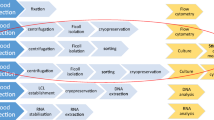
Abstract
Objective
The purpose of the article is to establish a quick enrichment and detection method using immunomagnetic beads and flow cytometry to analyze circulating tumor cells (CTCs) in the peripheral blood.
Results
After incubation with CD326-PE and CD45-APC antibodies, more than 60% MCF7 cells in M-Buffer could be detected while less than 10% of the same cells could be detected by flow cytometry (FCM) if spiked into blood. However, in combination with CD326 and CD45 immunomagnetic beads, detection rate of MCF7 cells in blood reached 57%. For circulating tumor cells, enrichment by CD326 and CD45 immunomagnetic beads improve the detection rate from nearly undetectable to more than 24.14%.
Conclusions
Live CTCs in peripheral blood can be effectively and sensitively detected by using a combination of immunomagnetic beads (CD45 and CD326) and flow cytometry.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alix-Panabieres C, Pantel K (2014) Challenges in circulating tumour cell research. Nat Rev Cancer 14(9):623–631
Alix-Panabieres C, Schwarzenbach H, Pantel K (2012) Circulating tumor cells and circulating tumor DNA. Annu Rev Med 63:199–215
Andree K, Mentink A, Zeune L, Terstappen L, Stoecklein N, Neves R, Driemel C, Lampignano R, Yang L, Neubauer H, Fehm T, Fischer J, Rossi E, Manicone M, Basso U, Marson P, Zamarchi R, Loriot Y, Lapierre V, Faugeroux V, Oulhen M, Farace F, Fowler G, Fontes M, Ebbs B, Lambros M, Crespo M, Flohr P, Bono J (2018) Toward a real liquid biopsy in metastatic breast and prostate cancer: diagnostic LeukApheresis increases CTC yields in a European prospective multicenter study (CTCTrap). Int J Cancer 143:2584–2591
Bankó P, Lee SY, Nagygyörgy V, Zrínyi M, Chae CH, Cho DH, Telekes A (2019) Technologies for circulating tumor cell separation from whole blood. J Hematol Oncol 12(1):48
Brungs D, Lynch D, Luk A, Minaei E, Ranson M, Aghmesheh M, Vine K, Carolan M, Jaber M, Souza P, Becker T (2018) Cryopreservation for delayed circulating tumor cell isolation is a valid strategy for prognostic association of circulating tumor cells in gastroesophageal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 24(7):810–818
Fusi A, Liu Z, Kümmerlen V, Nonnemacher A, Jeske J, Keilholz U (2012) Expression of chemokine receptors on circulating tumor cells in patients with solid tumors. J Transl Med 10:52
Hu Y, Fan L, Zheng J, Cui R, Liu W, He Y, Li X, Huang S (2010) Detection of circulating tumor cells in breast cancer patients utilizing multiparameter flow cytometry and assessment of the prognosis of patients in different CTCs levels. Cytom Part A 77(3):213–219
Martin VM, Siewert C, Scharl A, Harms T, Heinze R, Ohl S, Radbruch A, Miltenyi S, Schmitz J (1998) Immunomagnetic enrichment of disseminated epithelial tumor cells from peripheral blood by MACS. Exp Hematol 26(3):252–264
Mego M, De Giorgi U, Dawood S, Wang X, Valero V, Andreopoulou E, Handy B, Ueno NT, Reuben JM, Cristofanilli M (2011) Characterization of metastatic breast cancer patients with nondetectable circulating tumor cells. Int J Cancer 129(2):417–423
Miller MC, Doyle GV, Terstappen LW (2010) Significance of circulating tumor cells detected by the cell search system in patients with metastatic breast colorectal and prostate cancer. J Oncol 2010:617421
Nagrath S, Sequist L, Maheswaran S, Bell D, Irimia D, Ulkus L, Smith M, Kwak E, Digumarthy S, Muzikansky A, Ryan P, Balis U, Tompkins R, Haber D, Toner M (2007) Isolation of rare circulating tumour cells in cancer patients by microchip technology. Nature 450(7173):1235–1239
Park SM, Wong DJ, Ooi CC, Kurtz DM, Vermesh O, Aalipour A, Suh S, Pian KL, Chabon JJ, Lee SH, Jamali M, Say C, Carter JN, Lee LP, Kuschner WG, Schwartz EJ, Shrager JB, Neal JW, Wakelee HA, Diehn M, Nair VS, Wang SX, Gambhir SS (2016) Molecular profiling of single circulating tumor cells from lung cancer patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113(52):E8379–e8386
Ring AE, Zabaglo L, Ormerod MG, Smith IE, Dowsett M (2005) Detection of circulating epithelial cells in the blood of patients with breast cancer: comparison of three techniques. Br J Cancer 92(5):906–912
Schmiemann V, Bocking A, Kazimirek M, Onofre AS, Gabbert HE, Kappes R, Gerharz CD, Grote HJ (2005) Methylation assay for the diagnosis of lung cancer on bronchial aspirates: a cohort study. Clin Cancer Res 11(21):7728–7734
Takao M, Takeda K (2011) Enumeration, characterization, and collection of intact circulating tumor cells by cross contamination-free flow cytometry. Cytom Part A 79(2):107–117
Talmadge JE, Fidler IJ (2010) AACR centennial series: the biology of cancer metastasis: historical perspective. Can Res 70(14):5649–5669
Wang L, Wang Y, Liu Y, Cheng M, Wu X, Wei H (2009) Flow cytometric analysis of CK19 expression in the peripheral blood of breast carcinoma patients: relevance for circulating tumor cell detection. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 28:57
Yu M, Bardia A, Wittner BS, Stott SL, Smas ME, Ting DT, Isakoff SJ, Ciciliano JC, Wells MN, Shah AM, Concannon KF, Donaldson MC, Sequist LV, Brachtel E, Sgroi D, Baselga J, Ramaswamy S, Toner M, Haber DA, Maheswaran S (2013) Circulating breast tumor cells exhibit dynamic changes in epithelial and mesenchymal composition. Science 339(6119):580–584
Zhang L, Ridgway LD, Wetzel MD, Ngo J, Yin W, Kumar D, Goodman JC, Groves MD, Marchetti D (2013) The identification and characterization of breast cancer CTCs competent for brain metastasis. Sci Transl Med 5(180):180
Zhang L, Riethdorf S, Wu G, Wang T, Yang K, Peng G, Liu J, Pantel K (2012) Meta-analysis of the prognostic value of circulating tumor cells in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 18(20):5701–5710
Zhang X, Li H, Yu X, Li S, Lei Z, Li C, Zhang Q, Han Q, Li Y, Zhang K, Wang Y, Liu C, Mao Y, Wang X, Irwin D, Guo H, Liu G, Tan H (2018) Analysis of circulating tumor cells in ovarian cancer and their clinical value as a biomarker. Cell Physiol Biochem 48(5):1983–1994
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the 100-Talent Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81572948, 21772201, 21703254), the co-operative grant from Anhui Medical University and Center of Medical Physics and Technology (No. LHJJ202007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Lei Hu and Xueran Chen have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10529_2020_3007_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary Figure 1—Enriched CTC could be effectively detected by flow cytometry. Four venous blood species from Patient 4-7 with malignant tumors were collected. 20 µL of each 5 mL collected blood sample were immediately incubated with CD45-APC and CD326-PE antibodies while the rest samples sequential underwent CD45 and CD326 immunomagnetic beads enrichment followed by fluorescence antibodies label. All four groups (un-enriched, CD45+, CD326- and CD326+) were harvested by 300g centrifuge at 4 °C, 15min and detected by FCM. Supplementary file 1 (TIF 3759 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, L., Chen, X., Chen, M. et al. Enrichment and detection of circulating tumor cells by immunomagnetic beads and flow cytometry. Biotechnol Lett 43, 25–34 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-020-03007-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-020-03007-8