Abstract
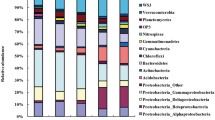
Comprehensive knowledge of bacterial ecology mainly in supraglacial habitats is pivotal particularly at the frontier of accelerated glacier retreat. In this study, bacterial diversity and community composition in glacial soil and meltwater runoff at the frontier of Baishui Glacier No.1 were evaluated using high throughput sequencing. Significant variations in the physiochemical parameters formed an ecological gradient between soil and meltwater runoff. Based on the richness and evenness indexes, the bacterial diversity was relatively higher in soil compared with meltwater runoff. Hierarchical clustering and bi-plot ordination revealed that the taxonomic composition of soil samples was highly similar and significantly influenced by the ecological parameters than the meltwater runoff. The overall relative abundance trend of bacterial phyla and genera were greatly varied in soil and water samples. The relative abundance of Proteobacteria was higher in water runoff samples (40.5–87%) compared with soil samples (32–52.7%). Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, and a little part of Cyanobacteria occupied a major portion of water runoff while the soil was dominated by Acidobacteria (6–16.2%), Actinobacteria (5–16%), Bacteroidetes (0.5–8.8%), and Cyanobacteria (0.1–8.3%) besides Proteobacteria and Firmicutes. Higher numbers of biomarkers were found in soil group compared with the water group. The study area is diverse in terms of richness, while community structures are not evenly distributed. This study provides a preliminary understanding of the bacterial diversity and shifts in community structure in soil and meltwater runoff at the frontier of the glacial. The findings revealed that the environmental factors are a significantly strong determinant of bacterial community structures in such a closely linked ecosystem.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anesio AM, Laybourn-Parry J (2012) Glaciers and ice sheets as a biome. Trends Ecol Evol 27:219–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2011.09.012
Hodson A, Anesio AM, Tranter M, Fountain A, Osborn M, Priscu J, Laybourn-Parry J, Sattler B (2008) Glacial ecosystems. Ecol Monogr 78:41–67
Butinar L, Spencer-Martins I, Gunde-Cimerman N (2007) Yeasts in high Arctic glaciers: the discovery of a new habitat for eukaryotic microorganisms. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 91(3):277–289
Anesio AM, Lutz S, Chrismas NAM, Benning LG (2017) The microbiome of glaciers and ice sheets. NPJ Biofilms Microbi 3(1):1–11
Ali B, Sajjad W, Ghimire PS, Shengyun C, Minghui W, Kang S (2019) Culture-dependent diversity of bacteria from Laohugou glacier, Qilian Mts., China and their resistance against metals. J Basic Microbiol 59(11):1065–1081. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201900385
Ali B, Sajjad W, Ghimire PS, Khan S, Din G, Kang S (2020) Culture independent diversity of bacterial communities indigenous to lower altitude at Laohugou glacial environment. Geomicrobiol J:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2020.1797946
Hassan N, Rafiq M, Hayat M, Nadeem S, Shah AA, Hasan F (2017) Potential of psychrotrophic fungi isolated from Siachen glacier, Pakistan, to produce antimicrobial metabolites. Appl Ecol Environ Res 15:1157–1171
Sajjad W, Din G, Rafiq M, Iqba A, Khan S, Zsada S, Ali B, Kang S (2020) Pigment production by cold-adapted bacteria and fungi: colorful tale of cryosphere with wide range applications. Extremophiles 24(4):447–473 (2020a. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-020-01180-2
Suyal DC, Joshi D, Kumar S, Soni R, Goel R (2019) Differential protein profiling of soil diazotroph Rhodococcus qingshengii S10107 towards low-temperature and nitrogen deficiency. Sci Rep 9(1):1–9
Suyal DC, Kumar S, Joshi D, Soni R, Goel R (2018) Quantitative proteomics of psychotrophic diazotroph in response to nitrogen deficiency and cold stress. J Proteome 187:235–242
Junge K, Christner B, Staley J (2011) Diversity of psychrophilic bacteria from sea ice and glacial ice communities. Extrem Handbook 11(2):793–815
Margesin R, Miteva V (2011) Diversity and ecology of psychrophilic microorganisms. Res Microbiol 162:346–361
Cowan DA, Makhalanyane TP, Dennis PG, Hopkins DW (2014) Microbial ecology and biogeochemistry of continental Antarctic soils. Front Microbiol 5:154
Ganzert L, Bajerski F, Wagner D (2014) Bacterial community composition and diversity of five different permafrost-affected soils of Northeast Greenland. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 89:426–441
Glaring MA, Vester JK, Lylloff JE, Al-Soud WA (2015) Microbial diversity in a permanently cold and alkaline environment in Greenland. PLoS One 10(4):e0124863
Zhang SH, Yang GL, Wang YT, Hou SG (2010) Abundance and community of snow bacteria from three glaciers in the Tibetan plateau. J Environ Sci 22:1418–1424
Rafiq M, Hayat M, Anesio AM, Jamil SUU, Hassan N, Shah AA et al (2017) Recovery of metallo-tolerant and antibiotic resistant psychrophilic bacteria from Siachen glacier, Pakistan. PLoS One 12(7):e0178180. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0178180
Rafiq M, Hayat M, Zada S, Sajjad W, Hassan N, Hasan F (2019) Geochemistry and bacterial recovery from Hindu Kush Range glacier and their potential for metal resistance and antibiotic production. Geomicrobiol J 36(4):326–338. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2018.1551947
Liu Y, Yao T, Jiao N, Kang S, Xu B, Zeng Y, Huang S, Liu X (2009) Bacteria diversity in the snow over Tibetan plateau glaciers. Extremophiles 13:411–423. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-009-0227-5
Zhang X, Ma X, Wang N, Yao T (2009) New subgroups of Bacteroidetes and diverse microorganisms in Tibetan plateau glacial ice provide a biological record of environmental conditions. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 67:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2008.00604.x
Takeuchi N, Koshima S (2004) A snow algal community on a Patagonian glacier, Tyndall glacier in the southern Patagonia Icefield. Arct Antarct Alp Res 36:91–98
Mueller DR, Pollard WH (2004) Gradient analysis of cryoconite ecosystems from two polar glaciers. Polar Biol 27:66–74
Bhatia M, Sharp M, Foght J (2006) Distinct bacterial communities exist beneath a high Arctic polythermal glacier. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5838–5845. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00595-06
Siles JA, Margesin R (2017) Seasonal soil microbial responses are limited to changes in functionality at two Alpine forest sites differing in altitude and vegetation. Sci Rep 7:2204
Foght J, Aislabie J, Turner S, Brown CE, Ryburn J, Saul DJ, Lawson W (2004) Culturable bacteria in subglacial sediments and ice from two Southern Hemisphere glaciers. Microb Ecol 47:329–340
Cavicchioli R, Charlton T, Ertan H, Omar SM (2011) Biotechnological uses of enzymes from psychrophiles. Microb Biotechnol 4:449–460
Joseph B, Ramteke PW (2013) Extracellular solvent stable cold-active lipase from psychrotrophic Bacillus sphaericus MTCC 7526: partial purification and characterization. Ann Microbiol 63:363–370
Margesin R, Fonteyne PA, Schinner F, Sampaio JP (2007) Novel psychrophilic basidiomycetous yeasts from Alpine environments: Rhodotorula psychrophila sp. nov., Rhodotorula psychrophenolica sp. nov. and Rhodotorula glacialis sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2179–2184
Ramana KV, Singh L, Dhaked RK (2002) Biotechnological application of psychrophiles and their habitat to low temperature. J Sci Ind Res 59(2):87–101
Sajjad W, Rafiq M, Din G, Hasan F, Iqbal A, Zada S, Ali B, Irfan M, Kang S (2020) Resurrection of inactive microbes and resistome present in the natural frozen world: reality or myth? Sci Total Environ 735:139275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139275
Yang GL, Hou SG, le Baoge R, Li ZG, Xu H, Liu YP, du WT, Liu YQ (2016) Differences in bacterial diversity and communities between glacial snow and glacial soil on the Chongce Ice Cap, West Kunlun Mountains. Sci Rep 6:36548. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep36548
Wilhelm L, Singer GA, Fasching C, Battin TJ, Besemer K (2013) Microbial biodiversity in glacier-fed streams. ISME J 7:1651–1660
Paudyal R, Kang S, Tripathee L, Guo J, Sharma CM, Huang J, Niu H, Sun S, Pu T (2019) Concentration, spatiotemporal distribution, and sources of mercury in Mt. Yulong, a remote site in southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:16457–16469. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05005-4
Wang S, Che Y, Pang H, du J, Zhang Z (2020) Accelerated changes of glaciers in the Yulong Snow Mountain, Southeast Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Reg Environ Chang 20:38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-020-01624-7
Niu H, Kang S, Shi X, He Y, Lu X, Shi X, Paudyal R, du J, Wang S, du J, Chen J (2017) Water-soluble elements in snow and ice on Mt. Yulong. Sci Total Environ 574:889–900
Niu HW, He YQ, Zhu GF, Xin HJ, Du JK, Pu T, Lu XX (2013) Environmental implications of the snow chemistry from Mt Yulong, southeastern Tibetan plateau. Quat Int 313–314:168–178
He Y, Theakstone WH, Zhonglin Z, Dian Z, Tandong Y, Tuo C, Yongping S, Hongxi P (2004) Asynchronous Holocene climatic change across China. Quat Res 61:52–63
Du J, He Y, Li S, Wang S, Niu H (2015) Mass balance of a typical monsoonal temperate glacier in Hengduan Mountains Region. Acta Geograph Sin 70(9):1415–1422
Allen SE, Grimshaw HM, Parkinson JA, Quarmby C (1974) Chemical analysis of ecological materials. Blackwell Scientific Publications
Sajjad W, Zheng G, Zhang G, Ma X, Xu W, Ali B, Rafiq M (2018) Diversity of prokaryotic communities indigenous to acid mine drainage and related rocks from Baiyin open-pit copper mine stope, China. Geomicrobiol J 35(7):580–600. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2018.1430873
Segata N, Izard J, Waldron L, Gevers D, Miropolsky L, Garrett W, Huttenhower C (2011) Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol 12(6):R60. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2011-12-6-r60
Edwards A (2015) Coming in from the cold: potential microbial threats from the terrestrial cryosphere. Front Earth Sci 3:12. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2015.00012
Griffiths GW (2012) Do we need a global strategy for microbial conservation? Trends Ecol Evol 27(1):1–2
Rogers SO, Starmer WT, Castello JD (2004) Recycling of pathogenic microbes through survival in ice. Med Hypotheses 63:773–777
Zhu Y, Zhang Y, Chen H, Wang Y, Cao F, Sun W, Qi X, Zhao Y, Xu F (2020) Soil properties and microbial diversity at the frontier of Laohugou glacier retreat in Qilian Mountains. Curr Microbiol 77(3):425–433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-019-01846-x
Zou JW, Rogers WE, DeWalt SJ, Siemann E (2006) The effect of Chinese tallow tree (Sapium sebiferum) ecotype on soil-plant system carbon and nitrogen processes. Oecologia 150:272–281
Yin H, Niu J, Ren Y, Cong J, Zhang X, Fan F, Xiao Y, Zhang X, Deng J, Xie M et al (2015) An integrated insight into the response of sedimentary microbial communities to heavy metal contamination. Sci Rep 5:14266
Sheik CS, Stevenson EI, Den Uyl PA, Arendt CA, Aciego SM, Dick GJ (2015) Microbial communities of the Lemon Creek glacier show subtle structural variation yet stable phylogenetic composition over space and time. Front Microbiol 6:495
Ambrosini R, Musitelli F, Navarra F, Tagliaferri I, Gandolfi I, Bestetti G, Smiraglia C (2017) Diversity and assembling processes of bacterial communities in cryoconite holes of a Karakoram glacier. Microb Ecol 73(4):827–837
Malešević M, Mirković N, Lozo J, Novović K, Filipić B, Kojić M, Jovčić B (2019) Bacterial diversity among the sediments of glacial lakes in the western Balkans: exploring the impact of human population. Geomicrobiol J 36(3):261–270
Kumar S, Suyal DC, Yadav A, Shouche Y, Goel R (2019) Microbial diversity and soil physiochemical characteristic of higher altitude. PLoS One 14(3):e0213844
Quince C, Lanzen A, Curtis TP, Davenport RJ, Hall N, Head IM, Sloan WT (2009) Accurate determination of microbial diversity from 454 pyrosequencing data. Nat Methods 6(9):639–641. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1361
Reeder J, Knight R (2009) The ‘rare biosphere’: a reality check. Nat Methods 6:636–637. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth0909-636
He Y, Zhou BJ, Deng GH, Jiang XT, Zhang H, Zhou HW (2013) Comparison of microbial diversity determined with the same variable tag sequence extracted from two different PCR amplicons. BMC Microbiol 13(1):208. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-13-208
Grzesiak J, Zdanowski MK, Górniak D, Świątecki A, Aleksandrzak-Piekarczyk T, Szatraj K, Sasin-Kurowska J, Nieckarz M (2015) Microbial community changes along the Ecology Glacier ablation zone (King George Island, Antarctica). Polar Biol 38:2069–2083
Zhong ZP, Solonenko NE, Gazitúa MC, Kenny DV, Mosley-Thompson E, Rich VI, Sullivan MB (2018) Clean low-biomass procedures and their application to ancient ice core microorganisms. Front Microbiol 9:1094
Yergeau E, Lawrence JR, Sanschagrin S, Waiser MJ, Korber DR, Greer CW (2012) Next-generation sequencing of microbial communities in the Athabasca River and its tributaries in relation to oil sands mining activities. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(21):7626–7637. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02036-12
Wilms R, Köpke B, Sass H, Chang TS, Cypionka H, Engelen B (2006) Deep-biosphere related bacteria within the subsurface of tidal flat sediments. Environ Microbiol 8(4):709–719. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.14622920.2005.00949.x
Luláková P, Perez-Mon C, Šantrůčková H, Ruethi J, Frey B (2019) High-Alpine permafrost and active-layer soil microbiomes differ in their response to elevated temperatures. Front Microbiol 10:668. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00668
Edwards A, Pachebat JA, Swain M, Hegarty M, Hodson AJ, Irvine-Fynn TD, Sattler B (2013) A metagenomic snapshot of taxonomic and functional diversity in an alpine glacier cryoconite ecosystem. Environ Res Lett 8:35003. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/8/3/035003
Ciccarelli FD, Doerks T, Mering CV, Creevey CJ, Snel B, Bork P (2006) Toward automatic reconstruction of a highly resolved tree of life. Science 311:1283–1287
Filippidou S, Junier T, Wunderlin T, Lo CC, Li PE, Chain PS et al (2015) Under-detection of endospore-forming Firmicutes in metagenomic data. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 13:299–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2015.04.002
Jones RT, Robeson MS, Lauber CL, Hamady M, Knight R, Fierer N (2009) A comprehensive survey of soil acidobacterial diversity using pyrosequencing and clone library analyses. ISME J 3(4):442–453. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2008.127
Dion P (2008) Extreme views on prokaryote evolution. In: Dion P, Nautiyal CS (eds) Microbiology of extreme soils. Springer, Berlin, pp 45–70
Sherpa MT, Najar IN, Das S, Thakur N (2018) Bacterial diversity in an alpine debris-free and debris-cover accumulation zone glacier ice, North Sikkim, India. Indian J Microbiol 58(4):470–478
Rondon J, Gomez W, Ball MM (2016) Diversity of culturable bacteria recovered from Pico Bolívar’s glacial and subglacial environments, at 4,950 m, in Venezuelan tropical Andes. Can J Microbiol 62(11):1–14
Franzetti A, Navarra F, Tagliaferri I, Gandolfi I, Bestetti G, Minora U, Azzoni RS, Diolaiuti G, Smiraglia C, Ambrosini R (2017) Potential sources of bacteria colonizing the cryoconite of an alpine glacier. PLoS One 12(3):e0174786
Munoz PA, Marquez SL, Nilo FDG, Miranda VM, Blamey JM (2017) Structure and application of antifreeze proteins from Antarctic bacteria. Microb Cell Factories 16:1–13
Singh P, Hanada Y, Singh SM, Tsuda S (2014) Antifreeze protein activity in Arctic cryoconite bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 351(1):14–22
Zhang B, Wu X, Zhang G, Li S, Zhang W, Chen X, Sun L, Zhang B, Liu G, Chen T (2016) The diversity and biogeography of the communities of Actinobacteria in the forelands of glaciers at a continental scale. Environ Res Lett 11(11):054012
Fierer N, Bradford MA, Jackson RB (2007) Towards an ecological classification of soil bacteria. Ecology 88:1354–1364. https://doi.org/10.1890/05-1839
Nemergut DR, Anderson SP, Cleveland CC, Martin AP, Miller AE, Seimon A, Schmidt SK (2007) Microbial community succession in an unvegetated, recently deglaciated soil. Microb Ecol 53:110–122
Liu JB et al (2016) Diversity and succession of autotrophic microbial community in high-elevation soils along deglaciation chronosequence. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 92:160
Agha R, Cires S, Wormer L, Dominguez JA, Quesada A (2012) Multiscale strategies for the monitoring of freshwater cyanobacteria: reducing the sources of uncertainty. Water Res 46(9):3043–3053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.03.005
Vincent W (2002) Cyanobacterial dominance in the polar regions. In: Whitton B, Potts M (eds) The ecology of cyanobacteria. Springer, Dordrecht
Strauss SL, Garcia-Pichel F, Day TA (2012) Soil microbial car- bon and nitrogen transformations at a glacial foreland on Anvers Island, Antarctic Peninsula. Polar Biol 35:1459–1471
Stres B, Sul WJ, Murovec B, Tiedje JM (2014) Recently deglaciated high-altitude soils of the Himalaya: diverse environments, heterogenous bacterial communities and long-range dust inputs from the upper troposphere. PLoS One 8:e76440
Larose C, Berger S, Ferrari C, Navarro E, Dommergue A, Schneider D, Vogel TM (2010) Microbial sequences retrieved from environmental samples from seasonal Arctic snow and meltwater from Svalbard, Norway. Extremophiles 14:205–212
Liu Y, Yao T, Jiao N, Tian L, Hu A, Yu W, Li S (2011) Microbial diversity in the snow, a moraine lake and a stream in Himalayan glacier. Extremophiles 15:411–421
Nicol GW, Tscherko D, Embley TM, Prosser JI (2005) Primary succession of soil Crenarchaeota across a receding glacier fore- land. Environ Microbiol 7:337–347
Walker CB, de la Torre JR, Klotz MG, Urakawa H, Pinel N, Arp DJ, Brochier-Armanet C, Chain PSG, Chan PP, Gollabgir A, Hemp J, Hugler M, Karr EA, Konneke M, Shin M, Lawton TJ, Lowe T, Martens-Habbena W, Sayavedra-Soto LA, Lang D, Sievert SM, Rosenzweig AC, Manning G, Stahl DA (2010) Nitrosopumilus maritimus genome reveals unique mechanisms for nitrification and autotrophy in glob- ally distributed marine crenarchaea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:8818–8882
Srinivas TN et al (2011) Comparison of bacterial diversity in proglacial soil from Kafni glacier, Himalayan Mountain ranges, India, with the bacterial diversity of other glaciers in the world. Extremophiles 15:673–690
Frey B, Rieder SR, Brunner I, Plötze M, Koetzsch S, Lapanje A, Brandl H, Furrer G (2010) Weathering-associated bacteria from the Damma glacier forefield: physiological capabilities and impact on granite dissolution. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:4788–4796
Xiang SR, Shang TC, Chen Y, Yao TD (2009) Deposition and postdeposition mechanisms as possible drivers of microbial population variability in glacier ice. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 70:165–176
Liu Y, Yao T, Jiao N, Kang S, Zeng Y, Huang S (2006) Microbial community structure in moraine lakes and glacial meltwaters. Mount Everest FEMS Microbiol Ecol 265:98–105
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the support provided by the second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research Program (STEP) (2019QZKK0605), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41630754, 41721091) and the State Key Laboratory of Cryospheric Science (SKLCS-ZZ-2020). Wasim Sajjad is supported by a PIFI Fellowship from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (2020PC0052).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2136 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sajjad, W., Ali, B., Bahadur, A. et al. Bacterial Diversity and Communities Structural Dynamics in Soil and Meltwater Runoff at the Frontier of Baishui Glacier No.1, China. Microb Ecol 81, 370–384 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-020-01600-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-020-01600-y