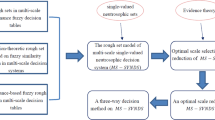
Abstract
The notion of covering based multigranulation fuzzy rough set (CMGFRS) models is a generalization of both granular computing and covering based fuzzy rough sets. Therefore it has become a powerful tool for coping with vague and multigranular information in cognition. In this paper we introduce three kinds of CMGFRS models by means of fuzzy β-neighborhoods and fuzzy complementary β-neighborhoods, and we investigate their axiomatic properties. We investigate three respective types of coverings based CMGFRS models, namely, optimistic, pessimistic and variable precision setups. In particular, by using multigranulation fuzzy measure degrees and multigranulation fuzzy complementary measure degrees, we derive three types of coverings based γ-optimistic (γ-pessimistic) CMGFRSs and E (F, G)-optimistic and E (F, G)-pessimistic CMGFRSs, respectively. We discuss the interrelationships among these three types of CMGFRS models and covering based Zhan-CMGFRS models. In view of the theoretical analysis for these three types of CMGFRS models, we put forward a novel methodology to multiple attribute group decision-making problem with evaluation of fuzzy information. An effective example is fully developed, hence concluding the applicability of the proposed methodology.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
From the point of view of group decision-making, this accuracy parameter in the model of 1-CMGFRS can account for the consistency consensus threshold among the group of decision-makers.
References
Abu-Donia GM (2012) Multi knowledge based rough approximations and applications. Knowl Based Syst 26(1):20–29
Alcantud JCR, Calle RDA (2017) The problem of collective identity in a fuzzy environment. Fuzzy Sets Syst 315:57–75
Alcantud JCR, Díaz S (2017) Rational fuzzy and sequential fuzzy choice. Fuzzy Sets Syst 315:76–98
Bargiela A, Pedrycz W (2005) Granular mappings. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cycle Part A 35(2):292–297
Bonikowski Z, Bryniarski E, Wybraniec-Skardowska U (1998) Extensions and intentions in rough set theory. Inform Sci 107:149–167
Cabrerizo FJ, Herrera-Viedma E, Pedrycz W (2013) A method based on PSO and granular computing of linguistic information to solve group decision making problems defined in heterogeneous contexts. Eur J Oper Res 230:624–633
Chen D, Li W, Zhang X, Kwong S (2014) Evidence-theory-based numerical algorithms of attribute reduction with neighborhood-covering rough sets. Int J Approx Reason 55:908–923
Chen Y, Kilgour D, Hipel K (2012) A decision rule aggregation approach to multiple criteria-multiple participant sorting. Group Decis Negot 21:727–745
Dai JH, Hu H, Wu WZ, Qian YH, Huang DB (2018) Maximal discernibility pairs based approach to attribute reduction in fuzzy rough sets. IEEE Tran Fuzzy Syst 26:2174–2187
Dai JH, Wei BJ, Zhang XH, Zhang QH (2017) Uncertainty measurement for incomplete interval-valued information systems based on \(\alpha\)-weak similarity. Knowl Based Syst 136:159–171
D’eer L, Cornelis C, Godo L (2017) Fuzzy neighborhood operators based on fuzzy coverings. Fuzzy Sets Syst 312:17–35
D’eer L, Restrepo M, Cornelis C, Gómez J (2016) Neighborhood operators for covering-based rough sets. Inform Sci 336:21–44
Deng T, Chen Y, Xu W, Dai Q (2007) A novel approach to fuzzy rough sets based on a fuzzy covering. Inform Sci 177:2308–2326
Dubois D, Prade H (1990) Rough fuzzy sets and fuzzy rough sets. Int J Gen Syst 17:191–209
Greco S, Matarazzo B, Slowinski R (2001) Rough set theory for multicritera decision analysis. Eur J Oper Res 129:11–47
Hong D, Choi C (2000) Multicriteria fuzzy decision-making problems based on vague set theory. Fuzzy Sets Syst 114:103–113
Huang B, Guo C, Zhang Y, Li H, Zhou X (2014) Intuitioistic fuzzy multigranulation rough sets. Inform Sci 277:299–320
Hwang CL, Yoon K (1981) Multiple attribute decision making methods and applications. Springer, Berlin
Hwang C, Lin M (1987) Group decision making under multiple criteria. Lecture notes in economics mathematical system. Springer, Berlin
Jensen R, Shen Q (2007) Fuzzy-rough sets assisted attribute selection. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 15(1):73–89
Li TJ, Leung Y, Zhang WX (2008) Generalized fuzzy rough approximation operators based on fuzzy covering. Int J Approx Reason 48:836–856
Liang JY, Qian YH (2006) Axiomatic approach of knowledge granulation in information systems. LNAI 4304:1074–1078
Liang JY, Wang F, Dang CY, Qian YH (2012) An efficient rough feature selection algorithm with a multi-granulation view. Int J Approx Reason 53(7):1080–1093
Lin GP, Liang JY, Qian YH (2013) Multigranulation rough sets: from partition to covering. Inform Sci 241:101–118
Lin GP, Qian YH, Li TJ (2012) NMGS: neighborhood-based multigranulation rough sets. Int J Approx Reason 53(7):1080–1093
Liu CH, Miao DQ, Qian J (2014) On multi-granulation covering rough sets. Int J Approx Reason 55(6):1404–1418
Liu GL, Sai Y (2009) A comparison of two types of rough sets induced by coverings. Int J Approx Reason 50:521–528
Liu CH, Pedrycz W (2016) Covering-based multi-granulation fuzzy rough sets. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 30:303–318
Liu H, Gegov A, Cocea M (2016) Rule-based systems: a granular computing perspective. Granul Comput 1:259–274
Ma L (2012) On some types of neighborhood-related covering rough sets. Int J Approx Reason 53:901–911
Ma L (2015) Some twin approximation operators on covering approximation spaces. Int J Approx Reason 56:59–70
Ma L (2016) Two fuzzy coverings rough set models and their generalizations over fuzzy lattices. Fuzzy Sets Syst 294:1–17
Mardani A, Jusoh A, Zavadskas EK (2015) Fuzzy multiple criteria decision-making techniques and applications-two decades review from 1994 to 2014. Expert Syst Appl 42(8):4126–4148
Pawlak Z (1982) Rough sets. Int J Comput Inform Sci 11(5):341–356
Pedrycz W (2002) Relational and directional aspects in the construction of information granules. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cycle Part A 32(5):605–614
Pedrycz W (2013) Granular computing analysis and design of intelligent systems. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Pedrycz W, Skowron A, Kreinovich V (eds) (2008) Handbook of granular computing. Wiley, New York
Pomykala JA (1987) Approximation operations in approximation spaces. Bull Pol Acad Sci Math 35:653–662
Qian YH, Liang J, Dang C (2010a) Incomplete multigranulation rough sets. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 20:420–431
Qian YH, Liang J, Yao YY, Dang C (2010b) MGRS: a multi-granulation rough set. Inform Sci 180:949–970
Qian YH, Li S, Liang J, Shi Z, Wang F (2014a) Pessimistic rough set based decision: a multigranulation fusion strategy. Inform Sci 264:196–210
Qian YH, Zhang H, Sang Y, Liang J (2014b) Multigranulation decision-theoretical rough sets. Int J Approx Reason 55:225–237
Radzikowska A, Kerre E (2002) A comparative study of fuzzy rough sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 126:137–155
She Y, He X (2012) On the structure of the mulitigranulation rough set model. Knowl Based Syst 36:81–92
Sun BZ, Ma W (2015) Multigranulation rough set theory over two universes. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 28:1251–1269
Sun BZ, Ma W (2016) An approach to evaluation of emergency plans for unconventional emergency events based on soft fuzzy rough set. Kybernetes 45(3):1–26
Sun BZ, Ma W (2015) An approach to consensus measurement of linguistic preference relations in multi-attribute group decision making and application. Omega 51:83–92
Sun BZ, Ma W (2017) Fuzzzy rough set over multi-universes and its application in decision making. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 32:1719–1734
Sun BZ, Ma W, Qian YH (2017a) Multigranulation fuzzy rough set over two universes and its application to decision making. Knowl Based Syst 123:61–74
Sun BZ, Ma W, Xiao X (2017b) Three-way group decision making based on multigranulation fuzzy decision-theoretic rough set over two universes. Int J Approx Reason 81:87–102
Tao Z, Han B, Chen H (2018) On intuitionistic fuzzy copula aggregation operators in multiple-attribute decision making. Cogn Comput 10:610–624
Tsang ECC, Chen D, Yeung DS (2008) Approximations and reducts with covering generalized rough sets. Comput Appl Math 56:279–289
Wang GY, Yang J, Xu J (2017) Granular computing: from granularity optimization to multi-granularity joint problem solving. Granul Comput 2(3):105–120
Wu WZ, Zhang WX (2004) Neighborhood operator systems and approximation operators. Inform Sci 159:233–254
Xu WH, Leung Y (1998) Theory and applications of granular labed partitions in multi-scale decision tables. Inform Sci 112:67–84
Xu WH, Sun W, Zhang X (2012) Multiple granulation rough set approach to ordered information systems. Int J Gen Syst 41:475–501
Xu WH, Wang Q, Luo S (2014) Multi-granulation fuzzy rough sets. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 26(3):1323–1340
Xu WH, Wang Q, Zhang X (2013) Multi-granulation rough sets based on tolerance relations. Soft Comput 17:1241–1252
Xu WH, Wang Q, Zhang X (2011) Multi-granulation fuzzy rough sets in a fuzzy tolerance approximation space. Int J Fuzzy Syst 13:246–259
Xu WH, Zhang WX (2007) Measuring roughness of generalized rough sets induced a covering. Fuzzy Sets Syst 158:2443–2455
Yager RR (1998) On ordered weighted averaging aggregation operators in multicriteria decisionmaking. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 18:183–190
Yang B, Hu BQ (2016) A fuzzy covering-based rough set model and its generalization over fuzzy lattice. Inform Sci 367–368:463–486
Yang B, Hu BQ (2017) On some types of fuzzy covering-based on rough sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 312:36–65
Yang XB, Qian YH, Yang J (2012a) Hierarchical atructures on multigranulation spaces. J Comput Sci Technol 27(6):1169–1183
Yang XB, Song X, Chen Z, Yang J (2012b) On multigranulation rough sets in incomplete information system. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 3:223–232
Yang XB, Song X, She Y, Yang J (2013) Hierarchy on multigranulation structures: a knowledge distance approach. Int J Gen Syst 42:754–773
Yao YY (2005) Perspectives of granular computing. Proc IEEE Int Conf Granul Comput 1(2005):85–90
Yao YY (1998) Relational interpretations of neighborhood operators and rough set approximation operators. Inform Sci 111:239–259
Yao YY (2016) Three-way decisions and cognitive computing. Cogn Comput 8(4):543–554
Yao YY (2010) Three-way decisions with probabilistic rough sets. Inform Sci 180:341–353
Yao YY, Yao B (2012) Covering based rough set approximations. Inform Sci 200:91–107
Yao YY, She YH (2015) Rough submodels in multigranulation spaces. Inform Sci 327:40–56
Yeung DS, Chen D, Lee J, Wang X (2015) On the generalization of fuzzy rough sets. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 13:343–361
Ye J (2018) Multiple attribute decision-making methods based on the expected value and the similarity measure of hesitant neutrosophic linguistic numbers. Cogn Comput 10:454–463
Zadeh LA (1997) Toward a theory of fuzzy information granulation and its centrality in human reasining and fuzzy logic. Fuzzy Sets Syst 90:111–127
Zhan J, Sun B, Alcantud JCR (2019a) Covering based multigranulation (\({\cal{I}}, {\cal{T}}\))-fuzzy rough set models and applications in multi-attribute group decision-making. Inform Sci 476:290–318
Zhan J, Zhang XH, Yao YY (2019b) Covering based multigranulation fuzzy rough sets and applications in multi-criteria group decision-making. Artif Intell Rev. 53(2020):1093–1126
Zhang B, Dong YY, Xu Y (2014) Multiple attribute consensus rules with minimum adjustments to support consensus reaching. Knowl Based Syst 67:35–48
Zhang QH, Guo YL, Xue YB (2015) Multi-granularity search algorithm based on probability statistics. Pattern Recog Artif Intell 28(5):422–427
Zhang XH, Miao D, Liu C, Le M (2016) Constructive methods of rough approximation operators and multigranulation rough sets. Knowl Based Syst 91:114–125
Zhu P (2011) Covering rough sets based on neighborhoods: an approach without using neighborhoods. Int J Approx Reason 52:461–472
Zhu W (2007) Topological approaches to covering rough sets. Inform Sci 177:1499–1508
Zhu W (2009) Relationships among basic concepts in covering-based rough sets. Inform Sci 179:2478–2486
Zhu W, Wang F (2007) On three types of covering rough sets. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 19:1131–1144
Acknowledgements
The authors are extremely grateful to the editors and three reviewers for their valuable comments and helpful suggestions which helped to improve the presentation of this paper. The first and the second authors were supported by the NNSFC of China (61866011; 11961025; 11561023). The third author was partly supported by the NNSFC of China (71571090), the National Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province of China (2017JM7022), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Key Strategic Research of Central Universities (JBZ170601).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, X., Zhan, J., Sun, B. et al. Novel classes of coverings based multigranulation fuzzy rough sets and corresponding applications to multiple attribute group decision-making. Artif Intell Rev 53, 6197–6256 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-020-09846-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-020-09846-1