Abstract
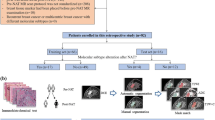
The volumetric assessment and accurate grading of meningiomas before surgery are highly relevant for therapy planning and prognosis prediction. This study was to design a deep learning algorithm and evaluate the performance in detecting meningioma lesions and grade classification. In total, 5088 patients with histopathologically confirmed meningioma were retrospectively included. The pyramid scene parsing network (PSPNet) was trained to automatically detect and delineate the meningiomas. The results were compared to manual segmentations by evaluating the mean intersection over union (mIoU). The performance of grade classification was evaluated by accuracy. For the automated detection and segmentation of meningiomas, the mean pixel accuracy, tumor accuracy, background accuracy and mIoU were 99.68%, 81.36%, 99.88% and 81.36% for all patients; 99.52%, 84.86%, 99.93% and 84.86% for grade I meningiomas; 99.57%, 80.11%, 99.92% and 80.12% for grade II meningiomas; and 99.75%, 78.40%, 99.99% and 78.40% for grade III meningiomas, respectively. For grade classification, the accuracy values of the training and test datasets were 99.93% and 81.52% for all patients; 99.98% and 98.51% for grade I meningiomas; 99.91% and 66.67% for grade II meningiomas; and 99.88% and 73.91% for grade III meningiomas, respectively. The automated detection, segmentation and grade classification of meningiomas based on deep learning were accurate and reliable and may improve the monitoring and treatment of this frequently occurring tumor entity. Furthermore, the method could function as a useful tool for preassessment and preselection for radiologists, offering auxiliary information for clinical decision making in presurgical evaluation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kunimatsu, A., Kunimatsu, N., Kamiya, K., Katsura, M., Mori, H., & Ohtomo, K. (2016). Variants of meningiomas: A review of imaging findings and clinical features. Jpn J Radiol, 34(7), 459–469.
Nanda, A., Javalkar, V., & Banerjee, A. D. (2011). Petroclival meningiomas: Study on outcomes, complications and recurrence rates. J Neurosurg, 114(5), 1268–1277.
Niranjan, A., Faramand, A., Lunsford, L.D. (2019). Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Low-Grade Gliomas. Progress in neurological surgery, 34(undefined), 184–190.
Yao, A., Pain, M., Balchandani, P., & Shrivastava, R. K. (2018). Can MRI predict meningioma consistency?: A correlation with tumor pathology and systematic review. Neurosurg Rev, 41(3), 745–753.
Holodny, A. I., Nusbaum, A. O., Festa, S., Pronin, I. N., Lee, H. J., & Kalnin, A. J. (1999). Correlation between the degree of contrast enhancement and the volume of peritumoral edema in meningiomas and malignant gliomas. Neuroradiology, 41(11), 820–825.
Viaene, A. N., Zhang, B., Martinez-Lage, M., Xiang, C., Tosi, U., Thawani, J. P., et al. (2019). Transcriptome signatures associated with meningioma progression. Acta neuropathologica communications, 7(1), 67.
Bejnordi, B. E., Veta, M., van Diest, P. J., van Ginneken, B., Karssemeijer, N., Litjens, G., et al. (2017). Diagnostic assessment of deep learning algorithms for detection of lymph node metastases in women with breast cancer. JAMA, 318(22), 2199–2210.
Berman, M., Triki, A.R., & Blaschko, M.B. (2017). The Lov\'asz-Softmax loss: A tractable surrogate for the optimization of the intersection-over-union measure in neural networks.
Mawrin, C., & Perry, A. (2010). Pathological classification and molecular genetics of meningiomas. J Neuro-Oncol, 99(3), 379–391.
Wang, C. W., Juan, C. J., Liu, Y. J., Hsu, H. H., Liu, H. S., Chen, C. Y., et al. (2009). Volume-dependent overestimation of spontaneous intracerebral hematoma volume by the ABC/2 formula. Acta radiologica (Stockholm, Sweden : 1987), 50(3), 306–311.
Louis, D. N., Perry, A., Reifenberger, G., von Deimling, A., Figarella-Branger, D., Cavenee, W. K., et al. (2016). The 2016 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system: A summary. Acta Neuropathol, 131(6), 803–820.
Zöllner, F. G., Emblem, K. E., & Schad, L. R. (2012). SVM-based glioma grading: Optimization by feature reduction analysis. Zeitschrift fur medizinische Physik, 22(3), 205–214.
Choy, G., Khalilzadeh, O., Michalski, M., Do, S., Samir, A. E., Pianykh, O. S., et al. (2018). Current applications and future impact of machine learning in radiology. Radiology, 288(2), 318–328.
Minniti, G., Clarke, E., Lanzetta, G., Osti, M.F., Trasimeni, G., Bozzao, A., et al. (2011). Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases: analysis of outcome and risk of brain radionecrosis. Radiation oncology (London, England), 6(undefined), 48.
Yamazaki, H., Shiomi, H., Tsubokura, T., Kodani, N., Nishimura, T., Aibe, N., et al. (2011). Quantitative assessment of inter-observer variability in target volume delineation on stereotactic radiotherapy treatment for pituitary adenoma and meningioma near optic tract. Radiation oncology (London, England), 6(undefined), 10.
Bø, H. K., Solheim, O., Jakola, A. S., Kvistad, K. A., Reinertsen, I., & Berntsen, E. M. (2017). Intra-rater variability in low-grade glioma segmentation. J Neuro-Oncol, 131(2), 393–402.
Wu, J., Qian, Z., Tao, L., Yin, J., Ding, S., Zhang, Y., et al. (2015). Resting state fMRI feature-based cerebral glioma grading by support vector machine. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg, 10(7), 1167–1174.
Mo, J.J., Zhang, J.G., Li, W.L., Chen, C., Zhou, N.J., Hu, W.H. et al. (2018). Clinical Value of Machine Learning in the Automated Detection of Focal Cortical Dysplasia Using Quantitative Multimodal Surface-Based Features. Frontiers in neuroscience, 12(undefined), 1008.
Hwang, K.L., Hwang, W.L., Bussière, M.R., & Shih, H.A. (2017). The role of radiotherapy in the management of high-grade meningiomas. Chinese clinical oncology, 6(null), S5.
Cho, M., Joo, J. D., Kim, I. A., Han, J. H., Oh, C. W., & Kim, C. Y. (2017). The role of adjuvant treatment in patients with high-grade meningioma. Journal of Korean Neurosurgical Society, 60(5), 527–533.
Monteiro, M., Figueiredo, M.A.T., & Oliveira, A.L. (n.d.) Conditional Random Fields as Recurrent Neural Networks for 3D Medical Imaging Segmentation.
Qiao, Z., Cui, Z., Niu, X., Geng, S., & Yu, Q.. (2017) Image Segmentation with Pyramid Dilated Convolution Based on ResNet and U-Net. In International Conference on Neural Information Processing.
Goldbrunner, R., Minniti, G., Preusser, M., Jenkinson, M. D., Sallabanda, K., Houdart, E., et al. (2016). EANO guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of meningiomas. The Lancet Oncology, 17(9), e383–e391.
Bonte, S., Goethals, I., & Van Holen, R. (2018). Machine learning based brain tumour segmentation on limited data using local texture and abnormality. Computers in biology and medicine, 98(undefined), 39–47.
Chidambaram, S., Pannullo, S. C., Roytman, M., Pisapia, D. J., Liechty, B., Magge, R. S., et al. (2019). Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging perfusion characteristics in meningiomas treated with resection and adjuvant radiosurgery. Neurosurg Focus, 46(6), E10.
Saraf, S., McCarthy, B. J., & Villano, J. L. (2011). Update on meningiomas. Oncologist, 16(11), 1604–1613.
Hong, S. J., Bernhardt, B. C., Caldairou, B., Hall, J. A., Guiot, M. C., Schrader, D., et al. (2017). Multimodal MRI profiling of focal cortical dysplasia type II. Neurology, 88(8), 734–742.
Wang, Y., Loe, K. F., & Wu, J. K. (2005). A dynamic conditional random field model for foreground and shadow segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 28(2), 279–289.
Zhang, X., Yan, L. F., Hu, Y. C., Li, G., Yang, Y., Han, Y., et al. (2017). Optimizing a machine learning based glioma grading system using multi-parametric MRI histogram and texture features. Oncotarget, 8(29), 47816–47830.
Qi, X. X., Shi, D. F., Ren, S. X., Zhang, S. Y., Li, L., Li, Q. C., et al. (2018). Histogram analysis of diffusion kurtosis imaging derived maps may distinguish between low and high grade gliomas before surgery. Eur Radiol, 28(4), 1748–1755.
Ishi, Y., Terasaka, S., Yamaguchi, S., Yoshida, M., Endo, S., Kobayashi, H., et al. (2016). Reliability of the Size Evaluation Method for Meningiomas: Maximum Diameter, ABC/2 Formula, and Planimetry Method. World neurosurgery, 94(undefined), 80–88.
Y. Yang, L.F. Yan, X. Zhang, Y. Han, H.Y. Nan, Y.C. Hu, et al. (2018). Glioma Grading on Conventional MR Images: A Deep Learning Study With Transfer Learning. Frontiers in neuroscience, 12(undefined), 804.
Akkus, Z., Galimzianova, A., Hoogi, A., Rubin, D. L., & Erickson, B. J. (2017). Deep learning for brain MRI segmentation: State of the art and future directions. J Digit Imaging, 30(4), 449–459.
Zada, G., & Jensen, R.L. (2016). Meningiomas: An Update on Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches. Neurosurgery Clinics of North America, 27(2), xiii-xiii.
Zhao, H., Shi, J., Qi, X., Wang, X., & Jia, J. (2016). Pyramid Scene Parsing Network.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Significance
1. The deep learning model improves the accuracy of meningioma detection and segmentation.
2. The deep learning model allows accurate meningioma grading in presurgical evaluation.
3. The utility of deep learning can offer clinicians auxiliary information for decision-making.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Mo, J., Jiang, H. et al. Deep Learning Model for the Automated Detection and Histopathological Prediction of Meningioma. Neuroinform 19, 393–402 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-020-09492-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-020-09492-6