Abstract
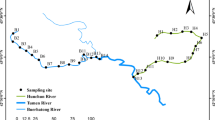
River Erguna is the Sino-Russian boundary river which has been widely concerned both by Russia and China due to the water quality and water resources management. As one class of persistent organic pollutants, no enough attention is paid to investigate the behavior characteristics and risk of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in the rivers originated from forests and grasslands distributing in the middle-high latitude belts. This work investigated the source and characteristics of OCPs and evaluated their health risk assessment in the water system of River Erguna for the first time. The concentrations of OCPs were ranged from not detected (N.D) to 5.4 ng L−1 with the average of 2.2 ng L−1. Source analysis indicated a recent DDTs (dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane) input from the application in agricultural and forestry ecosystem in the drainage basin, whereas HCHs (hexachlorocyclohexanes) mainly originated from long-distance transmission or degradation of technical HCHs. Both the non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic risks were in the acceptable range, which is safe for the residents living along the Sino-Russian boundary river. This work would provide basic data set for the water quality and water sources management to avoid environmental dispute between Russia and China.

Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baqar, M., Sadef, Y., Ahmad, S. R., Mahmood, A., Li, J., & Zhang, G. (2017). Organochlorine pesticides across the tributaries of River Ravi, Pakistan: Human health risk assessment through dermal exposure, ecological risks, source fingerprints and spatio-temporal distribution. Science of the Total Environment, 618, 291–305.
Dai, G., Liu, X., Liang, G., Han, X., Shi, L., Cheng, D., & Gong, W. (2011). Distribution of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) and poly chlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in surface water and sediments from Baiyangdian Lake in North China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 23, 1640–1649.
Dobaradaran, S., Mahvi, A. H., Nabizadeh, R., Mesdaghinia, A., Naddafi, K., Yunesian, M., Rastkari, N., & Nazmara, S. (2010). Hazardous organic compounds in groundwater near Tehran automobile industry. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 85, 530–533.
EPA, A. (1989). 'Risk assessment guidance for superfund. Volume I: Human health evaluation manual (part a)', EPA/540/1-89/002.
Fommei, E., Turci, R., Ripoli, A., Balzan, S., Bianchi, F., Morelli, L., & Coi, A. (2017). Evidence for persistent organochlorine pollutants in the human adrenal cortex. Journal of Applied Toxicology, 37(9), 1091–1097.
Hong, H., Chen, W., Xu, L., Wang, X., & Zhang, L. (1999). Distribution and fate of organochlorine pollutants in the Pearl River estuary. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 39, 376–382.
IARC (2006). Complete List of Agents evaluated and their classification. http://www.iare.fr/.
IRIS (1999). Integrated Risk Information System. Database developed and maintained by the USEPA. https://www.epa.gov/iris.
Jantunen, L., & Bidleman, T. (1998). Organochlorine pesticides and enantiomers of chiral pesticides in Arctic Ocean water. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 35, 218–228.
Lee, K. T., Tanabe, S., & Koh, C. H. (2001). Distribution of organochlorine pesticides in sediments from Kyeonggi Bay and nearby areas, Korea. Environmental Pollution, 114, 207–213.
Li, Y. F., Cai, D. J., Shan, Z. J., & Zhu, Z. L. (2001). Gridded usage inventories of technical hexachlorocyclohexane and lindane for China with 1/6 latitude by 1/4 longitude resolution. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 41, 261–266.
Li, T., He, M. C., Men, B., & Lin, C. Y. (2009). Distribution and sources of organochlorine pesticides in water and sediments from Daliao River estuary of Liaodong Bay, Bohai Sea (China). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 84, 119–127.
Liu, C., Yuan, G. L., Yang, Z. F., Yu, T., Xia, X. Q., Hou, Q. Y., & Chen, L. (2011). Levels of organochlorine pesticides in natural water along the Yangtze River, from headstream to estuary, and factors determining these levels. Environmental Earth Sciences, 62, 953–960.
Liu, W. X., He, W., Qin, N., Kong, X. Z., He, Q. S., Ouyang, H. L., Yang, B., Wang, Q. M., Yang, C., & Jiang, Y. J. (2012). Residues, distributions, sources, and ecological risks of OCPs in the water from Lake Chaohu, China. The Scientific World Journal, 2012, 897697.
Lü, C., Wang, B., He, J., Vogt, R. D., Zhou, B., Guan, R., Zuo, L., Wang, W., Xie, Z., & Wang, J. (2016). Responses of organic phosphorus fractionation to environmental conditions and lake evolution. Environmental Science & Technology, 55, 5007–5016.
Mahmood, A., Malik, R. N., Li, J., & Zhang, G. (2014). Levels, distribution pattern and ecological risk assessment of organochlorines pesticides (OCPs) in water and sediments from two tributaries of the Chenab River, Pakistan. Ecotoxicology, 23, 1713.
Mahmoud, A. F., Ikenaka, Y., Yohannes, Y. B., Darwish, W. S., Eldaly, E. A., Morshdy, A. E., Nakayama, S. M., Mizukawa, H., & Ishizuka, M. (2016). Distribution and health risk assessment of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) residue in edible cattle tissues from northeastern part of Egypt: High accumulation level of OCPs in tongue. Chemosphere, 144, 1365.
Mamontova, E. A., Tarasova, E. N., & Mamontov, A. A. (2017). PCBs and OCPs in human milk in eastern Siberia, Russia: Levels, temporal trends and infant exposure assessment. Chemosphere, 178, 239.
Miglioranza, K. S., Gonzalez, M., Ondarza, P. M., Shimabukuro, V. M., Isla, F. I., Fillmann, G., Aizpún, J. E., & Moreno, V. J. (2013). Assessment of Argentinean Patagonia pollution: PBDEs, OCPs and PCBs in different matrices from the Rio Negro basin. Science of the Total Environments, 452–453, 275–285.
Montuori, P., Cirillo, T., Fasano, E., Nardone, A., Esposito, F., & Triassi, M. (2014). Spatial distribution and partitioning of polychlorinated biphenyl and organochlorine pesticide in water and sediment from Sarno River and estuary, southern Italy. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 21, 5023–5035.
Müller, M. H., Polder, A., Brynildsrud, O. B., Karimi, M., Lie, E., Manyilizu, W. B., Mdegela, R. H., Mokiti, F., Murtadha, M., & Nonga, H. E. (2017). Organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in human breast milk and associated health risks to nursing infants in northern Tanzania. Environmental Research, 154, 425–434.
Raeisi, A., Arfaeinia, H., Seifi, M., Shirzad-Siboni, M., Keshtkar, M., & Dobaradaran, S. (2016). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in coastal sediments from urban and industrial areas of Asaluyeh Harbor, Iran: Distribution, potential source and ecological risk assessment. Water Science & Technology A Journal of the International Association on Water Pollution Research, 74, 957.
Riding, M. J., Doick, K. J., Martin, F. L., Jones, K. C., & Semple, K. T. (2013). Chemical measures of bioavailability/bioaccessibility of PAHs in soil: Fundamentals to application. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 261, 687–700.
Samoh, A. N. H. (2009). Organochlorine pesticide residues in the major rivers of southern Thailand. Environmentasia, 2, 30–34.
Sharma, B., Tyagi, S., Singh, R., & Singh, P. (2012). Monitoring of organochlorine pesticides in fresh water samples by gas chromatography and bioremediation approaches. National Academy Science Letters, 35, 401–413.
Sun, K., Zhao, Y., Gao, B., Liu, X., Zhang, Z., & Xing, B. (2009). Organochlorine pesticides and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in irrigated soils of Beijing, China: Levels, inventory and fate. Chemosphere, 77, 1199–1205.
Sun, J., Feng, J., Liu, Q., & Li, Q. (2010). Distribution and sources of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in sediments from upper reach of Huaihe River, East China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 184, 141–146.
Sun, H., Qi, Y., Zhang, D., Li, Q. X., & Wang, J. (2016). Concentrations, distribution, sources and risk assessment of organohalogenated contaminants in soils from Kenya, Eastern Africa. Environmental Pollution, 209, 177–185.
Thompson, L. A., Darwish, W. S., Ikenaka, Y., Nakayama, S. M. M., Mizukawa, H., & Ishizuka, M. (2017). Organochlorine pesticide contamination of foods in Africa: Incidence and public health significance. Journal of Veterinary Medical Science, 79, 751–764.
Walker, K., And, D. A. V., & Lewis, R. G. (1999). Factors influencing the distribution of lindane and other hexachlorocyclohexanes in the environment. Environmental Science & Technology, 33, 4373–4378.
Wang, W., Bai, J., Zhang, G., Wang, X., Jia, J., Cui, B., & Liu, X. (2017). Depth-distribution, possible sources, and toxic risk assessment of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in different river sediment cores affected by urbanization and reclamation in a Chinese delta. Environmental Pollution, 230, 1062–1072.
Yuan, L., Qi, S., Wu, X., Wu, C., Xing, X., & Gong, X. (2013). Spatial and temporal variations of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in water and sediments from Honghu Lake, China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 132, 181–187.
Zhang, J., Qi, S., Xing, X., Tan, L., Gong, X., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, J. (2011). Organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in soils and sediments, Southeast China: A case study in Xinghua Bay. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62, 1270–1275.
Zhang, D., Wang, Y., Yu, K., Li, P., Zhang, R., & Xu, Y. (2014). Occurrence, distribution and sources of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in surface sediments from the Lijiang River, a typical karst river of southwestern China. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 93, 580–585.
Zhang, Y., Qi, S., Xing, X., Yang, D., Devi, N. L., Qu, C., Liu, H., Zhang, J., & Zeng, F. (2018). Chapter 21 - Legacies of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in soil of China—A review, and cases in Southwest and Southeast China. In B. D. Vivo, H. E. Belkin, & A. Lima (Eds.), Environmental Geochemistry (2nd ed., pp. 543–565). Elsevier.
Zhao, Z., Zhang, L., Wu, J., Fan, C., & Shang, J. (2010). Assessment of the potential mutagenicity of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in contaminated sediments from Taihu Lake, China. Mutation Research, 696, 62.
Zhi, H., Zhao, Z., & Zhang, L. (2015). The fate of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in water from Poyang Lake, the largest freshwater lake in China. Chemosphere, 119, 1134–1140.
Zhou, R., Zhu, L., Yang, K., & Chen, Y. (2006). Distribution of organochlorine pesticides in surface water and sediments from Qiantang River, East China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 137, 68–75.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41763014), Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars of Inner Mongolia (2019JQ05), and Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin, China (16JCYBJC43700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, F., Xie, Z., Zhou, B. et al. Characteristics and Health Risk Assessment of Organochlorine Pesticides (OCPs) Residues Along Sino-Russian Boundary River. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 500 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04877-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04877-4