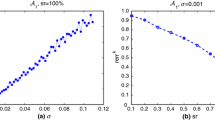
Abstract
This paper studies the problem of deterministic rank-one matrix completion. It is known that the simplest semidefinite programming relaxation, involving minimization of the nuclear norm, does not in general return the solution for this problem. In this paper, we show that in every instance where the problem has a unique solution, one can provably recover the original matrix through the level 2 Lasserre relaxation with minimization of the trace norm. We further show that the solution of the proposed semidefinite program is Lipschitz stable with respect to perturbations of the observed entries, unlike more basic algorithms such as nonlinear propagation or ridge regression. Our proof is based on recursively building a certificate of optimality corresponding to a dual sum-of-squares (SoS) polynomial. This SoS polynomial is built from the polynomial ideal generated by the completion constraints and the monomials provided by the minimization of the trace. The proposed relaxation fits in the framework of the Lasserre hierarchy, albeit with the key addition of the trace objective function. Finally, we show how to represent and manipulate the moment tensor in favorable complexity by means of a hierarchical low-rank factorization.












Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Note that in the case of convex optimization those conditions are necessary and sufficient.
Recall that we assumed \((\varvec{X}_0)_{ij}\ne 0\) for all (i, j).
An alternative representation would be given by the decomposition Trace + ideal of Sect. 2.3 and encoded as \(\varvec{I} - \varvec{Y}_1\).
References
A. A. Ahmadi, G. Hall, A. Papachristodoulou, J. Saunderson, and Y. Zheng. Improving efficiency and scalability of sum of squares optimization: Recent advances and limitations. arXiv:1710.01358, 2017.
A. S. Bandeira. Convex relaxations for certain inverse problems on graphs. 2015.
B. Barak and A. Moitra. Tensor prediction, Rademacher complexity and random 3-XOR. arXiv:1501.06521, 2015.
R. Berke and M. Onsjö. Propagation connectivity of random hypergraphs. In Stochastic Algorithms: Foundations and Applications, pages 117–126. Springer, 2009.
S. Burer and R. Monteiro. A nonlinear programming algorithm for solving semidefinite programs via low-rank factorization. Mathematical Programming, 95(2):329–357, 2003.
S. Burer and R. D. Monteiro. Local minima and convergence in low-rank semidefinite programming. Mathematical Programming, 103(3):427–444, 2005.
E. J. Candès, Y. C. Eldar, T. Strohmer, and V. Voroninski. Phase retrieval via matrix completion. SIAM review, 57(2):225–251, 2015.
E. J. Candès and C. Fernandez-Granda. Towards a mathematical theory of super-resolution. Communications on Pure and Applied Mathematics, 67(6):906–956, 2014.
E. J. Candès and Y. Plan. Matrix completion with noise. Proceedings of the IEEE, 98(6):925–936, 2010.
E. J. Candès and B. Recht. Exact matrix completion via convex optimization. Foundations of Computational mathematics, 9(6):717–772, 2009.
E. J. Candès, T. Strohmer, and V. Voroninski. Phaselift: Exact and stable signal recovery from magnitude measurements via convex programming. Communications on Pure and Applied Mathematics, 66(8):1241–1274, 2013.
E. J. Candès and T. Tao. The power of convex relaxation: Near-optimal matrix completion. Information Theory, IEEE Transactions on, 56(5):2053–2080, 2010.
A. Cosse and L. Demanet. Rank-one matrix completion is solved by the sum-of-squares relaxation of order two. In Proceedings of the 6th IEEE International Workshop on Computational Advances in Multi-Sensor Adaptive Processing (CAMSAP’15). IEEE, 2015.
C.-F. Cui, Y.-H. Dai, and J. Nie. All real eigenvalues of symmetric tensors. SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, 35(4):1582–1601, 2014.
L. Demanet and V. Jugnon. Convex recovery from interferometric measurements. arXiv:1307.6864, 2013.
M. Fazel. Matrix rank minimization with applications. PhD thesis, Stanford University, March 2002.
M. X. Goemans and D. P. Williamson. Improved approximation algorithms for maximum cut and satisfiability problems using semidefinite programming. Journal of the ACM (JACM), 42(6):1115–1145, 1995.
J. Gouveia, P. A. Parrilo, and R. R. Thomas. Theta bodies for polynomial ideals. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 20(4):2097–2118, 2010.
V. Jugnon and L. Demanet. Interferometric inversion: a robust approach to linear inverse problems. In Proceedings of SEG Annual Meeting, Houston, pages 5180–5184, 2013.
R. Keshavan, A. Montanari, and S. Oh. Matrix completion from noisy entries. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pages 952–960, 2009.
R. H. Keshavan, A. Montanari, and S. Oh. Learning low rank matrices from \(O(n)\) entries. In Communication, Control, and Computing, 2008 46th Annual Allerton Conference on, pages 1365–1372. IEEE, 2008.
R. H. Keshavan, A. Montanari, and S. Oh. Matrix completion from a few entries. Information Theory, IEEE Transactions on, 56(6):2980–2998, 2010.
F. Kiraly and L. Theran. Error-minimizing estimates and universal entry-wise error bounds for low-rank matrix completion. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pages 2364–2372, 2013.
F. Király and R. Tomioka. A combinatorial algebraic approach for the identifiability of low-rank matrix completion. arXiv:1206.6470, 2012.
F. J. Király, L. Theran, and R. Tomioka. The algebraic combinatorial approach for low-rank matrix completion. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 16:1391–1436, 2015.
J. B. Lasserre. Global optimization with polynomials and the problem of moments. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 11(3):796–817, 2001.
J. B. Lasserre. Convergent SDP-relaxations in polynomial optimization with sparsity. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 17(3):822–843, 2006.
M. Laurent. Sums of squares, moment matrices and optimization over polynomials. In Emerging applications of algebraic geometry, pages 157–270. Springer, 2009.
Y. Nesterov. Squared functional systems and optimization problems. In High performance optimization, pages 405–440. Springer, 2000.
J. Nie. An exact jacobian SDP relaxation for polynomial optimization. Mathematical Programming, 137(1-2):225–255, 2013.
J. Nie and J. Demmel. Sparse SoS relaxations for minimizing functions that are summations of small polynomials. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 19(4):1534–1558, 2008.
P. A. Parrilo. Structured semidefinite programs and semialgebraic geometry methods in robustness and optimization. PhD thesis, Citeseer, 2000.
P. A. Parrilo. Semidefinite programming relaxations for semialgebraic problems. Mathematical programming, 96(2):293–320, 2003.
B. Recht. A simpler approach to matrix completion. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 12:3413–3430, 2011.
B. Recht, M. Fazel, and P. Parrilo. Guaranteed minimum-rank solutions of linear matrix equations via nuclear norm minimization. SIAM Review, 52(3):471–501, 2010.
R. T. Rockafellar. Convex analysis. Number 28. Princeton university press, 1970.
N. Shor. Class of global minimum bounds of polynomial functions. Cybernetics and Systems Analysis, 23(6):731–734, 1987.
N. Z. Shor. Quadratic optimization problems. Soviet Journal of Computer and Systems Sciences, 25(6):1–11, 1987.
N. Z. Shor. An approach to obtaining global extremums in polynomial mathematical programming problems. Cybernetics, 23(5):695–700, 1988.
A. Singer and M. Cucuringu. Uniqueness of low-rank matrix completion by rigidity theory. SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, 31(4):1621–1641, 2010.
G. Tang and P. Shah. Guaranteed tensor decomposition: A moment approach. In Proceedings of The 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, pages 1491–1500, 2015.
Acknowledgements
Both authors were supported by a grant from the MISTI MIT-Belgium seed fund. AC is grateful to the FNRS, FSMP, BAEF and Francqui Foundations and is supported by EOARD Grant FA9550-18-1-7007. LD is supported by AFOSR Grant FA9550-17-1-0316, ONR Grant N00014-16-1-2122, and NSF Grant DMS-1255203. AC is grateful to MIT Math, Harvard IACS, the University of Chicago as well as NYU Courant Institute and Center for Data Science for hosting him during this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Thomas Strohmer.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cosse, A., Demanet, L. Stable Rank-One Matrix Completion is Solved by the Level 2 Lasserre Relaxation. Found Comput Math 21, 891–940 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10208-020-09471-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10208-020-09471-y
Keywords
- Matrix completion
- Convex optimization
- Semidefinite programming
- Semidefinite programming hierarchies
- Duality in optimization
- Sum-of-Squares polynomials