Abstract
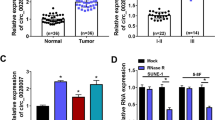
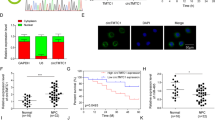
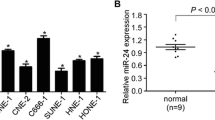
Circular RNA zinc finger protein 609 (circZNF609) has been reported to involve in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) tumorigenesis regulation. However, the role and the molecular mechanism of circZNF609 in NPC remain unclear. Levels of circZNF609, microRNA (miR)-338-3p, and GTPase HRas (HRAS) were detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction or Western blot. Cell proliferation, migration, and invasion were analyzed using cell counting kit-8 assay, colony formation assay, and transwell assay, respectively. Glucose metabolism was calculated by measuring glucose consumption, lactate production, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) levels, and HK2 activity. The interaction between miR-338-3p and circZNF609 or HRAS was analyzed by the dual-luciferase reporter assay. In vivo experiment was conducted using the murine xenograft model. CircZNF609 was elevated in NPC tissues and cell lines, and high circZNF609 expression had a poor prognosis. CircZNF609 knockdown suppressed NPC progression in vitro by inhibiting cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and glycolysis and hindered tumor growth in vivo. MiR-338-3p directly bound to circZNF609 and HRAS, and circZNF609 knockdown repressed NPC cell malignant properties by binding to miR-338-3p. MiR-338-3p was low in NPC, and miR-338-3p restoration performed anti-tumor effects in cells of NPC by targeting HRAS. Importantly, circZNF609 acted as a competing endogenous RNA of miR-338-3p to regulate HRAS. CircZNF609 knockdown suppressed cell tumorigenesis in NPC via regulating miR-338-3p/HRAS axis, suggesting a novel therapeutic strategy for NPC.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- circZNF609:
-
Circular RNA zinc finger protein 609
- NPC:
-
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- HRAS:
-
GTPase HRas
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
References
Chua ML, Wee JT, Hui EP, Chan AT (2016) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet 387:1012–1024
Zheng XH, Lu LX, Li XZ, Jia WH (2015) Quantification of epstein-barr virus DNA load in nasopharyngeal brushing samples in the diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in southern China. Cancer Sci 106:1196–1201
Blanchard P, Lee A, Marguet S, Leclercq J, Ng WT, Ma J, Chan AT, Huang P-Y, Benhamou E, Zhu G (2015) Chemotherapy and radiotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: an update of the MAC-NPC meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol 16:645–655
Yang W (2017) Preclinical advances in nasopharyngeal carcinoma treatment. Cell Cycle 16:1015
Ebbesen KK, Kjems J (1859) Hansen TB (2016) Circular RNAs: identification, biogenesis and function. Biochem Biophys Acta 1:163–168
Lei B, Tian Z, Fan W, Ni B (2019) Circular RNA: a novel biomarker and therapeutic target for human cancers. Int J Med Sci 16:292
Panda AC, Abdelmohsen K, Gorospe M (2017) SASP regulation by noncoding RNA. Mech Ageing Dev 168:37–43
Hombach S, Kretz M (2016) Non-coding RNAs: classification, biology and functioning. In: George A (ed) Non-coding RNAs in colorectal cancer. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 3–17
Qu S, Yang X, Li X, Wang J, Gao Y, Shang R, Sun W, Dou K, Li H (2015) Circular RNA: a new star of noncoding RNAs. Cancer Lett 365:141–148
Kristensen L, Hansen T, Venø M, Kjems J (2018) Circular RNAs in cancer: opportunities and challenges in the field. Oncogene 37:555
Pan JY, Bao XL, Zhu K (2019) Circular RNA_LARP4 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by repressing ROCK1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23(22):9915–9922
Zhong Q, Huang J, Wei J, Wu R (2019) Circular RNA CDR1as sponges miR-7-5p to enhance E2F3 stability and promote the growth of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int 19:252. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-019-0959-y
Jin C, Zhao W, Zhang Z, Liu W (2019) Silencing circular RNA circZNF609 restrains growth, migration and invasion by up-regulating microRNA-186-5p in prostate cancer. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47:3350–3358. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1648281
Wang S, Xue X, Wang R, Li X, Li Q, Wang Y, Xie P, Kang Y, Meng R, Feng X (2018) CircZNF609 promotes breast cancer cell growth, migration, and invasion by elevating p70S6K1 via sponging miR-145-5p. Cancer Manag Res 10:3881–3890. https://doi.org/10.2147/cmar.s174778
Wu W, Wei N, Shao G, Jiang C, Zhang S, Wang L (2019) circZNF609 promotes the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer by sponging miR-483-3p and regulating CDK6. Onco Targets Ther 12:8197–8205. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.s193031
Wu L, Xia J, Yang J, Shi Y, Xia H, Xiang X, Yu X (2018) Circ-ZNF609 promotes migration of colorectal cancer by inhibiting Gli1 expression via microRNA-150. J buon 23:1343–1349
Zhu L, Liu Y, Yang Y, Mao X, Yin Z (2019) CircRNA ZNF609 promotes growth and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by competing with microRNA-150-5p. Eur Review Med Pharmacol Sci 23:2817–2826
Ke Z, Xie F, Zheng C, Chen D (2019) CircHIPK3 promotes proliferation and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by abrogating miR-4288-induced ELF3 inhibition. J Cell Physiol 234:1699–1706. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27041
Liu Q, Shuai M, Xia Y (2019) Knockdown of EBV-encoded circRNA circRPMS1 suppresses nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation and metastasis through sponging multiple miRNAs. Cancer Manag Res 11:8023–8031. https://doi.org/10.2147/cmar.s218967
Xu XD, Shao SX, Jiang HP, Cao YW, Wang YH, Yang XC, Wang YL, Wang XS, Niu HT (2015) Warburg effect or reverse warburg effect? A review of cancer metabolism. Oncol Res Treat 38:117–122. https://doi.org/10.1159/000375435
Enzo E, Santinon G, Pocaterra A, Aragona M, Bresolin S, Forcato M, Grifoni D, Pession A, Zanconato F, Guzzo G, Bicciato S, Dupont S (2015) Aerobic glycolysis tunes YAP/TAZ transcriptional activity. Embo J 34(10):1349–1370
Ganapathy-Kanniappan S, Geschwind JF (2013) Tumor glycolysis as a target for cancer therapy: progress and prospects. Mol Cancer 12:152. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-12-152
Tan VP, Miyamoto S (2015) HK2/hexokinase-II integrates glycolysis and autophagy to confer cellular protection. Autophagy 11:963–964. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2015.1042195
Cheng Z, Yu C, Cui S, Wang H, Jin H, Wang C, Li B, Qin M, Yang C, He J, Zuo Q, Wang S, Liu J, Ye W, Lv Y, Zhao F, Yao M, Jiang L, Qin W (2019) circTP63 functions as a ceRNA to promote lung squamous cell carcinoma progression by upregulating FOXM1. Nat Commun 10:3200. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11162-4
Xiong DD, Dang YW, Lin P, Wen DY, He RQ, Luo DZ, Feng ZB, Chen G (2018) A circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network identification for exploring underlying pathogenesis and therapy strategy of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Transl Med 16:220. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-018-1593-5
Wang Y, Qin H (2018) miR-338-3p targets RAB23 and suppresses tumorigenicity of prostate cancer cells. Am J Cancer Res 8:2564–2574
Howe JRT, Li ES, Streeter SE, Rahme GJ, Chipumuro E, Russo GB, Litzky JF, Hills LB, Rodgers KR, Skelton PD, Luikart BW, (2017) MiR-338-3p regulates neuronal maturation and suppresses glioblastoma proliferation. PLoS ONE 12:e0177661. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0177661
Zhang P, Shao G, Lin X, Liu Y, Yang Z (2017) MiR-338-3p inhibits the growth and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting IRS2. Am J Cancer Res 7:53–63
Chen JS, Liang LL, Xu HX, Chen F, Shen SL, Chen W, Chen LZ, Su Q, Zhang LJ, Bi J, Zeng WT, Li W, Ma N, Huang XH (2017) miR-338-3p inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 8(42):71418–71429
Shan Y, Li X, You B, Shi S, Zhang Q, You Y (2015) MicroRNA-338 inhibits migration and proliferation by targeting hypoxia-induced factor 1alpha in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncol Rep 34:1943–1952. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2015.4195
Giehl K (2005) Oncogenic Ras in tumour progression and metastasis. Biol Chem 386:193–205. https://doi.org/10.1515/bc.2005.025
Aoki Y, Niihori T, Kawame H, Kurosawa K, Ohashi H, Tanaka Y, Filocamo M, Kato K, Suzuki Y, Kure S, Matsubara Y (2005) Germline mutations in HRAS proto-oncogene cause Costello syndrome. Nat Genet 37:1038–1040. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1641
Estep AL, Tidyman WE, Teitell MA, Cotter PD, Rauen KA (2006) HRAS mutations in Costello syndrome: detection of constitutional activating mutations in codon 12 and 13 and loss of wild-type allele in malignancy. Am J Med Genet A 140:8–16. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.a.31078
Zhang Y, Zhu R, Wang J, Cui Z, Wang Y, Zhao Y (2019) Upregulation of lncRNA H19 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma proliferation and metastasis in let-7 dependent manner. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47:3854–3861. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1669618
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no financial conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Liu, F., Wang, F. et al. CircZNF609 promotes cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and glycolysis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through regulating HRAS via miR-338-3p. Mol Cell Biochem 476, 175–186 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03894-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03894-5