Abstract
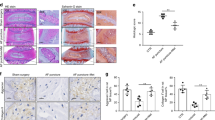
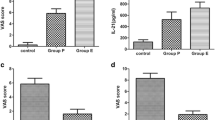
Intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) is a main contributor to low back pain. A close relationship exists between inflammation and pain. Estrogen can affect inflammation and may play a crucial role in IDD and pain. Substance P (SP) can also regulate the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in intervertebral disc (IVD). This study aimed to investigate the potential role of SP in estrogen regulation of IDD. Nine-week-old C57BL/6 female mice were divided into four groups as follows: sham surgery (sham), ovariectomy (OVX), ovariectomy plus estrogen replacement therapy (ERT) group (OVX+E2), and ovariectomy, ERT plus neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1R) agonist (OVX+E2+G). Serum E2, body, and uterus weight were recorded. Immunohistochemistry study and quantitative real-time PCR were used for SP, NK1R, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α examination and comparison in IVD at protein and gene levels. After OVX, the gene and protein expression of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, SP, and NK1R in NP cells significantly increased compared with the sham group. ERT can reverse these impacts. ERT plays anti-inflammatory and anti-hyperalgesic roles in IDD of OVX mice. The estrogen-induced changes of the pro-inflammatory cytokines, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, are significantly inhibited by NK1R agonists. SP may be a mediator of estrogen regulating pro-inflammatory factors in IDD. Estrogen may affect IVD inflammation through two ways: one is to directly affect the level of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the other is by means of modulation of SP.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bjorling, Dale E., and Zunyi Wang. 2001. Estrogen and neuroinflammation. Urology 57 (6): 40–46.
Buchbinder, R., M. van Tulder, B. Oberg, L.M. Costa, A. Woolf, M. Schoene, and P. Croft. 2018. Low back pain: a call for action. Lancet 391 (10137): 2384–2388. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(18)30488-4.
Budwit-Novotny, D.A., K.S. McCarty, E.B. Cox, J.T. Soper, D.G. Mutch, W.T. Creasman, J.L. Flowers, and K.S. McCarty Jr. 1986. Immunohistochemical analyses of estrogen receptor in endometrial adenocarcinoma using a monoclonal antibody. Cancer Research 46 (10): 5419–5425.
Cascieri, Margaret A., R.R.C. Huang, Tung Ming Fong, A.H. Cheung, S. Sadowski, E. Ber, and Catherine D. Strader. 1992. Determination of the amino acid residues in substance P conferring selectivity and specificity for the rat neurokinin receptors. Molecular Pharmacology 41 (6): 1096–1099.
Cerinic, Marco Matucci, Yrjo T. Konttinen, Sergio Generini, and Maurizio Cutolo. 1998. Neuropeptides and steroid hormones in arthritis. Current Opinion in Rheumatology 10 (3): 220–235.
Clouet, J., G. Grimandi, M. Pot-Vaucel, M. Masson, H.B. Fellah, L. Guigand, Y. Cherel, E. Bord, F. Rannou, P. Weiss, J. Guicheux, and C. Vinatier. 2009. Identification of phenotypic discriminating markers for intervertebral disc cells and articular chondrocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford) 48 (11): 1447–1450. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kep262.
Ding, M., R.P. Hart, and G.M. Jonakait. 1995. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces substance P in sympathetic ganglia through sequential induction of interleukin-1 and leukemia inhibitory factor. Journal of Neurobiology 28 (4): 445–454. https://doi.org/10.1002/neu.480280405.
Eyre, D.R., and H. Muir. 1976. Types I and II collagens in intervertebral disc. Interchanging radial distributions in annulus fibrosus. The Biochemical Journal 157 (1): 267–270. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj1570267.
Ferrari, Luiz F., Dioneia Araldi, Paul G. Green, and Jon D. Levine. 2017. Age-dependent sexual dimorphism in susceptibility to develop chronic pain in the rat. Neuroscience 387: 170–177.
Fujii, K., M. Yamazaki, J.D. Kang, M.V. Risbud, S.K. Cho, S.A. Qureshi, A.C. Hecht, and J.C. Iatridis. 2019. Discogenic back pain: literature review of definition, diagnosis, and treatment. JBMR Plus 3 (5): e10180. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm4.10180.
Gürgen, S.G., O. Sayın, F. Cetin, and A. Tuç Yücel. 2014. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) accelerates cutaneous wound healing and inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines. Inflammation 37 (3): 775–784. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9796-7.
Han, Y., C.M. Zhou, H. Shen, J. Tan, Q. Dong, L. Zhang, S.J. McGowan, J. Zhao, G.A. Sowa, J.D. Kang, L.J. Niedernhofer, P.D. Robbins, and N.N. Vo. 2020. Attenuation of ataxia telangiectasia mutated signalling mitigates age-associated intervertebral disc degeneration. Aging Cell 19 (7). https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.13162.
Hong, Hyun Sook, and Youngsook Son. 2014. Substance P ameliorates collagen II-induced arthritis in mice via suppression of the inflammatory response. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 453 (1): 179–184.
Jin, L.Y., Z.D. Lv, K. Wang, L. Qian, X.X. Song, X.F. Li, and H.X. Shen. 2018. Estradiol alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration through modulating the antioxidant enzymes and inhibiting autophagy in the model of menopause rats. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2018: 7890291–7890212. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7890291.
Jin, L.Y., X.X. Song, and X.F. Li. 2020. The role of estrogen in intervertebral disc degeneration. Steroids 154: 108549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2019.108549.
Kepler, Christopher K., Dessislava Markova, Alan S. Hilibrand, Alexander R. Vaccaro, Makarand V. Risbud, Todd J. Albert, and D. Anderson. 2013. Substance P stimulates production of inflammatory cytokines in human disc cells. Spine 38 (21): E1291–E1299.
Kepler, Christopher K., Dessislava Markova, Alan S. Hilibrand, Alexander R. Vaccaro, Makarand V. Risbud, Todd J. Albert, and D. Greg Anderson. 2012. Substance P stimulates production of inflammatory cytokines in human disc cells. The Spine Journal 12 (9): S109.
Kepler, Christopher K., Dessislava Markova, John D. Koerner, Joseph Mendelis, Chiuming Chen, Alexander R. Vaccaro, Makarand V. Risbud, Todd J. Albert, and D. Anderson. 2015. Substance P receptor antagonist suppresses inflammatory cytokine expression in human disc cells. Spine 40 (16): 1261–1269.
Kerdelhue, Bernard, Keith Gordon, Robert F. Williams, Veronique Lenoir, Valerie Fardin, Paul Chevalier, C. Garret, Pierre Duval, Paul Kolm, and Gary D. Hodgen. 1997. Stimulatory effect of a specific substance P antagonist (RPR 100893) of the human NK1 receptor on the estradiol-induced LH and FSH surges in the ovariectomized cynomolgus monkey. Journal of Neuroscience Research 50 (1): 94–103.
Koerner, John D., Dessislava Markova, Gregory D. Schroeder, Jeffery A. Rihn, Alan S. Hilibrand, Alexander R. Vaccaro, David Greg Anderson, and Christopher K. Kepler. 2016. The Effect of substance P on an intervertebral disc rat organ culture model. Spine 41 (24): 1851–1859.
Larsson, Caroline, Eva Ekvall Hansson, Kristina Sundquist, and Ulf Jakobsson. 2017. Chronic pain in older adults: prevalence, incidence, and risk factors. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 46 (4): 317–325.
Li, X.F., J. Yan, L.S. Jiang, and L.Y. Dai. 2011. Age-related variations of leptin receptor expression in the growth plate of spine and limb: gender- and region-specific changes. Histochemistry and Cell Biology 135 (5): 487–497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-011-0805-3.
Lou, C., H. Chen, L. Mei, W. Yu, K. Zhu, F. Liu, Z. Chen, G. Xiang, M. Chen, Q. Weng, and D. He. 2017. Association between menopause and lumbar disc degeneration: an MRI study of 1566 women and 1382 men. Menopause 24 (10): 1136–1144.
Martinmillan, Marta, and Santos Castaneda. 2013. Estrogens, osteoarthritis and inflammation. Joint, Bone, Spine 80 (4): 368–373.
Moran, Amy L., Steven A. Nelson, Rachel M. Landisch, Gordon L. Warren, and Dawn A. Lowe. 2007. Estradiol replacement reverses ovariectomy-induced muscle contractile and myosin dysfunction in mature female mice. Journal of Applied Physiology 102 (4): 1387–1393.
Navone, Stefania Elena, Giovanni Marfia, Amedeo Giannoni, Matteo Beretta, Laura Guarnaccia, Roberta Gualtierotti, Nicoli Daniele, P. Rampini, and Rolando Campanella. 2017. Inflammatory mediators and signalling pathways controlling intervertebral disc degeneration. Histology and Histopathology 32 (6): 523–542.
Peng, Yan, and Fengjuan Lv. 2015. Symptomatic versus asymptomatic intervertebral disc degeneration: is inflammation the key? Critical Reviews in Eukaryotic Gene Expression 25 (1): 13–21.
Rosen, S., Boram Ham, and Jeffrey S. Mogil. 2017. Sex differences in neuroimmunity and pain. Journal of Neuroscience Research 95: 500–508.
Sarajari, Susan, and Monica M. Oblinger. 2010. Estrogen effects on pain sensitivity and neuropeptide expression in rat sensory neurons. Experimental Neurology 224 (1): 163–169.
Shivers, Kaiyvonne, Nicole Amador, Lisa Abrams, Deirtra A. Hunter, Shirzad Jenab, and Vanya Quinonesjenab. 2015. Estrogen alters baseline and inflammatory-induced cytokine levels independent from hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity. Cytokine 72 (2): 121–129.
Silva, Morgana Duarte Da, Franciane Bobinski, K. Sato, Sandra J. Kolker, Kathleen A. Sluka, and Adair R.S. Santos. 2015. IL-10 cytokine released from M2 macrophages is crucial for analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of acupuncture in a model of inflammatory muscle pain. Molecular Neurobiology 51 (1): 19–31.
Song, X.X., S. Shi, Z. Guo, X.F. Li, and B.W. Yu. 2017. Estrogen receptors involvement in intervertebral discogenic pain of the elderly women: colocalization and correlation with the expression of substance P in nucleus pulposus. Oncotarget 8 (24): 38136–38144. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.15421.
Song, X.X., Y.J. Yu, X.F. Li, Z.D. Liu, B.W. Yu, and Z. Guo. 2014. Estrogen receptor expression in lumbar intervertebral disc of the elderly: gender- and degeneration degree-related variations. Joint, Bone, Spine 81 (3): 250–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2013.09.002.
Tang, Z., B. Hu, F. Zang, J. Wang, X. Zhang, and H. Chen. 2019. Nrf2 drives oxidative stress-induced autophagy in nucleus pulposus cells via a Keap1/Nrf2/p62 feedback loop to protect intervertebral disc from degeneration. Cell Death & Disease 10 (7): 510. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1701-3.
Wang, Y.X.J. 2017. Menopause as a potential cause for higher prevalence of low back pain in women than in age-matched men. Journal of Orthopaedic Translation 8: 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jot.2016.05.012.
Watt, Fiona E. 2018. Musculoskeletal pain and menopause. Post Reproductive Health 24 (1): 34–43. https://doi.org/10.1177/2053369118757537.
Yang, Yan, Ming Yan, Haitao Zhang, and Xuping Wang. 2013. Substance P participates in immune-mediated hepatic injury induced by concanavalin A in mice and stimulates cytokine synthesis in Kupffer cells. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 6 (2): 459–464.
Yoshida, Atsuhiko, Toru Morihara, Kenichi Matsuda, Hirotaka Sakamoto, Yuji Arai, Yoshikazu Kida, Mitsuhiro Kawata, and Toshikazu Kubo. 2012. Immunohistochemical analysis of the effects of estrogen on intraarticular neurogenic inflammation in a rat anterior cruciate ligament transection model of osteoarthritis. Connective Tissue Research 53 (3): 197–206.
Zheng, Xinfeng, B. Li, Yuehui Zhang, Yuehua Yang, Xiangyu Meng, Shengdan Jiang, and Leisheng Jiang. 2013. Blockade of substance P receptor attenuates osteoporotic pain, but not bone loss, in ovariectomized mice. Menopause 20 (10): 1074–1083.
Zhong, Weixia, S. Chebolu, and N.A. Darmani. 2019. Intracellular emetic signaling cascades by which the selective neurokinin type 1 receptor (NK1R) agonist GR73632 evokes vomiting in the least shrew (Cryptotis parva). Neurochemistry International 122: 106–119.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81400910, 81772292, and 81270027).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This study was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Xiao-Xing Song and Lin-Yu Jin are co-first authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, XX., Jin, LY., Li, XF. et al. Substance P Mediates Estrogen Modulation Proinflammatory Cytokines Release in Intervertebral Disc. Inflammation 44, 506–517 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01347-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01347-1