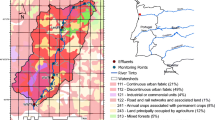
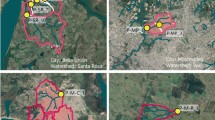
Abstract
Poor water quality in urban streams places at risk the health of urban residents and the integrity of urban environments, ultimately leading to the “urban stream syndrome.” In response to growing concerns regarding urban streams in Uruguay, we evaluated the spatiotemporal variation in water quality parameters in two urban streams, the Ceibal and La Curtiembre streams, over 12–18 months. A proposal for an Urban Water Quality Index (UWQI) was developed based on national water quality standards for two stream classes to assess variability in overall stream condition over time. Both streams displayed extremely high levels of fecal coliform concentrations in mid-downstream sites and relatively high levels of total dissolved phosphorus and ammonia well above the national standards of 0.025 mg/L and 0.02 mg/L, respectively. Nitrate was consistently below the national maximum of 44.3 mg/L, calling to question the adequacy of this standard for designated uses. Over 40% of samples had oxygen levels below the national standard of 5 mg/L, and a dead zone (average 1.5 mg/L) was detected in the downstream reach of the La Curtiembre stream. Despite differences in land use and urban context, monthly observations of nutrients and coliforms indicated high levels of contamination in mid-downstream reaches, which could present a health risk for the populations in Paysandú and Salto. This study highlights the degradation of urban streams in two major cities in Uruguay and the need for a comparative diagnosis of stream condition as a basis for decision-making regarding urban development and water resources.






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
14 October 2020
The original version of this article unfortunately contained an error in the published paper.
References
Albert, M. T., Richon, M., Vinals, M. J., & Witcomb, A. (2012). Community development through world heritage. World Heritage papers 31.© UNESCO 2012. ISBN: 978-92-3-001024-9. Printed by Universitat Politècnica de València Spain.
Alexander, R. B., Boyer, E. W., Smith, R. A., Schwarz, G. E., & Moore, R. B. (2007). The role of headwater streams in downstream water quality 1. JAWRA Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 43(1), 41–59.
Almeida, C. A., Quintar, S., González, P., & Mallea, M. A. (2007). Influence of urbanization and tourist activities on the water quality of the Potrero de los Funes River (San Luis–Argentina). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 133(1–3), 459–465.
Alonso, A. Capandeguy, C. Chreties, A. Cuadrado, A. Gamarra, P. Guido, J. P. Martínez, N. Mazzeo, M. Mena, A. Piperno, F. Quintans, N. Rezzano, G. Sanguinet, P. Sierra, L. Silveira, J. Taks. (2015). Aguas urbanas en Uruguay. Avances y desafíos hacia una gestión integrada, Ed. Piperno A., Quintans F., Conde D. Interamerican Network of Academies of Sciences (IANAS). Available: http://unesdoc.unesco.org/images/0024/002452/245202s.pdf. .
Alvareda E., Teixeira de Mello F., Sapriza G., Russo P., Erasun V., Gamazo P., Texeira R., Piperno A. (2018). Raising awareness of urban and suburban hydric resource pollution in promoting urban water management in Northwest Uruguay. Proceedings of the 3rd World Congress on Civil, Structural, and Environmental Engineering (CSEE’18) Budapest, Hungary – April 8–10, 2018 Paper No. ICESDP 125 DOI: https://doi.org/10.11159/icesdp18.125. https://avestia.com/CSEE2018_Proceedings/files/paper/ICESDP/ICESDP_125.pdf. Accessed 31 July 2018.
American Public Health Association (APHA). (2017). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (p. 2017). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Arocena, R. (1998). Statistical analysis of benthic communities to assess suspected degradation and recuperation zones in an urban stream (Uruguay). Internationale Vereinigung für theoretische und angewandte Limnologie: Verhandlungen, 26(3), 1188–1192.
Arvanitidou, M., Kanellou, K., Katsouyannopoulos, V., & Tsakris, A. (2002). Occurrence and densities of fungi from northern Greek coastal bathing waters and their relation with faecal pollution indicators. Water Research, 36(20), 5127–5131.
Aubriot, L., Delbene, L., Haakonsson, S., Somma, A., Hirsch, F., & Bonilla, S. (2017). Evolución de la eutrofización en el Río Santa Lucía: influencia de la intensificación productiva y perspectivas. Innotec, 14.
Benejam, L., Teixeira de Mello, F., Meerhoff, M., Loureiro, M., Jeppesen, E., & Brucet, S. (2016). Assessing effects of change in land use on size-related variables of fish in subtropical streams. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 556, 73, 547. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjfas-2015-0025.
Bittner, A. A. B. (2000). Nepal drinking water quality assessment: nitrates and ammonia. Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Doctoral dissertation.
Bonilla, S., Haakonsson, S., Somma, A., Gravier, A., Britos, A., Vidal, L., De León, L., Brena, B., Pírez, M., Piccini, C., & de la Escalera, G. M. (2015). Cianobacterias y cianotoxinas en ecosistemas límnicos de Uruguay. Innotec, 9–22.
Booth, D. B. (2005). Challenges and prospects for restoring urban streams: a perspective from the Pacific Northwest of North America: BRIDGES is a recurring feature of J-NABS intended to provide a forum for the interchange of ideas and information between basic and applied researchers in benthic science. Articles in this series will focus on topical research areas and linkages between basic and applied aspects of research, monitoring, policy, and education. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 737, 24(3), 724.
Camargo, J. A., Alonso, A., & Salamanca, A. (2005). Nitrate toxicity to aquatic animals: a review with new data for freshwater invertebrates. Chemosphere, 58(9), 1255–1267.
CARU. (2019). Comision Administradora del Río Uruguay. http://www.caru.org.uy/web/actividades/planes-de-monitoreo/. .
Chalar, G. (2009). The use of phytoplankton patterns of diversity for algae bloom management. Limnologica, 39, 200–208.
Chalar, G., Arocena, R., Pacheco, J. P., & Fabián, D. (2011). Trophic assessment of streams in Uruguay: a trophic State Index for Benthic Invertebrates (TSI-BI). Ecological Indicators, 11(2), 362–369.
Chalar, G., Garcia-Pesenti, P., Silva-Pablo, M., Perdomo, C., Olivero, V., & Arocena, R. (2017). Weighting the impacts to stream water quality in small basins devoted to forage crops, dairy and beef cow production. Limnologica, 65, 76–84.
Couceiro, S. R., Hamada, N., Luz, S. L., Forsberg, B. R., & Pimentel, T. P. (2007). Deforestation and sewage effects on aquatic macroinvertebrates in urban streams in Manaus, Amazonas, Brazil. Hydrobiologia, 575(1), 271–284.
Cude, C. G. (2001). Oregon water quality index a tool for evaluating water quality management effectiveness 1. JAWRA Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 37(1), 125–137.
DINAMA. National Directorate of the Environment of the Uruguayan Housing, Land use planning and Environment Ministry, Uruguay. https://www.mvotma.gub.uy/dinama. Accessed 26 October 2019.
Dodds, W. K., & Smith, V. H. (2016). Nitrogen, phosphorus, and eutrophication in streams. Inland Waters, 6(2), 155–164.
Dunca, A. M. (2018). Water pollution and water quality assessment of major transboundary rivers from Banat Romania. Journal of Chemistry, 2018, 1–8.
EEMAC. (2020). Monthly climatological summary data. Estación Experimental Mario A. Cassinoni – EEMAC: Paysandú, Facultad de Agronomía, Universidad de la Republica, Uruguay http://www.eemac.edu.uy/index.php/servicios/estacion-meteorologica-automatica.
Fernandez D.S. and Hidalgo M. (2012). Desarrollo de un índice de calidad de aguas para la cuenca del rio Colorado provincia de Tucuman, Conference paper. VII Congreso Nacional Ambiental, Tucuman Argentina. October 2012. Unpublished results. Acces link: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/265794300_Desarrollo_de_un_indice_de_calidad_de_aguas_para_la_cuenca_del_rio_Colorado_provincia_de_Tucuman.
Fierro, P., Valdovinos, C., Vargas-Chacoff, L., Bertrán, C., & Arismendi, I. (2017). Macroinvertebrates and fishes as bioindicators of stream water pollution. In Water Quality. Intechopen (pp. 23–38). Rijeka.
Fu, Q., Zheng, B., Zhao, X., Wang, L., & Liu, C. (2012). Ammonia pollution characteristics of centralized drinking water sources in China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 24(10), 1739–1743.
Gleik P. (2000). The changing water paradigm a look at twenty-first century water resources development,” IWRA, Water International, 25:1, 127–137.
Goyenola, G., Meerhoff, M., Teixeira-de Mello, F., González-Bergonzoni, I., Graeber, D., Fosalba, C., Vidal, N., Mazzeo, N., Ovesen, N. B., Jeppesen, E., & Kronvang, B. (2015). Monitoring strategies of stream phosphorus under contrasting climate-driven flow regimes. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 19, 4099–4111. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-19-4099-2015.
Haakonsson, S., Rodríguez-Gallego, L., Somma, A., & Bonilla, S. (2017). Temperature and precipitation shape the distribution of harmful cyanobacteria in subtropical lotic and lentic ecosystems. Science of the Total Environment, 609, 1132–1139.
Haider, H., & Ali, W. (2013). Evaluation of water quality management alternatives to control dissolved oxygen and un-ionized ammonia for Ravi River in Pakistan. Environmental Modeling and Assessment, 18(4), 451–469.
IGM. (2012). Planes Cartográficos: plan cartográfico nacional. http://www.sgm.gub.uy/2012/03/17/planes-cartograficos/.
INIA-GRAS. (2020). Database of agro-climate data. Salto Grande station daily accumulated precipitation data (mm) from Dec-2016 to July 2018. Available online to the public http://www.inia.uy/gras/Clima/Banco-datos-agroclimatico. Accessed 06–2020.
Karr, J. R. (1981). Assessment of biotic integrity using fish communities. Fisheries, 6(6), 21–27.
Kaurish, F. W., & Younos, T. (2007). Developing a standardized water quality index for evaluating surface water quality 1. JAWRA Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 43(2), 533–545.
Kjellén, M. (2018). Wastewater governance and the local, regional and global environments. Water Alternatives, 11(2), 219–237.
Koroleff, F. (1970). Direct determination of ammonia in natural waters as indophenol blue. Information on techniques and methods for seawater analysis, 19–22.
Kruk, C., Martínez, A., de la Escalera, G. M., Trinchin, R., Manta, G., Segura, A. M., Piccini, C., Brena, B., Fabiano, G., Pírez, M., & Gabito, L. (2019). Floración excepcional de cianobacterias tóxicas en la costa de Uruguay, verano 2019. Innotec, 18, 36–68.
Lamparelli, M. C. (2004). Graus de trofia em corpos d\'água do estado de São Paulo: avaliação dos métodos de monitoramento. Universidade de São Paulo: Doctoral dissertation.
Li, G., Fang, C., Wang, S., & Sun, S. (2016). The effect of economic growth, urbanization, and industrialization on fine particulate matter (PM2. 5) concentrations in China. Environmental Science & Technology, 50(21), 11452–11459.
Lintern, A., Webb, J. A., Ryu, D., Liu, S., Bende-Michl, U., Waters, D., Leahy, P., Wilson, P., & Western, A. W. (2017). Key factors influencing differences in-stream water quality across space. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews Water, 5(1), e1260.
Loucks, D. P., and Van Beek, E. (2017). Water resources systems planning and management: an introduction to methods, models and applications. World Report on the Development of Water Resources. ISBN: 978-92-3-300058-2, Springer. https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000247647. .
Mañay, N., Cousillas, A. Z., Alvarez, C., & Heller, T. (2008). Lead contamination in Uruguay: the “La Teja” neighborhood case, In Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology (pp. 93–115). New York: Springer.
Mazurek, R., Kowalska, J., Gąsiorek, M., Zadrożny, P., Józefowska, A., Zaleski, T., & Orłowska, K. (2017). Assessment of heavy metals contamination in surface layers of Roztocze National Park forest soils (SE Poland) by indices of pollution. Chemosphere, 168, 839–850.
Mellander, P. E., Jordan, P., Shore, M., Melland, A. R., & Shortle, G. (2015). Flow paths and phosphorus transfer pathways in two agricultural streams with contrasting flow controls. Hydrological Processes, 29(16), 3504–3518.
Morley, S. A., & Karr, J. R. (2002). Assessing and restoring the health of urban streams in the Puget Sound basin. Conservation Biology, 16(6), 1498–1509.
Müller, R., & Wiedemann, F. (1955). Die Bestimmung des Nitrats in Wasser. Jahrb. Wasserchem. Wasserreinigungstechnik. Verlag Chimie, 12, 247–271.
Muniz, P., Venturini, N., Martins, C. C., Munshi, A. B., García-Rodríguez, F., Brugnoli, E., Dauner, A. L. L., Bícego, M. C., & García-Alonso, J. (2015). Integrated assessment of contaminants and monitoring of an urbanized temperate harbor (Montevideo, Uruguay): a 12-year comparison. Brazilian Journal of Oceanography, 63(3), 311–330.
Murphey, J., & Riley, J. P. (1962). Phosphorus analysis procedure. Methods of soil analysis. Part, 2, 413–426.
MVOTMA (2004). Uruguayan Housing, Land use planning and Environment Ministry. Proceedings of the Second National Communications of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change,44-46. Available: http://www.cambioclimatico.gub.uy/images/stories/documentos/plan_nacional/proyectos_estrategicos/urync2.pdf. Access 21 June 2018.
MVOTMA (2016). Indicadores Ambientales de Uruguay. Concentración de amoníaco libre en agua superficial (NH3). https://www.dinama.gub.uy/oan/documentos/uploads/2016/12/Indicador-NH3-Libre-26.07.2016-ER_rosinaeditado.pdf, .
MVOTMA (2017). Uruguayan Housing, Land use planning and Environment Ministry. https://mvotma.gub.uy/component/k2/item/10010068-planes-de-aguas-urbanas-en-el-uruguay-ciudad-de-salto , .
National Decree, 2019 Dec. 253/79 of Uruguay, Standards to prevent Environmental Pollution by controlling the contamination of the waters, https://www.impo.com.uy/bases/decretos/253-1979. .
NIAU. (2015). Núcleo Interdisciplinario de Aguas urbanas. Proyecto del Espacio Interdisciplinario: Universidad de la República, Uruguay http://www.aguasurbanas.ei.udelar.edu.uy/index.php/proyecto-de-evaluacion-de-canadas-urbanas/.
NIS (2011). National Institute of Statistics: 8° Censo nacional de población 2011, http://www.ine.gub.uy/web/guest/censos-2011. .
Novotny, V. (1994). Water quality: prevention, identification and management of diffuse pollution. Van Nostrand-Reinhold Publishers.
Odino, R., Delmonte, D., Feola, G., Velez, A., & Cacho, C. (1998). Heavy metals in Pantanoso and Miguelete small stream; Metales pesados en los arroyos Pantanoso y Miguelete.
O'Farrell, I., Lombardo, R. J., de Tezanos Pinto, P., & Loez, C. (2002). The assessment of water quality in the lower Luján River (Buenos Aires, Argentina): phytoplankton and algal bioassays. Environmental Pollution, 120(2), 207–218.
Ogorzaly, L., Tissier, A., Bertrand, I., Maul, A., & Gantzer, C. (2009). Relationship between F-specific RNA phage genogroups, faecal pollution indicators and human adenoviruses in river water. Water Research, 43(5), 1257–1264.
Paul, J. P., & Meyer, J. L. (2001). Streams in the urban landscape. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 32, 333–365.
Perdomo, C. H., Casanova, O. N., & Ciganda, V. S. (2001). Contaminación de aguas subterráneas con nitratos y coliformes en el litoral sudoeste del Uruguay. Agrociencia, 5(1), 10–22.
Pesce, S. F., & Wunderlin, D. A. (2000). Use of water quality indices to verify the impact of Córdoba City (Argentina) on Suquı́a river. Water Research, 34(11), 2915–2926.
Pfeifer, L. R., & Bennett, E. M. (2011). Environmental and social predictors of phosphorus in urban streams on the island of Montréal, Québec. Urban Ecosystem, 14(3), 485–499.
Plan Local de Ordenamiento Territorial y Desarrollo Sostenible de la Ciudad de Paysandú, 2019. https://paysandu.gub.uy/destacadas/9124-plan-local-de-ordenamiento-territorial-se-consolida-como-herramienta-de-desarrollo-estrategico-para-el-departamento, .
QGIS Development Team. (2014). QGIS geographic information system Open Source Geospatial Foundation Project. http://qgis.osgeo.org/.
R Core Team. (2019). R: a language and environment for statistical computing. In R Foundation for statistical computing. Vienna: Austria. URL https://www.R-project.org/.
Randall, D. J., & Tsui, T. K. N. (2002). Ammonia toxicity in fish. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 45(1–12), 17–23.
Sánchez, E., Colmenarejo, M. F., Vicente, J., Rubio, A., García, M. G., Travieso, L., & Borja, R. (2007). Use of the water quality index and dissolved oxygen deficit as simple indicators of watersheds pollution. Ecological Indicators, 7(2), 315–328.
Sekabira, K., Origa, H. O., Basamba, T. A., Mutumba, G., & Kakudidi, E. (2010). Assessment of heavy metal pollution in the urban stream sediments and its tributaries. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 7(3), 435–446.
Shibata, T., Solo-Gabriele, H. M., Fleming, L. E., & Elmir, S. (2004). Monitoring marine recreational water quality using multiple microbial indicators in an urban tropical environment. Water Research, 38(13), 3119–3131.
SINAE (2018). National emergency system, Uruguay. http://sinae.gub.uy/. .
Smith, D. G. (1990). A better water quality indexing system for rivers and streams. Water Research, 24(10), 1237–1244.
Stranko, S. A., Hilderbrand, R. H., & Palmer, M. A. (2012). Comparing the fish and benthic macroinvertebrate diversity of restored urban streams to reference streams. Restoration Ecology, 20(6), 747–755.
Széchenyi plan. (2013). Danube Region Strategy. Action 7 of the EUSDR: “To legislate at the appropriate level to limit the presence of phosphates in detergents”. Association Justice and Environment, on the request of PA4 of the EUSDR. https://waterquality.danube-region.eu/wp-content/uploads/sites/13/sites/13/2019/09/EUSDR_PA4_Action_7_milestone_2_study-1.pdf, Accessed 11 February 2019.
Teixeira-de Mello, F., Gonzalez-Bergonzoni, I., & Loureiro, M. (2011). Peces de agua dulce de Uruguay. PPR-MGAP, 188.
Teixeira-de Mello, F., Meerhoff, M., Baattrup-Pedersen, A., Maigaard, T., Kristensen, P., Andersen, T., Masdeu, M., Clemente, J. M., Fosalba, C., Mazzeo, N., et al. (2012). Community structure of fish in lowland streams differ substantially between subtropical and temperate climates. Hydrobiologia, 684(1), 143–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-011-0979-7.
Torres-Franco, A. F., Alatrista-Góngora, G. R., Guzmán-Rodríguez, N. P., Calizaya-Anco, J. A., Mota, C. R., & Figueredo, C. C. (2019). Physicochemical and diatom trophic state indexes: A complementary approach for improving water sustainability in a high Andean urban stream. Ecohydrology and Hydrobiology, 19(4), 577–587.
Tyagi, S., Sharma, B., Singh, P., & Dobhal, R. (2013). Water quality assessment in terms of water quality index. American Journal of water resources, 1(3), 34–38.
Valderrama, J. C. (1981). The simultaneous analysis of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in natural waters. Marine Chemistry, 10, 109–122.
Ventura, A. S., Maccor, T. A., & Momo, F. R. (1997). Contaminación del río Luján (Buenos Aires, Argentina). In Caracterización física y química de la calidad del agua. Resúmenes II Congreso Argentino de Limnología, 157.
Victoria, M., Lopez Tort, L. F., García, M., Lizasoain, A., Maya, L., Leite, J. P. G., Miagostovich, M. P., Cristina, J., & Colina, R. (2014). Assessment of gastroenteric viruses from wastewater directly discharged into Uruguay River, Uruguay. Food Environ Virol, 6, 116–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-014-9143-7.
Wade, T. J., Calderon, R. L., Sams, E., Beach, M., Brenner, K. P., Williams, A. H., & Dufour, A. P. (2005). Rapidly measured indicators of recreational water quality are predictive of swimming-associated gastrointestinal illness. Environmental Health Perspectives, 114(1), 24–28.
Walsh, C. J., Roy, A. H., Feminella, J. W., Cottingham, P. D., Groffman, P. M., & Morgan, R. P. (2005). The urban stream syndrome: current knowledge and the search for a cure. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 24(3), 706–723.
Wetzel, R. G. (2001). Limnology: lake and river ecosystems. Gulf professional publishing.
WHO. World Health Organization (1999). Health-based monitoring of recreational waters: the feasibility of a new approach (The ‘Annapolis protocol). Protection of the human environment water, sanitation and health series. WHO/SDE/ WSG/99.1, 1999.
WHO. World Health Organization. (2002). The World Health Report 2002: reducing risks. Promoting Healthy Life, World Health Organization, Geneva, 2002.
WHO. World Health Organization. (2004). WHO guidelines for drinking-water quality (3th ed.. Recommendations https://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/GDWQ2004web.pdf) .
WHO. World Health Organization, (2011). Background document for development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality. https://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/chemicals/nitratenitrite2ndadd.pdf. .
Wicks, B. J., & Randall, D. J. (2002). The effect of sub-lethal ammonia exposure on fed and unfed rainbow trout: the role of glutamine in regulation of ammonia. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology, 132(2), 275–285.
Wicks, B. J., Joensen, R., Tang, Q., & Randall, D. J. (2002). Swimming and ammonia toxicity in salmonids: the effect of sub lethal ammonia exposure on the swimming performance of coho salmon and the acute toxicity of ammonia in swimming and resting rainbow trout. Aquatic Toxicology, 59(1–2), 55–69.
Wilhm, J. L., & Dorris, T. C. (1968). Biological parameters for water quality criteria. Bioscience, 18, 477–481.
WWAP (2018). World Water Assessment Programme. 2018. The United Nations World Water Development Report 2018. Nature based solutions for water. Paris: UNESCO. http://unesdoc.unesco.org/images/0026/002614/261424e.pdf
Yu, H., Song, Y., Chang, X., Gao, H., & Peng, J. (2018). A scheme for a sustainable urban water environmental system during the urbanization process in China. Engineering, 4(2), 190–193.
Zhao, Y., Yang, Z., & Li, Y. (2010). Investigation of water pollution in Baiyangdian Lake, China. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2, 737–748.
Acknowledgments
We thank for their support the Núcleo Interdisciplinario Agua y Ciudad; the Government of the Paysandu Department, Barrio Casa Molle—Paysandu; and Prof. Julian Ramos from Departamento del Agua for Ceibal sampling collaboration and Prof. Cecilia Papalardo from Departamento de Matemática for statistical collaboration, both from Universidad de la República, CENUR Litoral Norte Uruguay, as well as Claudia Fosalba for the nutrient water analysis from Departmento de Ecología y Gestión Ambiental, Universidad de la República, CURE.
This work was supported by the Universidad de la República—Espacio Interdisciplinario and Comisión Sectorial de Investigación Cientifica (CSIC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 438 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alvareda, E., Lucas, C., Paradiso, M. et al. Water quality evaluation of two urban streams in Northwest Uruguay: are national regulations for urban stream quality sufficient?. Environ Monit Assess 192, 661 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08614-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08614-6