Iwantsch GF (1980) Host Regulation by Insect Parasitoids. Q Rev Biol 55:143–165
Visser ME, Rosenheim JA (1998) The Influence of Competition between Foragers on Clutch Size Decisions in Insect Parasitoids. Biol Control 11:169–174. https://doi.org/10.1006/bcon.1997.0589
Webb BA, Dahlman DL (1985) Developmental pathology of Heliothis virescens larvae parasitized by Microplitis croceipes: Parasite-mediated host developmental arrest. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 2:131–143. https://doi.org/10.1002/arch.940020203
Zebelo S, Piorkowski J, Disi J, Fadamiro H (2014) Secretions from the ventral eversible gland of Spodoptera exigua caterpillars activate defense-related genes and induce emission of volatile organic compounds in tomato, Solanum lycopersicum. BMC Plant Biol 14:140. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-14-140
Zhang J-H, Gu L-Q, Wang C-Z (2010) Superparasitism behavior and host discrimination of Campoletis chlorideae (Ichneumonidae: Hymenoptera) toward Mythimna separata (Noctuidae: Lepidoptera). Environ Entomol 39:1249–1254. https://doi.org/10.1603/EN09174
Acknowledgements
We thank Brandice Kopishke and Jean Linn for rearing the insects used for this study. This study was supported by Auburn University and the Alabama Agricultural Experiment Station.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 120 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kafle, B.D., Morawo, T. & Fadamiro, H. Host-Induced Plant Volatiles Mediate Ability of the Parasitoid Microplitis croceipes to Discriminate Between Unparasitized and Parasitized Heliothis virescens Larvae and Avoid Superparasitism. J Chem Ecol 46, 967–977 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-020-01218-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-020-01218-x